A Geographic Exploration Of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent Of Diversity And Potential
A Geographic Exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential
Related Articles: A Geographic Exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Geographic Exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographic Exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential

Sub-Saharan Africa, a vast and diverse region encompassing the entirety of the African continent south of the Sahara Desert, presents a tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and economies. This region, home to over 1 billion people, is a vibrant hub of human history, natural wonders, and burgeoning development. Understanding the individual countries that make up this expansive region is crucial for appreciating its multifaceted nature and the potential it holds for the future.
Mapping the Landscape: A Geographic Overview
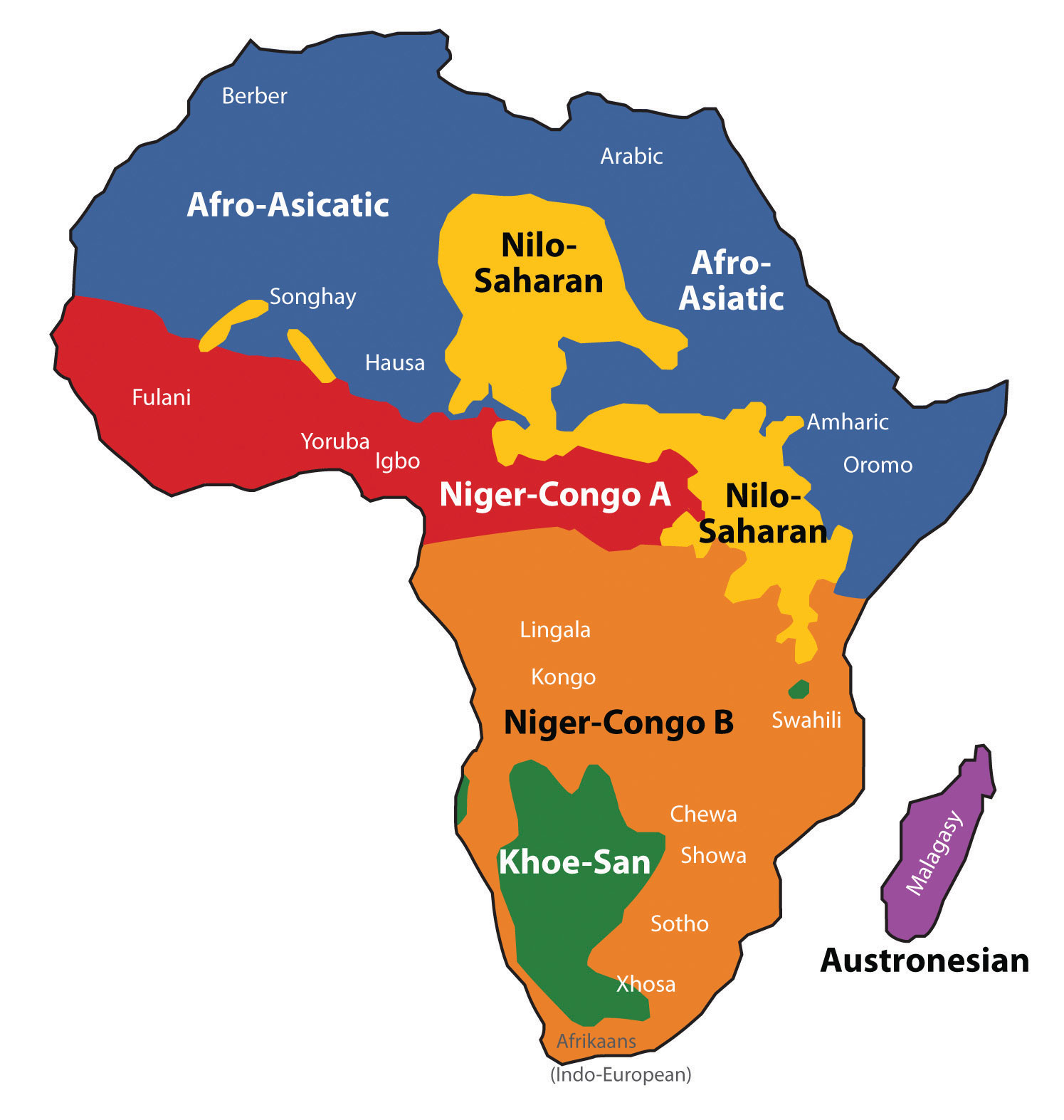
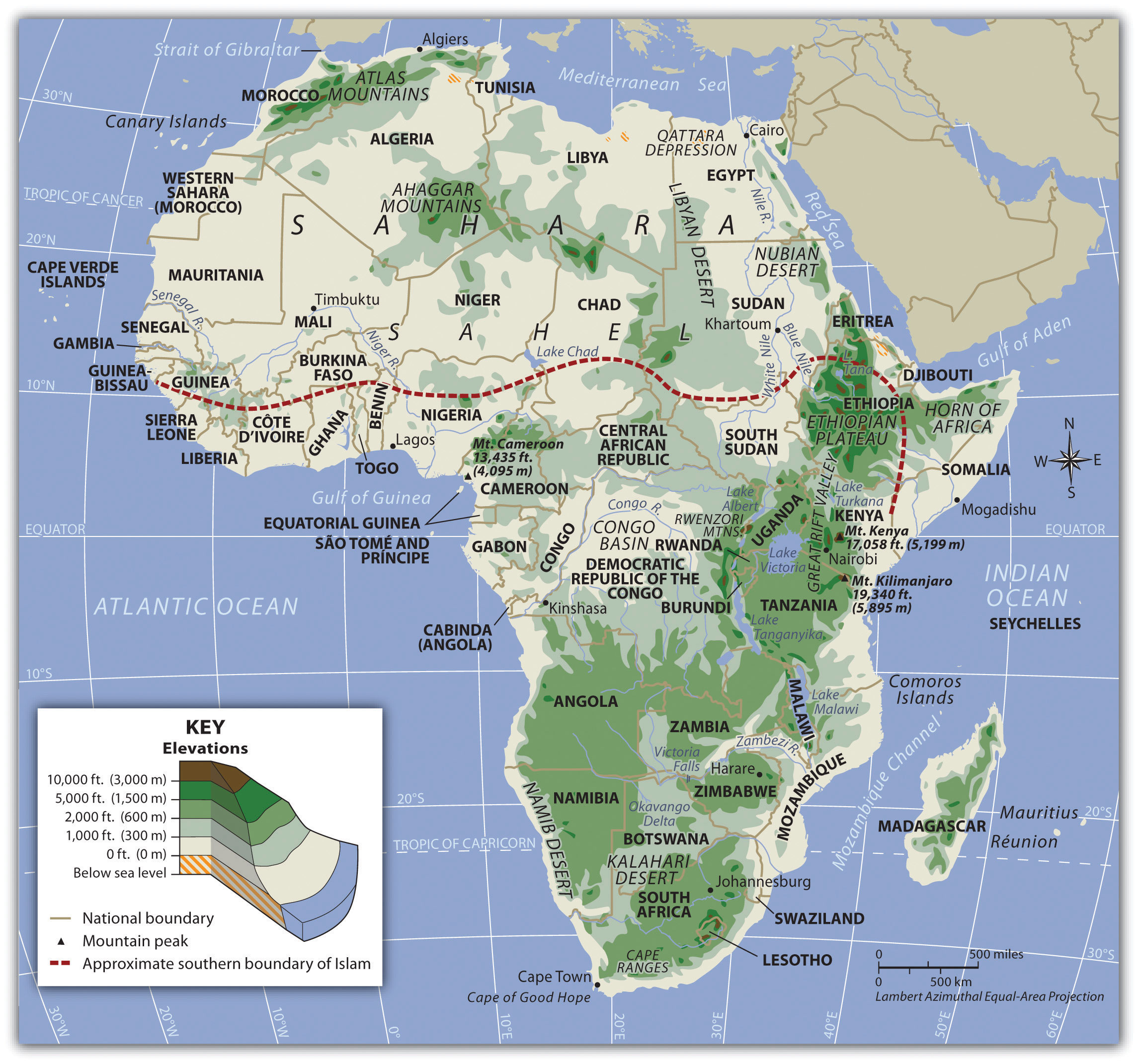
Sub-Saharan Africa encompasses 48 countries, each with its unique characteristics and contributions to the continent’s identity. The region is geographically diverse, ranging from the lush rainforests of the Congo Basin to the arid deserts of the Sahel, and from the towering peaks of Mount Kilimanjaro to the vast plains of the Serengeti. This diversity is reflected in the region’s rich cultural tapestry, with hundreds of distinct languages, traditions, and belief systems.
A Glimpse into the Countries:
West Africa:
- Senegal: A vibrant nation known for its rich cultural heritage, particularly its music, dance, and literature. Dakar, its capital, is a bustling hub of commerce and culture.
- Mali: Home to the ancient city of Timbuktu, Mali boasts a rich history and is a key player in the Sahel region’s cultural and economic landscape.
- Burkina Faso: This landlocked nation is known for its diverse ecosystems, from the savanna to the rocky plateaus. It is also a significant producer of cotton and gold.
- Ghana: A nation with a rich history, Ghana was the first sub-Saharan African country to achieve independence. It is known for its cocoa production and its vibrant coastal cities.
- Nigeria: The most populous country in Africa, Nigeria is a major economic powerhouse with vast reserves of oil and natural gas. It is also a cultural melting pot with a diverse population.
- Cameroon: A nation with a rich biodiversity, Cameroon is home to numerous national parks and reserves. It is also a significant producer of coffee and cocoa.
Central Africa:
- Democratic Republic of Congo: The largest country in Central Africa, the DRC is a vast and resource-rich nation with significant deposits of minerals. However, it has faced challenges with political instability and conflict.
- Republic of Congo: A country with vast reserves of oil and natural gas, the Republic of Congo is also a major producer of timber.
- Gabon: A nation known for its pristine rainforests and abundant wildlife, Gabon is a significant producer of oil and manganese.
- Central African Republic: A landlocked nation with a challenging history, the Central African Republic is rich in natural resources but faces significant challenges with poverty and instability.
- Equatorial Guinea: A small nation with significant oil reserves, Equatorial Guinea is one of the wealthiest countries in Central Africa.
East Africa:
- Ethiopia: A country with a rich history and ancient culture, Ethiopia is known for its unique coffee and its stunning landscapes, including the Simien Mountains and the Omo Valley.
- Kenya: A country renowned for its wildlife, particularly the Maasai Mara National Reserve, Kenya is a major tourist destination and is also a significant agricultural producer.
- Tanzania: Home to Mount Kilimanjaro and the Serengeti National Park, Tanzania is a country with breathtaking natural beauty and a rich cultural heritage.
- Uganda: A country known for its diverse wildlife, including mountain gorillas and chimpanzees, Uganda is also a significant agricultural producer and is home to Lake Victoria, the largest lake in Africa.
- Rwanda: A country that has overcome a tragic past, Rwanda is now known for its stunning scenery, including the Volcanoes National Park, and its commitment to sustainable development.
- Burundi: A small country with a challenging history, Burundi is known for its coffee production and its stunning landscapes.
Southern Africa:
- South Africa: The most developed country in Africa, South Africa is a major economic powerhouse with a diverse population and a rich cultural heritage. It is also known for its stunning landscapes, including the Cape Town coastline and the Drakensberg Mountains.
- Namibia: A country with breathtaking scenery, including the Namib Desert and the Etosha National Park, Namibia is a major producer of diamonds and uranium.
- Botswana: A country known for its vast savannas and its abundant wildlife, Botswana is also a major producer of diamonds.
- Zimbabwe: A country with a rich history and culture, Zimbabwe is known for its stunning ruins of Great Zimbabwe and its diverse wildlife, including elephants and lions.
- Zambia: A country known for its breathtaking waterfalls, including Victoria Falls, Zambia is also a major producer of copper and cobalt.
- Malawi: A landlocked country known for its stunning lakes, including Lake Malawi, Malawi is also a significant agricultural producer.
- Mozambique: A coastal nation with stunning beaches and diverse wildlife, Mozambique is a major producer of coal and natural gas.
- Swaziland: A small country with a rich cultural heritage, Swaziland is known for its stunning landscapes and its production of sugar cane and timber.
- Lesotho: A landlocked country with stunning mountain scenery, Lesotho is known for its production of diamonds and wool.
Beyond the Borders: The Importance of Sub-Saharan Africa
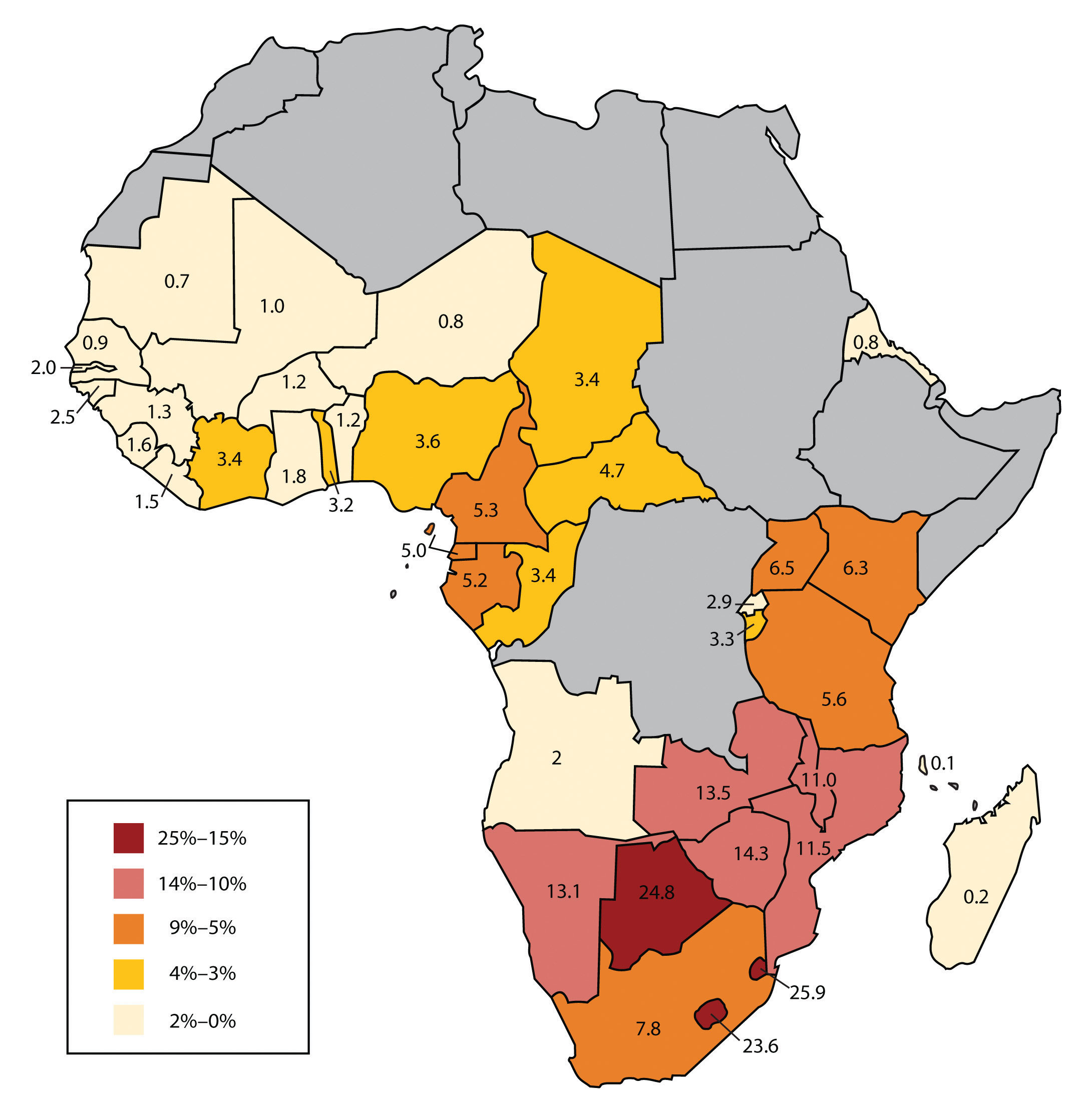
The countries of Sub-Saharan Africa are not merely geographic entities on a map. They represent a continent of immense potential, with a rich history, diverse cultures, and a wealth of natural resources. The region is crucial to the global economy, playing a significant role in the production of commodities like oil, minerals, and agricultural products.
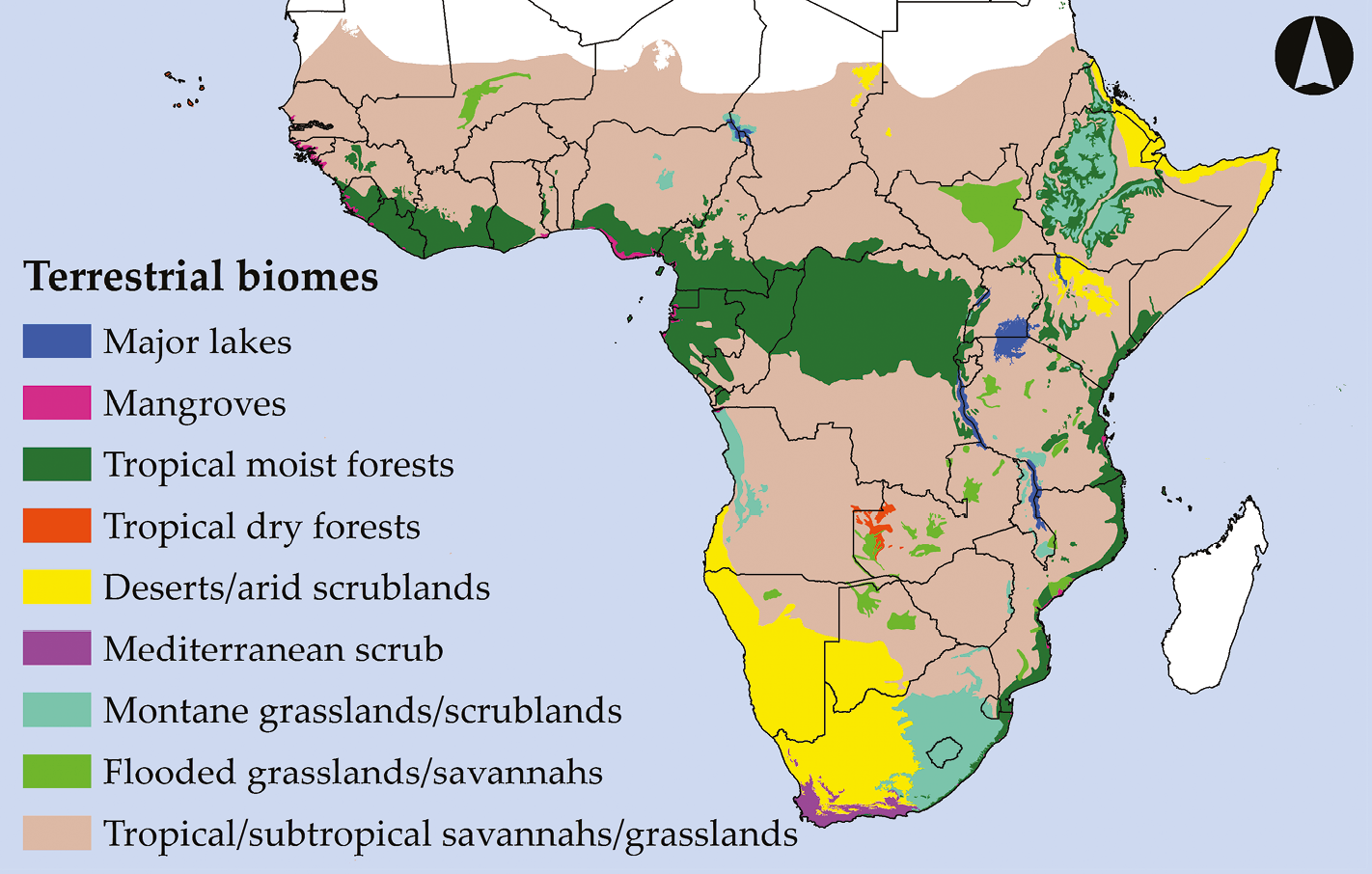
Beyond economic importance, Sub-Saharan Africa is a vital contributor to global biodiversity and cultural diversity. Its vast landscapes, from rainforests to deserts, harbor a remarkable array of plant and animal life, many of which are unique to the region. Its diverse cultures, languages, and traditions contribute to the richness of human experience and offer valuable insights into the human story.
FAQs about Sub-Saharan Africa:
Q: What are the major challenges facing Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: Sub-Saharan Africa faces numerous challenges, including poverty, inequality, conflict, climate change, and disease. These challenges are interconnected and often exacerbate each other, making it difficult to achieve sustainable development.
Q: What are the key opportunities for development in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: Sub-Saharan Africa has significant potential for development, particularly in the areas of agriculture, infrastructure, technology, and tourism. The region is also home to a growing and increasingly skilled workforce, which can contribute to economic growth and development.
Q: What role can international cooperation play in supporting development in Sub-Saharan Africa?
A: International cooperation is crucial for supporting development in Sub-Saharan Africa. This can involve providing financial assistance, technical expertise, and capacity building. It also includes promoting trade and investment, and addressing global challenges like climate change.
Tips for Engaging with Sub-Saharan Africa:
- Learn about the region’s diverse cultures and histories: Understanding the unique characteristics of each country is crucial for engaging with the region effectively.
- Support sustainable development initiatives: By supporting projects that promote economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability, you can contribute to a brighter future for Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Engage with local communities: Building relationships with people in Sub-Saharan Africa can foster understanding and cooperation.
- Advocate for policies that promote peace and stability: Supporting efforts to resolve conflicts and build lasting peace is essential for the region’s future.
Conclusion:
Sub-Saharan Africa is a continent of immense potential, facing both challenges and opportunities. Understanding the individual countries that make up this vast region is crucial for appreciating its diversity and potential. By engaging with the region in a responsible and respectful manner, we can contribute to a brighter future for all its people.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographic Exploration of Sub-Saharan Africa: A Continent of Diversity and Potential. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!