A Geographical Exploration Of The European Union: A Map Of Unity And Diversity
A Geographical Exploration of the European Union: A Map of Unity and Diversity
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of the European Union: A Map of Unity and Diversity
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of the European Union: A Map of Unity and Diversity. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of the European Union: A Map of Unity and Diversity

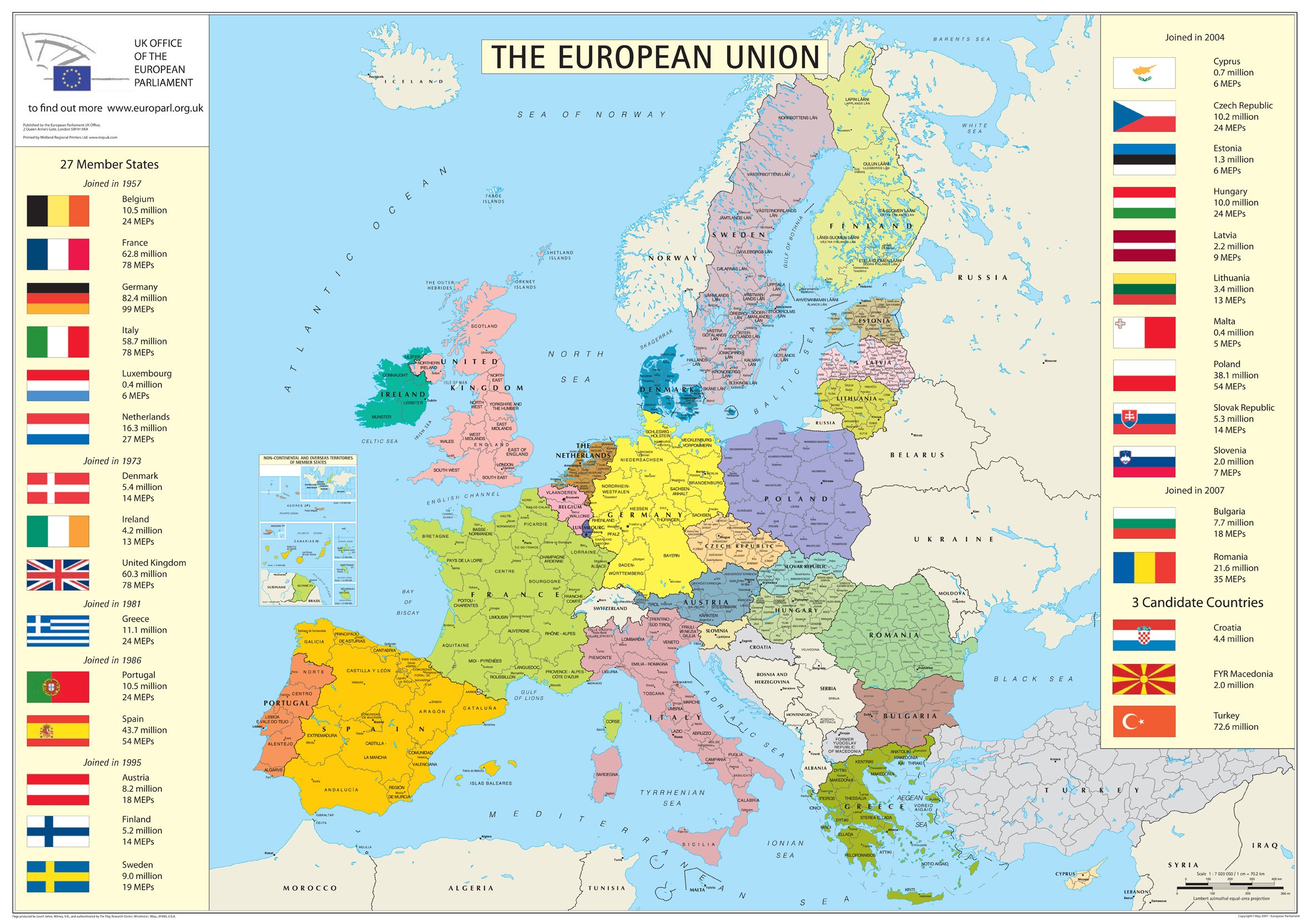
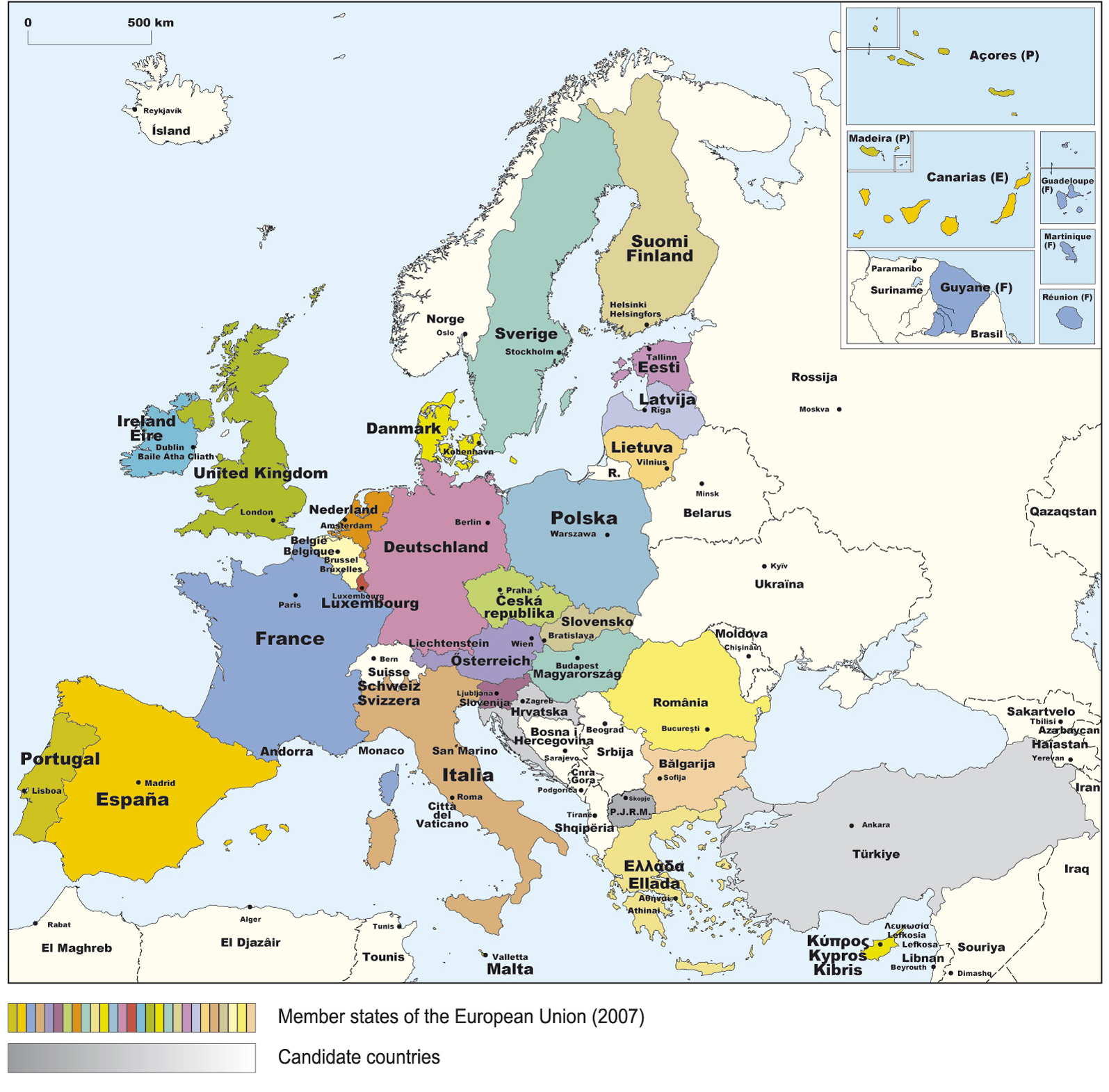
The European Union (EU), a political and economic union of 27 European countries, is a complex and fascinating entity. Understanding its geographical makeup is crucial to grasping its multifaceted nature. This article delves into the geographical aspects of the EU, exploring the individual countries that compose it and the significance of their collective presence on the map of Europe.
A Mosaic of Nations:
The EU’s geographical footprint spans a vast area across Western, Central, and Eastern Europe. Its member states, each with its unique history, culture, and identity, contribute to a diverse tapestry of languages, traditions, and landscapes.
- Western Europe: This region forms the core of the EU, encompassing countries like France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Portugal, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Ireland, and the United Kingdom (although the UK withdrew from the EU in 2020). These nations are characterized by a long history of political and economic integration, contributing significantly to the EU’s development.
- Central Europe: Countries in this region joined the EU in the 2004 enlargement, including Poland, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Slovenia, and Austria. This region is known for its rich cultural heritage and its transition from communist rule to democratic systems.
- Eastern Europe: This region comprises the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), Bulgaria, Romania, and Croatia, which joined the EU in 2004 and 2013. These countries, often referred to as "new member states," have undergone significant economic and social transformation since their accession, contributing to the EU’s eastward expansion.
Beyond Borders: A Shared Identity:
While each EU member state retains its sovereignty and distinct identity, their collective presence on the map signifies a shared vision of cooperation and integration. The EU’s geographic expanse embodies a commitment to overcoming historical divisions and fostering unity amongst diverse European nations.
The Importance of Geographical Context:
The EU’s geographical makeup is not merely a collection of countries on a map; it is a dynamic force shaping the union’s identity and its role in the world.
- Economic Interdependence: The interconnectedness of EU member states fosters trade and investment, driving economic growth and prosperity. The free movement of goods, services, capital, and people within the EU’s borders facilitates economic integration and strengthens the single market.
- Political Cooperation: The EU’s geographical footprint allows for collective action on issues of common interest, such as security, foreign policy, and climate change. Its presence on the global stage strengthens its influence and promotes cooperation among its members.
- Cultural Exchange: The EU’s geographical diversity fosters cultural exchange and understanding. The free movement of people allows for the exchange of ideas, experiences, and artistic expressions, enriching the cultural fabric of Europe.
FAQs:
1. What are the benefits of being in the EU?
Membership in the EU offers numerous benefits, including:
- Access to the single market, facilitating trade and investment.
- Free movement of people, goods, services, and capital within the EU.
- Participation in EU-funded projects and initiatives.
- Enhanced security and stability through collective action.
- Influence on the global stage through a unified voice.
2. How does the EU’s geography impact its policies?
The EU’s geographical position and the diverse interests of its member states influence its policy decisions. For example, the EU’s policies on migration, energy, and security are shaped by its location and the challenges it faces from its neighbors.
3. What are the challenges facing the EU?
The EU faces various challenges, including:
- Economic disparities between member states.
- Political divisions on key issues like immigration and the eurozone.
- External threats from terrorism, climate change, and global instability.
4. What is the future of the EU?
The future of the EU is uncertain, but its ability to adapt and evolve is crucial to its success. Addressing the challenges it faces and fostering unity among its members will be essential for its continued relevance and prosperity.
Tips:
- Travel to different EU member states to experience their unique cultures and landscapes.
- Learn about the history and development of the EU to better understand its current challenges and opportunities.
- Engage in discussions about EU policies and their impact on your life.
- Support organizations working to promote understanding and cooperation within the EU.
Conclusion:
The EU’s geographical footprint represents a powerful symbol of unity and cooperation amongst diverse European nations. Its map is not simply a collection of countries; it is a testament to the shared vision of a united Europe, striving for peace, prosperity, and shared values. Understanding the geographical context of the EU is crucial for appreciating its complexities, its challenges, and its enduring relevance in the 21st century.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of the European Union: A Map of Unity and Diversity. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!