A Journey Through Time: Exploring The Ancient Roman World With Maps
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps
Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps
- 3.1 Unveiling the Tapestry of Roman Power: The Importance of Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.2 Deciphering the Details: Key Features of Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.3 Navigating the Past: Understanding the Limitations of Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.4 Unveiling the Secrets: The Importance of Studying Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.5 FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.6 Tips: Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Roman Maps
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Legacy of Maps and Knowledge
- 4 Closure
A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps

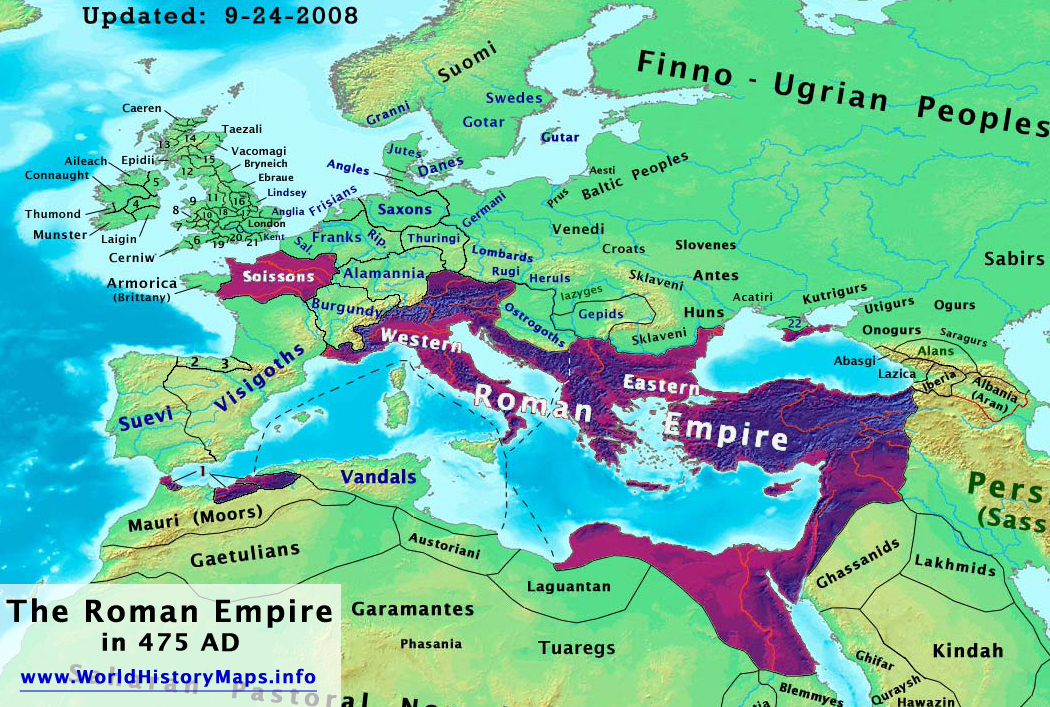
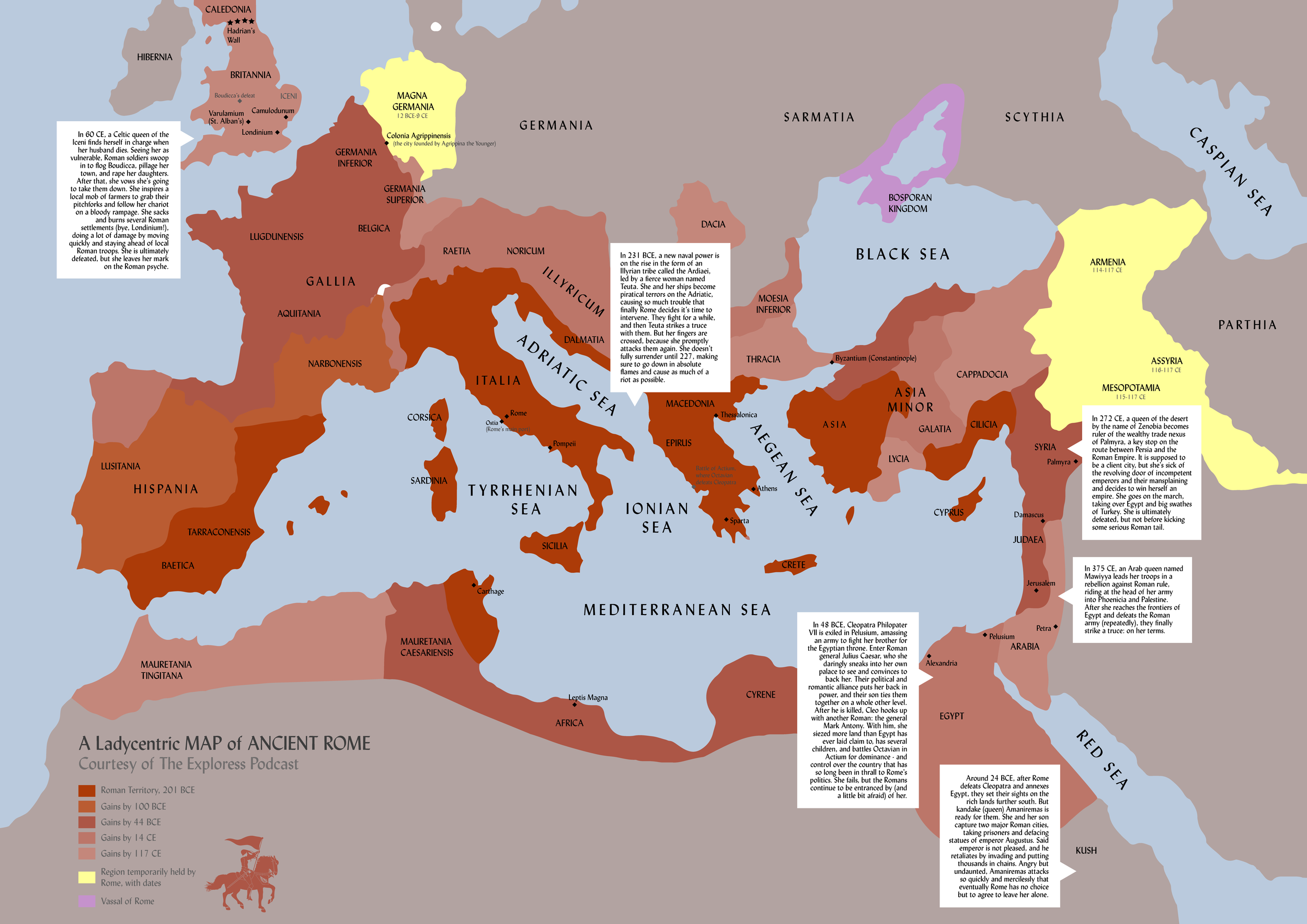
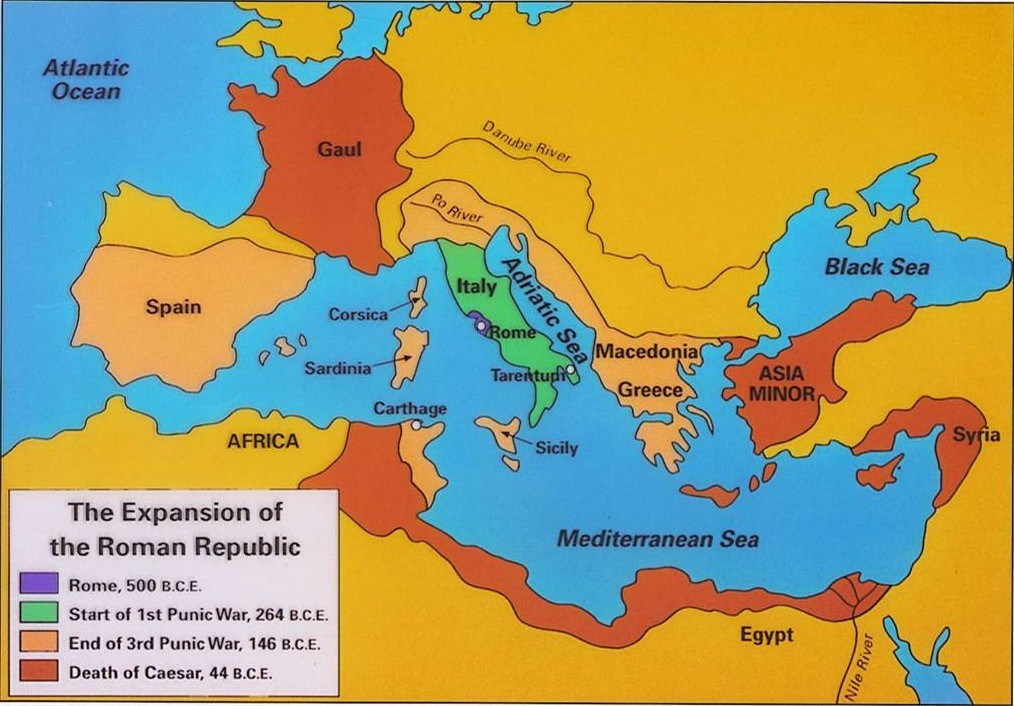
The Roman Empire, a sprawling dominion that shaped the course of Western civilization, remains a captivating subject of study. Its vast geographical expanse, encompassing diverse cultures and landscapes, is best understood through the lens of maps. Ancient Roman maps, though often incomplete or stylized, provide invaluable insights into the political, social, and economic structures of this powerful civilization.
Unveiling the Tapestry of Roman Power: The Importance of Ancient Roman Maps
Ancient Roman maps, though often fragmented and incomplete, serve as vital historical documents. They offer a unique perspective on the Roman world, revealing the empire’s intricate web of roads, cities, and provinces. These maps are essential for understanding:
- The Scope of Roman Domination: Maps clearly illustrate the geographical extent of the Roman Empire, highlighting its vast influence across continents. From the British Isles in the north to the deserts of North Africa in the south, and from Spain in the west to the Euphrates River in the east, the Roman Empire encompassed a remarkable range of territories.
- The Importance of Infrastructure: Roman maps showcase the empire’s impressive infrastructure, particularly its extensive network of roads. These roads, meticulously engineered and maintained, facilitated trade, communication, and military movement, connecting far-flung corners of the empire.
- The Administrative Structure: Maps provide insights into the administrative divisions of the Roman Empire. Provinces, each with its own governor and administrative apparatus, were strategically organized to ensure efficient governance and control.
- The Cultural and Economic Landscape: Ancient Roman maps reveal the distribution of key cities, towns, and settlements. This information allows historians to understand the economic activity, cultural centers, and social dynamics of the empire.
Deciphering the Details: Key Features of Ancient Roman Maps
Ancient Roman maps, while diverse in their forms and purposes, often share common features:
- The "Orbis Terrarum": The "world map," often known as the "Orbis Terrarum," was a common motif in Roman cartography. It depicted the known world centered on the Mediterranean Sea, with landmasses arranged according to geographical knowledge at the time.
- The "Tabula Peutingeriana": This famous Roman road map, dating back to the 4th century AD, provides a detailed representation of the Roman road network. It depicts major cities, roads, and distances, offering valuable information about Roman travel and communication.
- The "Forma Urbis Romae": This large-scale marble plan of the city of Rome, created in the 3rd century AD, provides a detailed representation of the city’s layout, including streets, buildings, and monuments. It offers valuable insights into Roman urban planning and architecture.
- The "Itineraria": These travel guides, often in the form of written itineraries, provided detailed descriptions of routes, distances, and points of interest. They were essential for travelers and merchants navigating the vast Roman road network.
Navigating the Past: Understanding the Limitations of Ancient Roman Maps
While offering valuable insights, ancient Roman maps also exhibit limitations:
- Stylized Representations: Ancient Roman maps often employed stylized representations of geographical features, focusing on depicting key locations and routes rather than precise geographical accuracy.
- Limited Geographical Knowledge: The Romans had limited knowledge of distant lands and continents, resulting in incomplete and sometimes inaccurate representations of the world.
- Incomplete Documentation: Many ancient Roman maps have been lost or damaged over time, leaving gaps in our understanding of the empire’s geographical knowledge.
Unveiling the Secrets: The Importance of Studying Ancient Roman Maps
Studying ancient Roman maps is crucial for understanding the empire’s history, culture, and society. They provide a tangible link to the past, allowing historians and researchers to:
- Visualize the Roman World: Maps provide a visual representation of the Roman Empire, helping to understand its vastness, organization, and interconnectedness.
- Analyze Roman Infrastructure: Maps reveal the intricate network of roads, aqueducts, and other infrastructure that supported the empire’s growth and prosperity.
- Reconstruct Roman Cities: Maps, particularly the "Forma Urbis Romae," provide detailed plans of cities, offering insights into urban planning, architecture, and daily life.
- Trace Trade Routes and Economic Activity: Maps show the distribution of cities, towns, and settlements, revealing patterns of trade and economic activity within the empire.
FAQs: Exploring the Nuances of Ancient Roman Maps
1. What materials were used to create ancient Roman maps?
Ancient Roman maps were created using a variety of materials, including papyrus, parchment, and marble. Some maps were painted on walls, while others were inscribed on bronze tablets.
2. How accurate were ancient Roman maps?
The accuracy of ancient Roman maps varied depending on the purpose and the geographical knowledge available at the time. While some maps provided detailed representations of local areas, others were more stylized and focused on depicting key locations and routes.
3. What are the most famous examples of ancient Roman maps?
The most famous examples of ancient Roman maps include the "Tabula Peutingeriana," the "Forma Urbis Romae," and the "Orbis Terrarum."
4. How have ancient Roman maps influenced modern cartography?
Ancient Roman maps have had a significant influence on modern cartography. Their use of grids, scales, and symbols laid the groundwork for the development of modern mapping techniques.
Tips: Unlocking the Secrets of Ancient Roman Maps
- Consult Historical Resources: Use historical texts, archaeological evidence, and other sources to gain a deeper understanding of the context and purpose of ancient Roman maps.
- Compare and Contrast Maps: Compare different maps to identify similarities and differences in their representations of the Roman world.
- Analyze Map Symbols and Conventions: Pay attention to the symbols and conventions used on ancient Roman maps to understand their meaning and how they were used to represent geographical features.
- Explore Online Resources: Several online resources provide digital versions of ancient Roman maps, allowing for interactive exploration and analysis.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Maps and Knowledge
Ancient Roman maps, though often incomplete or stylized, offer a unique and valuable window into the past. They provide a tangible link to the Roman world, allowing historians and researchers to understand the empire’s vastness, organization, and influence. By studying these maps, we gain a deeper appreciation for the ingenuity and achievements of the Roman people, who left behind a legacy of knowledge and innovation that continues to inspire and inform us today.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Journey Through Time: Exploring the Ancient Roman World with Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!