A Tapestry Of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges
A Tapestry of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges
Related Articles: A Tapestry of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Tapestry of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Tapestry of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges

North America, a continent of diverse landscapes, boasts a striking array of mountain ranges that have profoundly shaped its geography, climate, and history. These towering peaks, from the majestic Rockies to the volcanic Cascade Range, offer a captivating panorama of natural beauty, while simultaneously playing a crucial role in the continent’s ecosystem and human development.
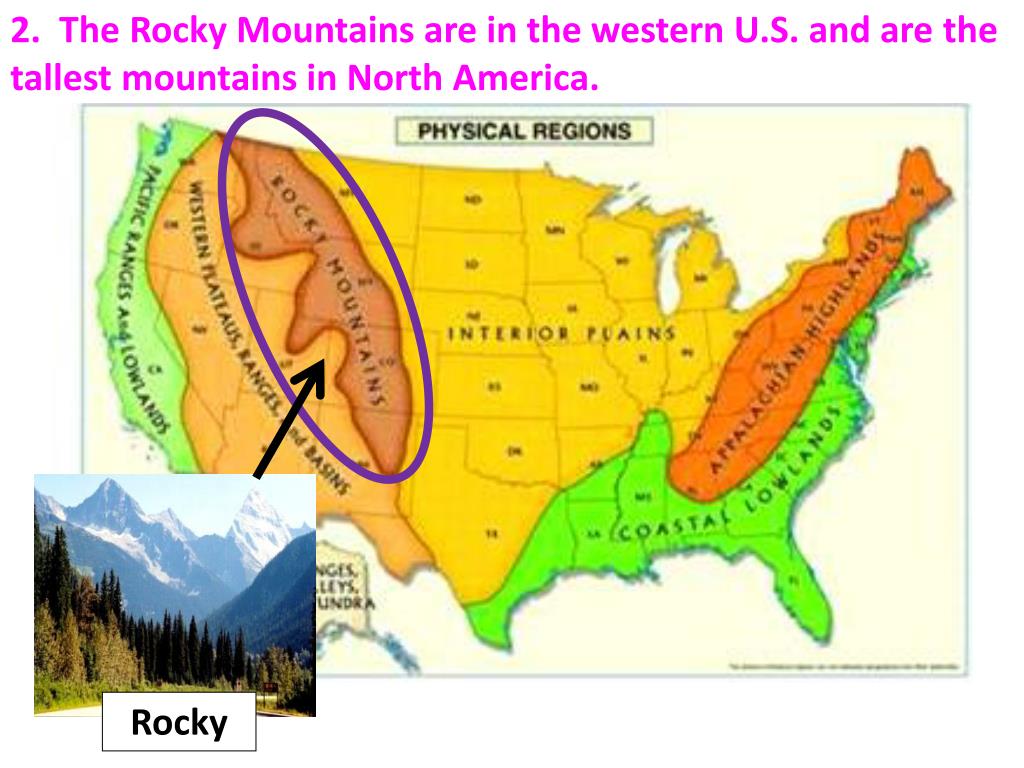
A Continental Backbone: The Rocky Mountains
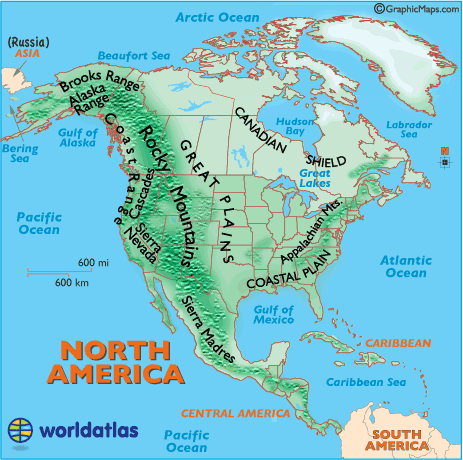
The Rocky Mountains, often referred to as the "backbone of North America," stretch over 3,000 miles from northern Canada to the southern United States. This formidable range, formed by tectonic plate collisions millions of years ago, is characterized by its rugged peaks, deep canyons, and expansive alpine meadows. The Rockies are a vital source of freshwater, supplying numerous rivers that irrigate the surrounding plains and support diverse ecosystems.
Western Frontiers: The Coast Mountains and the Cascade Range
Parallel to the Pacific Coast, the Coast Mountains of British Columbia and the Cascade Range of the United States stand as a testament to the continent’s geological dynamism. These ranges, formed by volcanic activity and tectonic uplift, are known for their dramatic peaks, glacier-carved valleys, and active volcanoes like Mount Rainier and Mount Shasta. The Coast Mountains are home to vast forests and abundant wildlife, while the Cascade Range attracts adventurers and nature enthusiasts with its stunning scenery and challenging hiking trails.
Eastern Highlands: The Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, stretching from Newfoundland to Alabama, represent a much older mountain range, formed over 480 million years ago. While less dramatic than the Rockies, the Appalachians are no less significant. Their rounded peaks, rolling hills, and fertile valleys have played a central role in shaping the eastern United States, providing fertile farmland, abundant natural resources, and scenic landscapes.
Beyond the Peaks: The Importance of North America’s Mountains
The mountains of North America are more than just breathtaking scenery. They are vital components of the continent’s ecosystem and play a critical role in regulating climate, supporting biodiversity, and providing essential resources for human populations.
Climate Regulation: Mountains act as natural barriers, influencing wind patterns and precipitation. They create rain shadows, where one side of the range receives abundant rainfall while the other remains dry. This phenomenon is evident in the arid regions east of the Sierra Nevada in California and the dry plains east of the Rockies.
Biodiversity Hotspots: The unique habitats and varied elevations of mountain ranges support a remarkable diversity of plant and animal life. From alpine meadows teeming with wildflowers to dense forests sheltering rare species, mountains are hotspots of biodiversity.
Water Resources: Mountains are the source of countless rivers and streams, providing freshwater for drinking, irrigation, and hydroelectric power generation. The snowpack accumulated on mountain peaks acts as a natural reservoir, releasing water gradually throughout the year, ensuring a steady supply for downstream communities.
Economic Significance: Mountains have long been a source of natural resources, including timber, minerals, and energy. Mining, logging, and tourism industries thrive in mountainous regions, contributing significantly to local economies.
Cultural Heritage: Mountains have held cultural significance for indigenous communities for millennia. They are often considered sacred places, imbued with spiritual meaning and rich traditions. Many indigenous cultures have developed unique adaptations and knowledge systems to thrive in these challenging environments.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While mountains provide numerous benefits, they also present challenges. Climate change is impacting mountain ecosystems, leading to glacial retreat, altered precipitation patterns, and increased risk of wildfires. These changes threaten biodiversity, water resources, and human communities.
However, these challenges also present opportunities. Sustainable practices in forestry, mining, and tourism can mitigate environmental impacts and ensure the long-term health of mountain ecosystems. Conservation efforts focused on protecting biodiversity and managing water resources are crucial for the future of North America’s mountains.
FAQs:
Q: What is the highest mountain in North America?
A: Denali, formerly known as Mount McKinley, located in Alaska, is the highest mountain in North America, reaching an elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190 meters).
Q: What are the major mountain ranges in North America?
A: The major mountain ranges in North America include the Rocky Mountains, the Coast Mountains, the Cascade Range, the Sierra Nevada, the Appalachian Mountains, and the Mexican Volcanic Belt.
Q: How do mountains influence climate?
A: Mountains act as natural barriers, influencing wind patterns and precipitation. They create rain shadows, where one side of the range receives abundant rainfall while the other remains dry.
Q: What are some of the environmental challenges facing North America’s mountains?
A: Climate change, deforestation, mining activities, and pollution are some of the major environmental challenges facing North America’s mountains.
Q: What can be done to protect North America’s mountains?
A: Conservation efforts, sustainable resource management, and promoting responsible tourism are essential for protecting North America’s mountains.
Tips for Exploring North America’s Mountains:
- Plan your trip: Research the specific mountain range and trail you plan to visit, considering altitude, weather conditions, and potential hazards.
- Prepare for the unexpected: Pack appropriate clothing and gear, including layers for varying temperatures, sturdy footwear, and a first-aid kit.
- Respect the environment: Stay on designated trails, pack out all trash, and avoid disturbing wildlife.
- Be aware of altitude sickness: Ascend gradually to acclimatize to higher altitudes.
- Seek local guidance: Consult with park rangers or experienced hikers for advice and safety tips.
Conclusion:
North America’s mountains are a testament to the continent’s geological history and a vital part of its ecosystem. From the towering peaks of the Rockies to the rolling hills of the Appalachians, these ranges offer breathtaking beauty, essential resources, and unique cultural significance. Understanding and protecting these natural wonders is crucial for the well-being of the continent and its future generations.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Tapestry of Peaks: Understanding North America’s Mountain Ranges. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!