Charting The Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps Of Jerusalem
Charting the Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps of Jerusalem
Related Articles: Charting the Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps of Jerusalem
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Charting the Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps of Jerusalem. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps of Jerusalem

Jerusalem, a city steeped in history and religious significance, has captivated cartographers for centuries. Old maps of Jerusalem, far more than mere representations of geography, offer a unique window into the past, revealing not only the physical landscape but also the evolving understanding of the city’s importance and its place within the world. These maps, crafted with meticulous detail and infused with the perspectives of their creators, provide invaluable insights into the city’s development, its religious and cultural context, and the shifting power dynamics that have shaped its history.
Tracing the Evolution of Jerusalem: A Cartographic Timeline
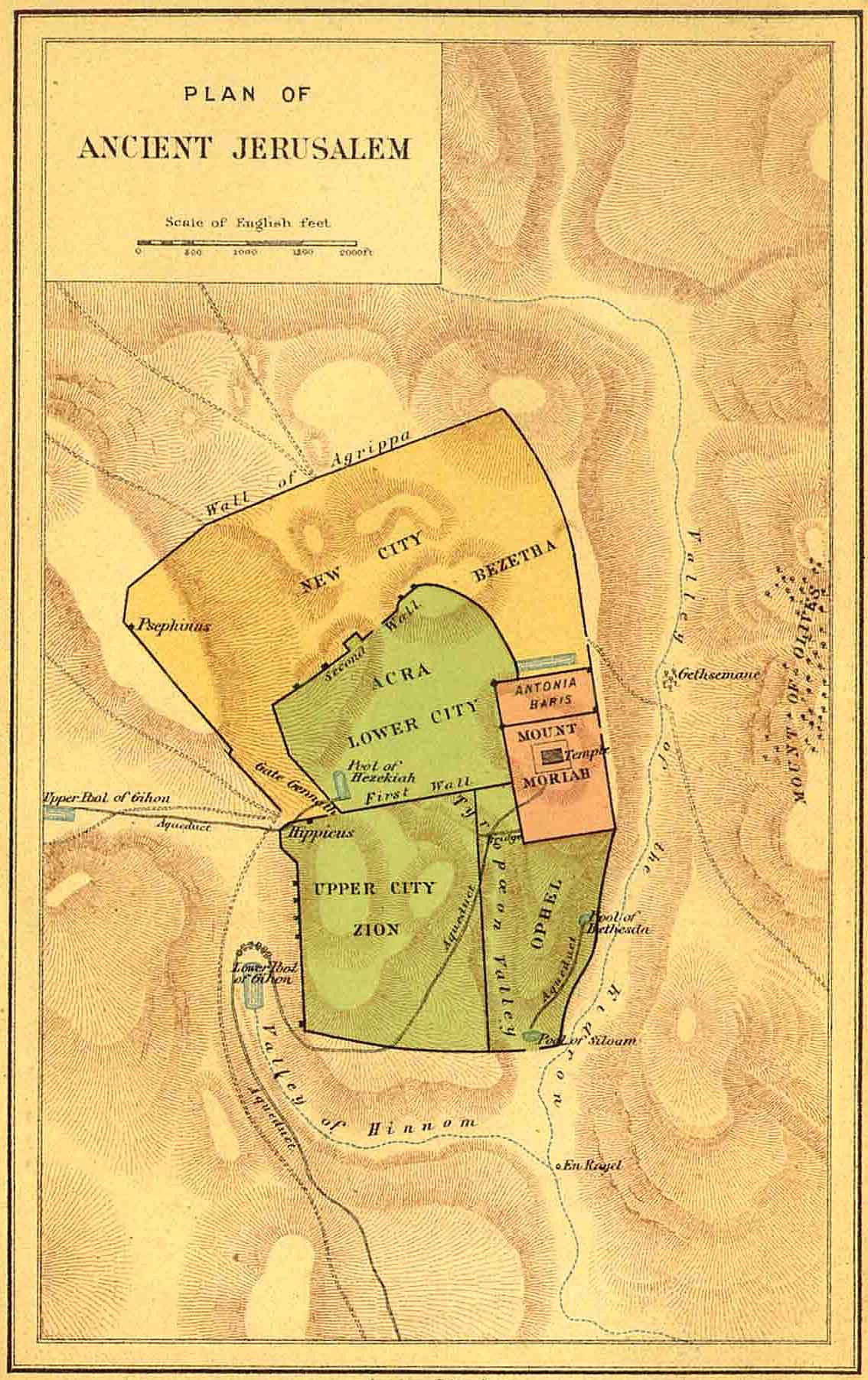
The earliest known maps of Jerusalem, dating back to the Roman period, are primarily schematic in nature, focusing on the city’s layout and its key religious sites. The "Madaba Map," a remarkable mosaic floor from a 6th-century church in Jordan, provides a detailed depiction of Jerusalem, showcasing its walls, streets, and significant buildings, including the Temple Mount and the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
The Middle Ages saw a surge in mapmaking, driven by the growing influence of Christianity and the pilgrimages to the Holy Land. Maps from this period, often produced by European cartographers, reflect a blend of accuracy and symbolic representation. The "Tabula Peutingeriana," a Roman road map dating back to the 4th century, includes a depiction of Jerusalem, highlighting its importance as a key stop on the pilgrimage route.
During the Renaissance, the pursuit of scientific knowledge and the development of printing technology further fueled the creation of maps. Maps of Jerusalem from this era often incorporated more detailed geographical information, including the surrounding topography and the locations of nearby settlements. The "Cosmographia" by Sebastian Münster, published in 1544, is a notable example, featuring a comprehensive map of Jerusalem and its environs.
The 17th and 18th centuries witnessed the emergence of more accurate and detailed maps, driven by advancements in surveying and cartographic techniques. Maps from this period, often commissioned by European powers, reveal a growing interest in the city’s strategic importance and its potential for colonization. The maps of Pierre Jacotin, produced during the Napoleonic campaign in Egypt and Syria, are significant examples, showcasing the city’s fortifications and urban layout with remarkable precision.
Beyond Geography: Unveiling the Cultural and Religious Context
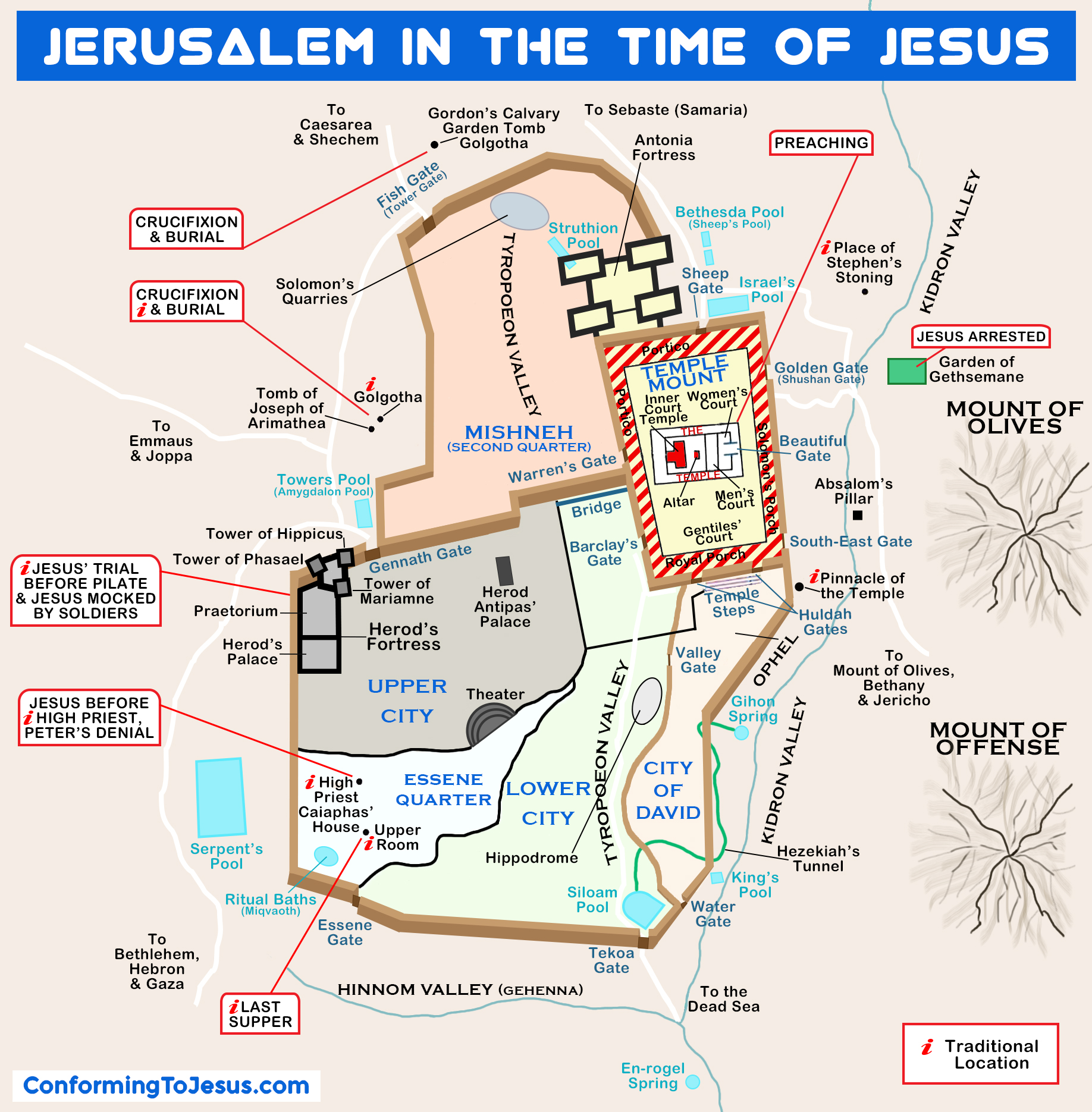
Old maps of Jerusalem offer more than just a visual representation of the city; they also provide valuable insights into the cultural and religious context in which they were created. Maps produced during the Crusades, for example, often emphasized the city’s Christian significance, depicting the key churches and pilgrimage sites with prominence. The "Itinerarium Burdigalense," a 4th-century travelogue describing a pilgrimage to Jerusalem, includes a rudimentary map that highlights the locations of important Christian sites.
Maps from the Ottoman period, on the other hand, reflect the city’s Islamic heritage, showcasing the mosques, shrines, and other significant Islamic structures. The "Book of Wonders," a 13th-century manuscript by Zakariya al-Qazwini, includes a detailed map of Jerusalem that illustrates its religious importance within the Islamic world.
The Power of Perspective: Maps as Instruments of Influence
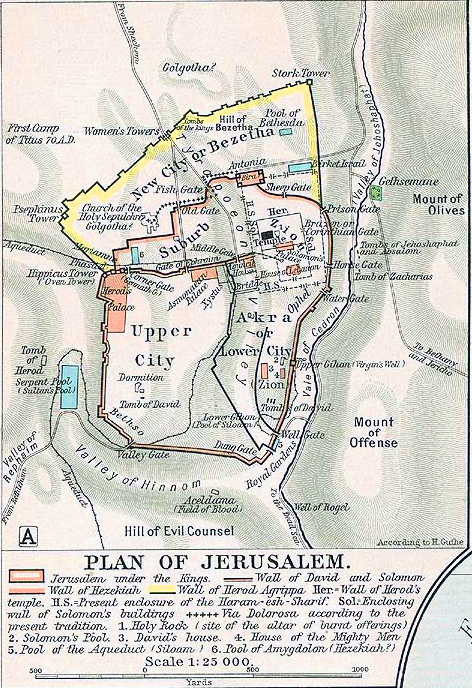
Old maps of Jerusalem were not merely neutral representations of the city; they often served as instruments of power and influence. Maps produced by European powers during the colonial era, for example, frequently depicted Jerusalem in a way that emphasized their own dominance and control. The "Plan of Jerusalem," created by the British military during the 19th century, provides a clear example, showcasing the city’s fortifications and strategic locations from a perspective that underscored British military superiority.
FAQs: Unraveling the Mysteries of Old Maps of Jerusalem
What can old maps of Jerusalem tell us about the city’s history?
Old maps of Jerusalem provide invaluable insights into the city’s development over time, revealing the changing urban landscape, the evolution of its religious and cultural significance, and the shifting power dynamics that have shaped its history.
How did the maps of Jerusalem change over time?
Maps of Jerusalem evolved from rudimentary schematic representations to more detailed and accurate depictions, reflecting advancements in cartographic techniques, the growing importance of the city, and the changing perspectives of its creators.
What are the key features that are typically depicted on old maps of Jerusalem?
Key features often depicted on old maps of Jerusalem include the city walls, the Temple Mount, the Church of the Holy Sepulchre, mosques, shrines, and other significant religious and historical landmarks.
What can we learn about the cultural and religious context of Jerusalem from old maps?
Maps of Jerusalem reveal the cultural and religious perspectives of their creators, highlighting the city’s importance to different faiths and the ways in which it was understood and interpreted within different historical periods.
What are some of the most famous old maps of Jerusalem?
Some of the most famous old maps of Jerusalem include the "Madaba Map," the "Tabula Peutingeriana," the "Cosmographia" by Sebastian Münster, and the maps of Pierre Jacotin.
Tips for Understanding Old Maps of Jerusalem
- Context is Key: Consider the historical context in which the map was created, including the political, religious, and cultural influences of the time.
- Examine the Details: Pay close attention to the map’s symbols, legends, and annotations, as these can provide valuable clues about the mapmaker’s intentions and the significance of the depicted features.
- Compare and Contrast: Compare different maps of Jerusalem from different periods to understand how the city’s representation evolved over time.
- Seek Expert Guidance: Consult historical sources and scholarly works on cartography and the history of Jerusalem to gain a deeper understanding of the maps and their significance.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Maps and a City of Timeless Importance
Old maps of Jerusalem, far more than mere representations of geography, offer a fascinating journey through time, revealing the city’s evolution, its enduring religious significance, and the complex interplay of power and perspective that has shaped its history. As we continue to explore these cartographic treasures, we gain a deeper appreciation for the timeless importance of Jerusalem and its enduring place within the human story.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the Sacred: A Journey Through Old Maps of Jerusalem. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!