Deciphering The French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To The Administrative Map
Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Map
Related Articles: Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Map

The political map of France, a complex tapestry woven from history, geography, and societal evolution, offers a fascinating glimpse into the country’s administrative structure and its nuanced political dynamics. This guide delves into the intricate details of this map, exploring its key components and highlighting their significance in shaping the nation’s governance.
Understanding the Foundation: Administrative Divisions
France’s political map is structured around a hierarchical system of administrative divisions, each with its own specific responsibilities and functions.
-
Regions (Régions): The top tier of the administrative structure, France is currently divided into 18 regions, including the overseas regions of Guadeloupe, Martinique, French Guiana, Réunion, and Mayotte. These regions are responsible for regional planning, economic development, education, and cultural affairs.
-
Departments (Départements): Within each region, there are departments, totaling 101 in mainland France and 5 in overseas territories. Departments oversee social welfare, infrastructure, and public safety.
-
Arrondissements (Arrondissements): Departments are further subdivided into arrondissements, which are primarily administrative units responsible for local governance.
-
Communes (Communes): The smallest unit of local government, communes represent towns and villages. They manage local services like sanitation, public transportation, and cultural activities.
The Impact of Decentralization: Shifting Power Dynamics
Since the 1980s, France has witnessed a significant shift in power dynamics through decentralization. This process has transferred authority from the central government to regional and local entities. This decentralization has led to:
- Increased Regional Autonomy: Regions now have greater control over their budgets, policies, and development projects.
- Enhanced Local Participation: Communes have gained more autonomy in managing local affairs, fostering a sense of community involvement.
- More Efficient Governance: Decentralization aims to improve the efficiency of governance by bringing decision-making closer to the people.
The Political Landscape: A Mosaic of Diversity
The French political landscape is characterized by a diverse array of political parties and movements, each with its own ideologies and agendas.
-
The Traditional Parties: The two major political parties, the right-wing Les Républicains (LR) and the left-wing Parti Socialiste (PS), have dominated French politics for decades. These parties often compete for power in national elections and form coalitions to govern.
-
Emerging Forces: In recent years, new political movements have emerged, challenging the established order. These include the far-right Rassemblement National (RN), the centrist La République En Marche! (LREM), and various environmental and social justice parties.
-
Political Divisions: Despite the presence of diverse political forces, France often experiences significant political divisions, particularly between left and right-wing ideologies. These divisions manifest in debates on economic policies, social welfare, immigration, and European integration.
The Importance of the Political Map: A Framework for Governance
The political map of France plays a crucial role in shaping the country’s governance and political discourse. It provides a framework for:
- Allocating Resources: The administrative divisions determine how resources are distributed across regions and departments.
- Enacting Policies: The political map facilitates the implementation of policies at different levels of government, from national to local.
- Representing Citizens: The electoral system is structured based on these administrative divisions, ensuring that citizens have a voice in government through elections.
FAQs: Delving Deeper into the French Political Map
1. What is the significance of the overseas regions in the French political map?
Overseas regions, despite their geographical distance from mainland France, are integral parts of the French Republic. They are represented in the French Parliament and enjoy the same rights and responsibilities as mainland regions.
2. How does the electoral system work in France?
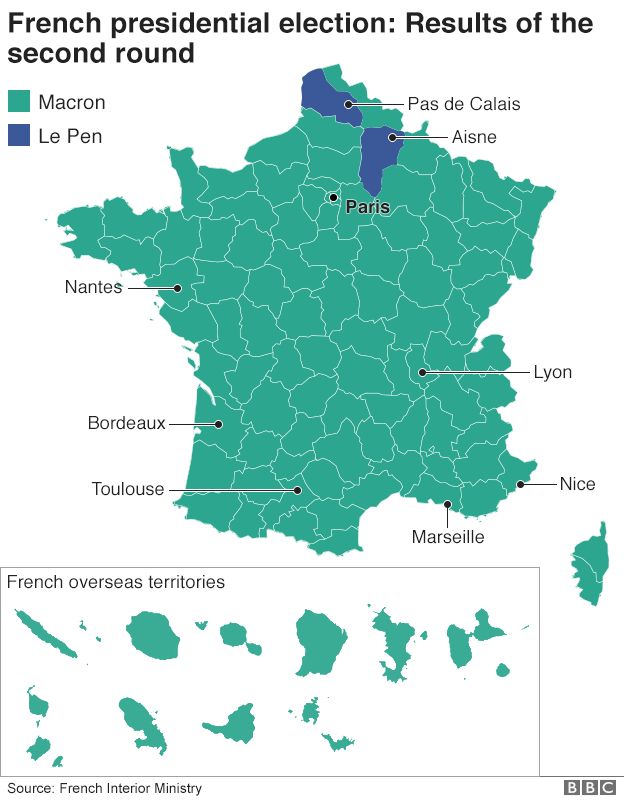
France has a two-round system for presidential and parliamentary elections. In the first round, all candidates compete. If no candidate receives a majority, a second round is held between the two top candidates.
3. What are the main challenges facing French governance today?
Contemporary challenges include economic inequality, social unrest, immigration, environmental concerns, and the rise of populism.
4. How does the French political map reflect the country’s history?
The current administrative divisions are the result of centuries of historical evolution, including the French Revolution, the Napoleonic era, and the post-World War II period.
5. What are the future prospects for the French political map?
The future of the French political map is likely to be shaped by ongoing debates on decentralization, regional autonomy, and the evolving political landscape.
Tips: Navigating the French Political Map
- Consult Reliable Sources: Utilize reputable news outlets, academic journals, and government websites for accurate and up-to-date information.
- Analyze Political Data: Explore data on electoral results, opinion polls, and demographic trends to understand the nuances of the political landscape.
- Engage with Different Perspectives: Seek out diverse viewpoints on political issues to develop a comprehensive understanding of the complexities of French politics.
Conclusion: A Dynamic and Ever-Evolving Landscape
The political map of France is a dynamic and ever-evolving landscape, reflecting the country’s rich history, diverse political forces, and ongoing societal transformations. Understanding its intricacies is essential for comprehending the complexities of French governance and its impact on the lives of its citizens. By analyzing its structure, exploring its historical context, and engaging with the ongoing political debates, one can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of this influential and multifaceted nation.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the French Political Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to the Administrative Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!