Deciphering The Language Of The Skies: A Comprehensive Guide To Weather Map Symbols
Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Symbols
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Symbols
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Symbols
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sky-cover_key-58b740215f9b5880804caa18.png)
Weather maps, those colorful diagrams adorned with various symbols and lines, hold the key to understanding the atmospheric conditions that shape our world. These maps, a product of intricate meteorological data collection and analysis, present a snapshot of the weather across a region or even the globe, enabling informed decision-making for individuals, industries, and governments alike.
To effectively interpret these maps and glean valuable insights from their intricate patterns, a thorough understanding of the symbols employed is essential. This guide provides a comprehensive exploration of the common weather map symbols, their meanings, and how they contribute to our understanding of the ever-changing atmosphere.
The Foundation: Temperature and Pressure
At the heart of weather map interpretation lies the interplay of temperature and pressure. These fundamental forces drive atmospheric circulation and influence weather patterns.
-
Isotherms: These lines, typically depicted in blue or red on weather maps, connect locations with equal temperatures. Their spacing and orientation reveal temperature gradients, highlighting areas of significant temperature change and potential for weather events.
-
Isobars: These lines, usually drawn in black or brown, connect locations with equal atmospheric pressure. Their closeness or distance indicates the strength of pressure gradients, influencing wind speed and direction. Areas with tightly packed isobars signify strong winds, while widely spaced isobars indicate calmer conditions.
Visualizing Precipitation: The Art of Symbolism
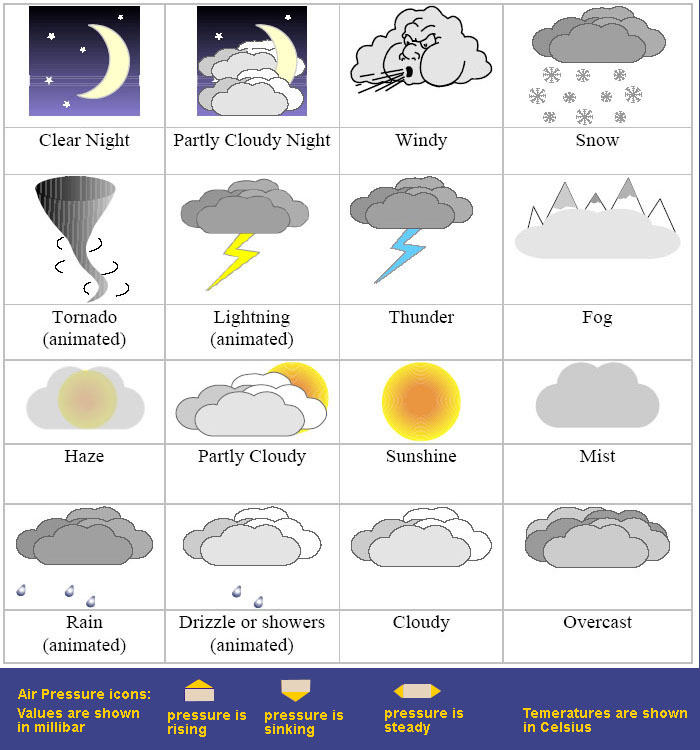
Precipitation, a crucial aspect of weather, is represented on maps through a variety of symbols, each conveying specific types and intensities.
-
Rain: Various symbols depict rain, ranging from small dots for light rain to heavier dots and lines for moderate and heavy rainfall. Shaded areas can also be used to indicate widespread rainfall.
-
Snow: Snow is represented by snowflake symbols, with varying sizes and densities reflecting the intensity of snowfall. Shaded areas can denote heavy snow.
-
Freezing Rain: This hazardous weather phenomenon is depicted by a mix of rain and snowflake symbols, highlighting the risk of ice accumulation.
-
Sleet: A combination of rain and snowflake symbols, often with a small dot within, represents sleet, a mix of rain and frozen precipitation.
-
Hail: Hail is indicated by small circles with a solid fill, often with a diameter proportional to the size of the hail.
Winds: Direction and Strength
Wind, the movement of air, plays a critical role in weather patterns and is depicted on maps using arrows and barbs.
-
Wind Direction: The arrowhead points in the direction from which the wind is blowing. For example, an arrow pointing west indicates a wind blowing from the west.
-
Wind Speed: The length of the arrow or the number of barbs on the arrow tail represent wind speed. A longer arrow or more barbs indicate stronger winds.
Fronts: Boundaries of Change
Fronts, boundaries between air masses of different temperatures and densities, are critical in determining weather patterns.
-
Cold Front: Depicted as a blue line with triangular points facing the direction of movement, cold fronts bring rapid temperature drops, strong winds, and often precipitation.
-
Warm Front: Represented by a red line with semi-circles facing the direction of movement, warm fronts bring gradual temperature increases and often precipitation, usually light rain or drizzle.
-
Stationary Front: A combination of blue triangles and red semi-circles, stationary fronts indicate a boundary where air masses are not moving significantly. They can bring prolonged periods of precipitation or fog.
-
Occluded Front: A purple line with alternating triangles and semi-circles, occluded fronts form when a cold front overtakes a warm front. They can bring complex weather patterns, including heavy precipitation and thunderstorms.
Other Symbols: Expanding the Narrative
Beyond the core symbols, weather maps often incorporate additional symbols to convey further information:
-
Thunderstorms: A lightning bolt symbol indicates the presence of thunderstorms, often accompanied by heavy rain, strong winds, and hail.
-
Fog: A circle with a diagonal line through it represents fog, a condition of reduced visibility caused by water droplets suspended in the air.
-
Tornado: A spiral symbol, often with a funnel shape, indicates the potential for tornado formation.
-
Hurricane: A large circle with a central dot represents a hurricane, a powerful storm characterized by strong winds, heavy rain, and storm surges.
Understanding the Power of Weather Maps
The ability to interpret weather map symbols is crucial for various applications:
-
Personal Safety: Understanding weather patterns helps individuals make informed decisions about outdoor activities, travel, and personal safety.
-
Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather forecasts to plan planting, irrigation, and harvesting schedules, ensuring optimal crop yields.
-
Transportation: Airlines, shipping companies, and road authorities utilize weather information to ensure safe and efficient operations.
-
Emergency Management: Weather forecasts are essential for disaster preparedness, enabling authorities to issue timely warnings and coordinate emergency response efforts.
-
Research and Science: Meteorologists and climate scientists use weather maps to study atmospheric processes, understand climate change, and develop more accurate weather models.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are the different types of weather maps?
A: Weather maps come in various formats, including surface maps, upper-air maps, radar maps, and satellite images. Each type provides a different perspective on the weather.
Q: How often are weather maps updated?
A: Weather maps are typically updated every few hours, reflecting the dynamic nature of the atmosphere.
Q: What are the limitations of weather maps?
A: Weather maps are based on data collected at specific locations and times, meaning they may not capture all weather events accurately, especially in areas with limited data coverage.
Tips for Interpreting Weather Maps
-
Start with the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the basic symbols and their meanings before delving into more complex maps.
-
Pay Attention to Scale: Understand the scale of the map to accurately interpret the distance between locations and the intensity of weather events.
-
Consider the Context: Take into account factors such as time of year, geographic location, and recent weather patterns to interpret the map effectively.
-
Use Multiple Resources: Consult multiple weather maps and sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
Conclusion
Weather maps are essential tools for understanding and predicting weather patterns. By mastering the language of weather map symbols, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the forces shaping our climate, make informed decisions about personal safety and activities, and contribute to a safer and more informed society. The ability to interpret these maps empowers us to navigate the ever-changing world of weather with greater confidence and preparedness.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Comprehensive Guide to Weather Map Symbols. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!