Deciphering The Language Of The Skies: A Guide To Weather Map Key Symbols
Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Guide to Weather Map Key Symbols
Related Articles: Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Guide to Weather Map Key Symbols
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Guide to Weather Map Key Symbols. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Guide to Weather Map Key Symbols
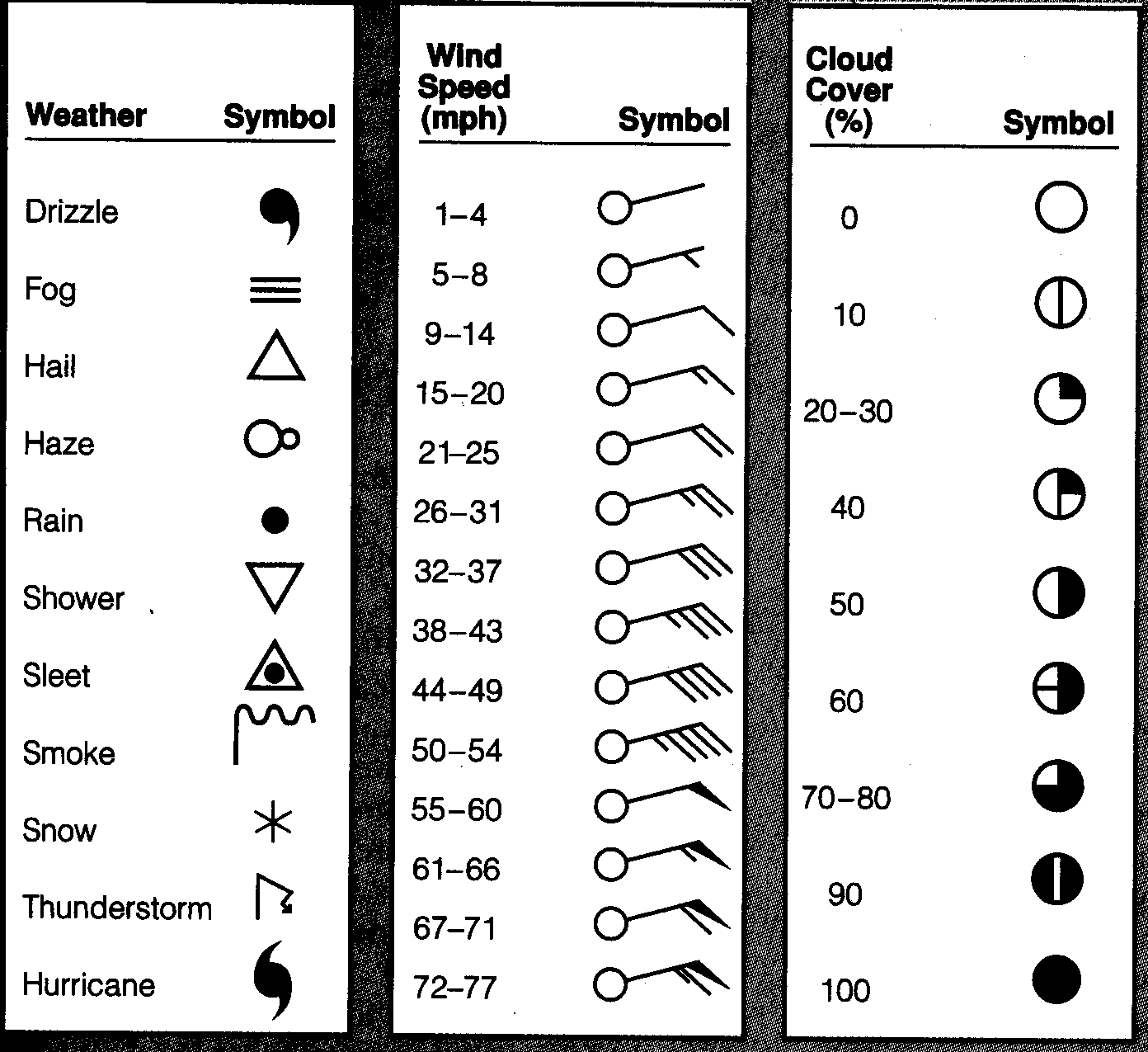
Weather maps are visual representations of meteorological data, providing a snapshot of atmospheric conditions across a region. Understanding the key symbols used on these maps is crucial for interpreting weather patterns, predicting potential hazards, and making informed decisions regarding outdoor activities, travel, and even personal health.
This comprehensive guide explores the key symbols commonly used on weather maps, offering a detailed explanation of their meaning and significance. We will delve into the various symbols representing temperature, precipitation, wind, cloud cover, and other crucial meteorological elements.
Temperature Symbols:
- Isotherms: These lines connect points of equal temperature on a map. They are typically drawn in intervals of 5°C or 10°F, allowing for the identification of temperature gradients and the location of warm and cold fronts.
- Thermal Contours: Similar to isotherms, thermal contours connect points of equal temperature at a specific altitude, often used to depict the temperature profile of the atmosphere.
- Temperature Stations: These symbols represent locations where temperature readings are taken. They often include the actual temperature reading alongside the symbol.
Precipitation Symbols:
- Rain: A simple rain drop symbol represents rainfall. The size and density of the symbol can indicate the intensity of rainfall, with larger and denser symbols representing heavier precipitation.
- Snow: A snowflake symbol signifies snowfall. The size and density of the snowflake can indicate the intensity of snowfall, with larger and denser symbols representing heavier snowfall.
- Sleet: A combination of rain and snow symbols represents sleet, a form of precipitation consisting of small, ice pellets.
- Freezing Rain: A rain symbol with a small ice crystal inside signifies freezing rain, a form of precipitation that falls as liquid rain but freezes upon contact with surfaces.
- Hail: A symbol resembling a small, solid circle with a small dot in the center represents hail, a form of precipitation consisting of solid pieces of ice.
- Thunderstorms: A symbol representing a cloud with lightning bolts emanating from it indicates thunderstorms.
Wind Symbols:
- Wind Barbs: These symbols, typically depicted as a line with small barbs, represent wind direction and speed. The direction of the line indicates the wind direction, while the number and length of the barbs represent the wind speed. Each full barb represents 10 knots (nautical miles per hour), while half barbs represent 5 knots. A flag represents 50 knots.
- Wind Arrows: These symbols, resembling arrows, represent wind direction and speed. The arrowhead points in the direction of the wind, and the length of the arrow represents the wind speed.
- Wind Isotachs: These lines connect points of equal wind speed, allowing for the identification of areas with strong and weak winds.
Cloud Cover Symbols:
- Cloud Coverage: These symbols represent the amount of cloud cover in the sky. They typically consist of a circle representing the sky, with different patterns within the circle to indicate the cloud coverage. A completely filled circle indicates overcast skies, while a circle with a few small dots indicates scattered clouds.
- Cloud Types: Different symbols are used to represent different cloud types, such as cumulus, stratus, and cirrus clouds. These symbols provide information about the height, shape, and composition of clouds, which can be helpful in predicting weather conditions.
Other Important Symbols:
- Fronts: These lines represent boundaries between different air masses. Cold fronts are depicted as blue lines with triangles, while warm fronts are depicted as red lines with half circles. Stationary fronts are represented by alternating blue and red lines with triangles and half circles.
- Pressure Systems: High-pressure systems are typically represented by an "H" symbol, while low-pressure systems are represented by an "L" symbol.
- Visibility: Symbols representing visibility are often used to indicate the distance at which objects can be seen.
FAQs on Weather Map Key Symbols:
Q: What is the difference between a cold front and a warm front?
A: A cold front is a boundary between a cold air mass and a warmer air mass, where the cold air is pushing into the warmer air. This can lead to rapid changes in weather, including thunderstorms, strong winds, and heavy precipitation. A warm front is a boundary between a warm air mass and a cooler air mass, where the warm air is pushing into the cooler air. This can lead to gradual changes in weather, including light rain, fog, and rising temperatures.
Q: What is the significance of high-pressure and low-pressure systems?
A: High-pressure systems are associated with clear skies and calm weather, while low-pressure systems are associated with cloudy skies, precipitation, and windy conditions.
Q: How can I use weather map symbols to predict future weather conditions?
A: By understanding the symbols representing fronts, pressure systems, and other meteorological elements, you can gain insights into the direction and speed of weather systems. For example, the movement of a cold front can indicate the potential for severe weather, while the presence of a high-pressure system can suggest a period of stable weather.
Q: Where can I find weather maps with key symbols?
A: Weather maps are readily available online from various sources, including national meteorological agencies, private weather companies, and news outlets. You can also find weather maps in newspapers and weather apps.
Tips for Interpreting Weather Map Key Symbols:
- Familiarize yourself with the symbols: Spend time studying the symbols and their meanings to ensure you can accurately interpret weather maps.
- Look for patterns and trends: Pay attention to the overall pattern of symbols on the map, such as the movement of fronts or the location of pressure systems.
- Consider the time of year: The interpretation of weather map symbols can vary depending on the season. For example, a snowflake symbol in the summer might indicate hail, while a rain symbol in the winter might indicate freezing rain.
- Consult multiple sources: It’s always a good idea to consult multiple weather maps and forecasts from different sources to get a more comprehensive understanding of the weather situation.
Conclusion:
Weather map key symbols provide a crucial language for understanding and interpreting weather patterns. By mastering the meaning of these symbols, individuals can gain valuable insights into current and future weather conditions, enabling them to make informed decisions regarding safety, travel, and outdoor activities. Understanding the language of the skies empowers individuals to navigate the world with greater awareness and preparedness, enhancing their ability to enjoy the wonders of nature while minimizing potential risks.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sky-cover_key-58b740215f9b5880804caa18.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stationplot-58b740273df78c060e194bdc.gif)
/weather_fronts-labeled-nws-58b7402a3df78c060e1953fd.png)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/currentwxsymbols-58b740243df78c060e194464.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Deciphering the Language of the Skies: A Guide to Weather Map Key Symbols. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!