Exploring The Map Of Khalistan: A Historical And Political Analysis
Exploring the Map of Khalistan: A Historical and Political Analysis
Related Articles: Exploring the Map of Khalistan: A Historical and Political Analysis
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Map of Khalistan: A Historical and Political Analysis. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Exploring the Map of Khalistan: A Historical and Political Analysis

The concept of Khalistan, a proposed independent Sikh state, has been a subject of intense debate and controversy for decades. While the idea has gained traction among certain segments of the Sikh community, it remains a highly contested notion, with significant implications for the political landscape of the Indian subcontinent. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the map of Khalistan, its historical context, and the various political and social factors that have contributed to its emergence.
Historical Context:
The Sikh community in India has a rich and complex history, marked by periods of both persecution and resilience. The rise of Sikhism in the 15th century coincided with the decline of the Mughal Empire, creating a power vacuum that the Sikhs exploited to establish their own kingdoms in the Punjab region. This period of relative autonomy, however, was short-lived, as the Sikhs faced renewed pressure from the expanding British Empire in the 19th century.
The British, after conquering the Punjab, implemented policies that alienated the Sikh community, leading to a series of rebellions. The annexation of Punjab in 1849 marked the end of Sikh rule, but the community continued to play a significant role in the Indian independence movement.
Following India’s independence in 1947, the partition of the country resulted in widespread violence and displacement. The Punjab region, which was divided between India and Pakistan, became the epicenter of this communal strife. The Sikhs, caught between the two newly formed nations, faced immense hardship and a sense of disenfranchisement.
The Emergence of Khalistan:
The post-partition period witnessed a growing sense of alienation among Sikhs in India. The perception of discrimination and marginalization within the Indian political system fueled the demand for a separate Sikh state. The movement for Khalistan gained momentum in the 1970s and 1980s, spearheaded by various Sikh organizations advocating for self-determination.
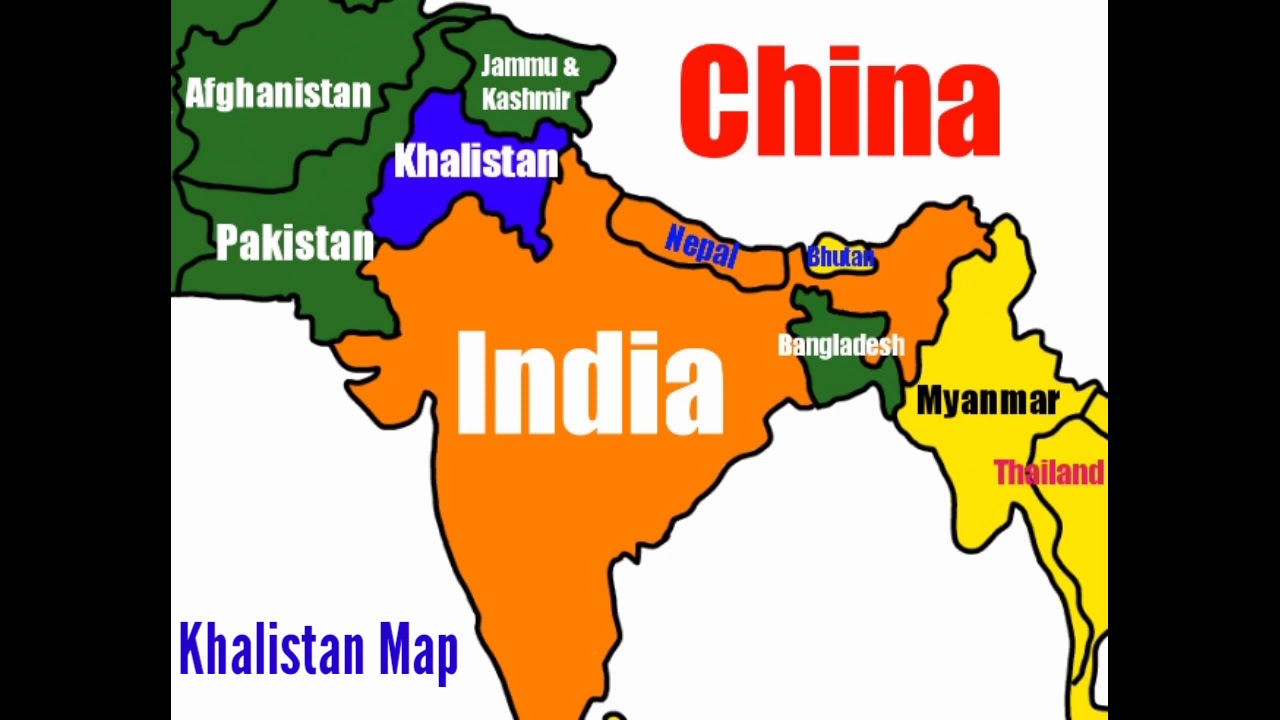
The map of Khalistan, often depicted as encompassing the majority-Sikh areas of Punjab in India, became a symbol of this movement. It represented a vision of a sovereign Sikh nation, free from the perceived injustices of the Indian government. The movement’s demands ranged from greater autonomy within India to complete independence.
Political and Social Factors:
Several factors contributed to the rise of the Khalistan movement. These include:
- Religious Identity: The Sikh community, with its distinct religious beliefs and cultural practices, felt a strong sense of identity separate from the broader Hindu and Muslim populations.
- Political Marginalization: The Sikhs perceived themselves as being underrepresented and ignored by the Indian government, leading to a sense of grievance and resentment.
- Economic Disparity: The Punjab region, historically a prosperous agricultural hub, faced economic challenges following partition. This economic hardship fueled discontent and contributed to the movement’s appeal.
- Human Rights Violations: The movement gained traction following reports of alleged human rights abuses committed against Sikhs by the Indian government. These accusations, while disputed, further alienated the Sikh community.
The Armed Conflict:
The Khalistan movement took a violent turn in the 1980s, with the emergence of armed groups like the Babbar Khalsa International and the Khalistan Liberation Force. These groups resorted to terrorism and violence, targeting government officials and civilians, in an attempt to achieve their political objectives.
The Indian government responded with a military crackdown, leading to a period of intense conflict and bloodshed. The situation reached a climax with the storming of the Golden Temple in Amritsar, the holiest shrine for Sikhs, by the Indian Army in 1984. This event, which resulted in significant casualties, further inflamed tensions and polarized the Sikh community.
The Aftermath:
The Khalistan movement has witnessed a decline in recent years, with the armed struggle largely subdued. However, the issue remains sensitive and continues to be a source of debate and tension between the Sikh community and the Indian government.
FAQs about the Map of Khalistan:
Q: What is the geographical extent of the proposed Khalistan?
A: The map of Khalistan typically depicts the majority-Sikh areas of Punjab in India, although there are variations in the specific boundaries proposed by different groups.
Q: What are the arguments in favor of Khalistan?
A: Proponents of Khalistan argue that it is necessary to protect the Sikh community from discrimination and oppression within India. They believe that a separate Sikh state would ensure the preservation of their cultural and religious identity and provide them with greater political autonomy.
Q: What are the arguments against Khalistan?
A: Opponents of Khalistan argue that it is a divisive and unrealistic proposition that would lead to further violence and instability in the region. They believe that the Sikh community can achieve its aspirations within the framework of a united India.
Q: What is the current status of the Khalistan movement?
A: The Khalistan movement has lost much of its momentum in recent years, with armed groups largely inactive. However, the demand for a separate Sikh state remains a contentious issue, with some groups continuing to advocate for its creation.
Tips for Understanding the Map of Khalistan:
- Historical Perspective: It is essential to understand the historical context of the Khalistan movement, including the Sikh community’s experiences with partition and the subsequent years of perceived discrimination.
- Political Context: Understanding the political dynamics within India, particularly the relationship between the Sikh community and the government, is crucial for comprehending the movement’s motivations.
- Social Factors: The social and cultural factors that contribute to the Sikh community’s identity and aspirations should be considered.
- International Perspective: The Khalistan movement has also attracted international attention, with groups and individuals advocating for its recognition.
Conclusion:
The map of Khalistan represents a complex and multifaceted issue with deep historical and political roots. While the movement has lost its former momentum, the demand for a separate Sikh state remains a potent symbol of the Sikh community’s aspirations for self-determination and cultural preservation.
Understanding the map of Khalistan requires a nuanced and informed perspective, taking into account the historical context, political dynamics, and social factors that have shaped its emergence. It is crucial to approach this sensitive topic with respect and understanding, recognizing the complexities of the issue and the diverse perspectives involved.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Map of Khalistan: A Historical and Political Analysis. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!