Jordan: A Crossroads Of History And Geography In The Middle East
Jordan: A Crossroads of History and Geography in the Middle East
Related Articles: Jordan: A Crossroads of History and Geography in the Middle East
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Jordan: A Crossroads of History and Geography in the Middle East. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Jordan: A Crossroads of History and Geography in the Middle East
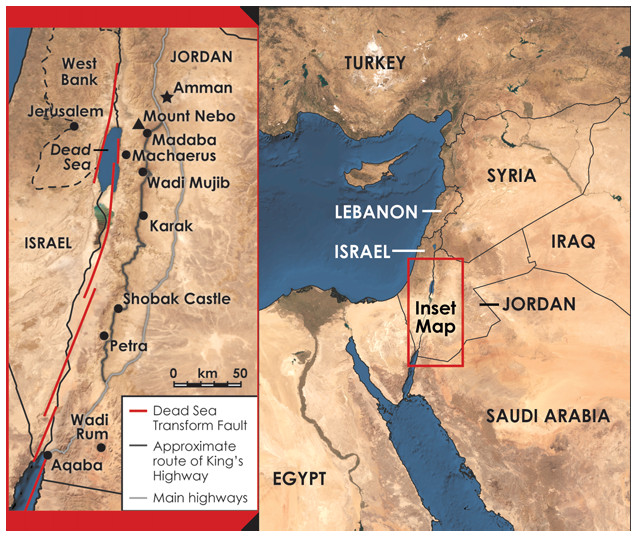
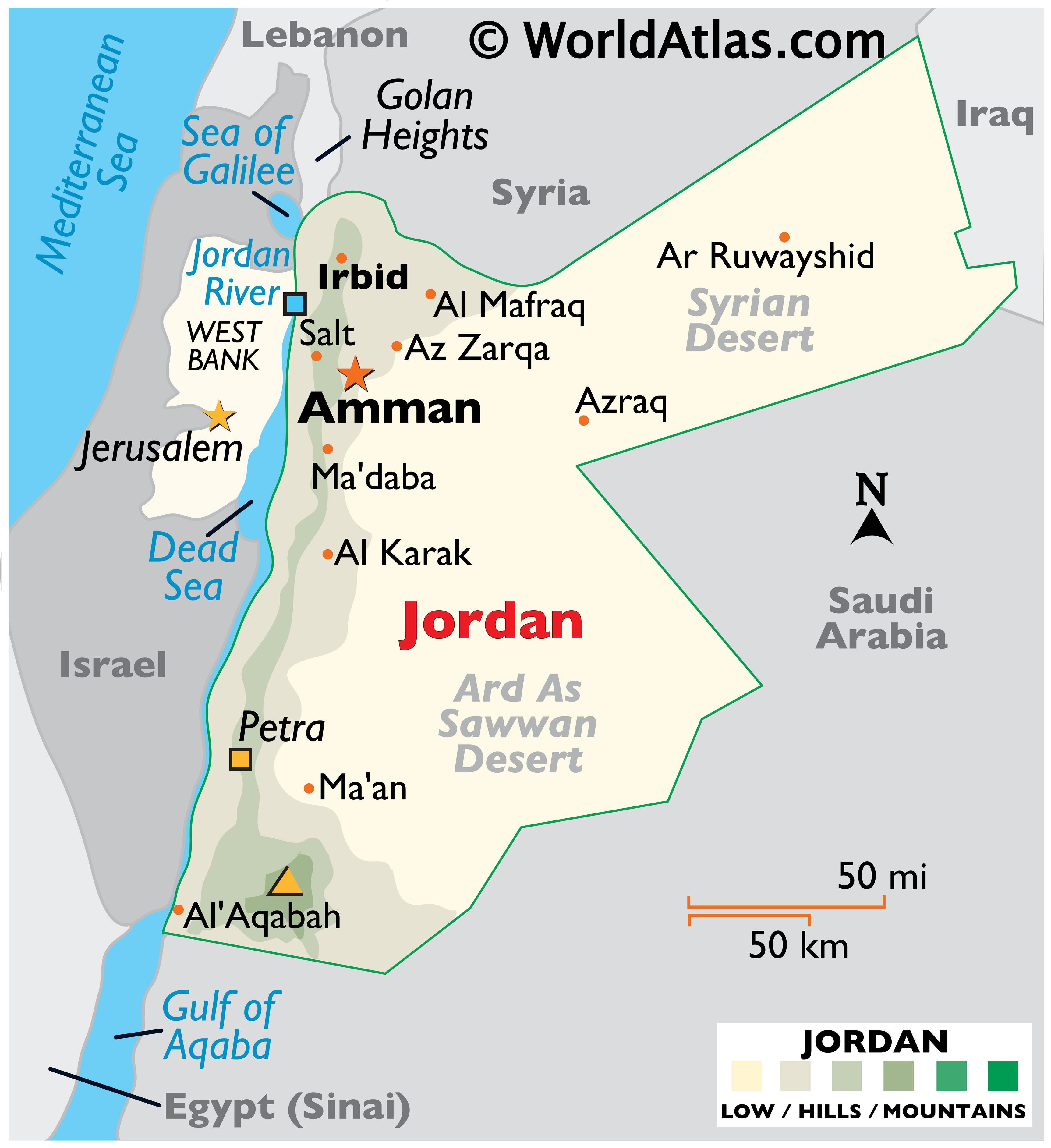
Jordan, a nation nestled in the heart of the Middle East, holds a strategic and historical significance that extends far beyond its relatively small size. Its location, bordering on Saudi Arabia, Iraq, Syria, Israel, and the Palestinian territories, has positioned it as a crucial crossroads for trade, migration, and cultural exchange throughout history. Understanding Jordan’s geographical context is essential for grasping its unique cultural identity, its geopolitical role, and its challenges and opportunities in the 21st century.
A Land of Diverse Landscapes:
Jordan’s geography is a tapestry of contrasting landscapes, each contributing to the country’s character.
- The Jordan Rift Valley: This geological feature, a dramatic depression cutting through the Middle East, dominates the western portion of Jordan. It is home to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on Earth, and the Jordan River, a vital source of water for the region. The rift valley’s arid climate and mineral-rich waters create a unique ecosystem and hold immense economic potential.
- The Eastern Plateau: Rising eastward from the rift valley, the eastern plateau is characterized by vast desert landscapes, dotted with rocky canyons and mesas. This region, largely uninhabitable due to its aridity, holds significant mineral resources and serves as a buffer zone for Jordan’s western border.
- The Wadi Rum Desert: A UNESCO World Heritage Site, Wadi Rum is a breathtaking desert landscape of towering sandstone cliffs, sculpted canyons, and ancient petroglyphs. It is a popular destination for adventure tourism and holds archaeological significance, offering insights into the region’s prehistoric past.
- The highlands: In the north, Jordan’s landscape transitions to rolling hills and fertile valleys, offering a more hospitable environment for agriculture and settlements. This region is home to the ancient city of Jerash, a well-preserved Roman metropolis, and the Ajloun Forest Reserve, a haven for biodiversity.
Jordan’s Strategic Location:
Jordan’s geographical position has profoundly shaped its history and its role in the Middle East.
- A Bridge Between Cultures: Situated at the intersection of the Arabian Peninsula, the Levant, and North Africa, Jordan has served as a bridge between cultures for millennia. This has resulted in a rich cultural tapestry, with influences from Arabic, Byzantine, Ottoman, and Bedouin traditions.
- A Crossroads of Trade: From ancient caravan routes to modern highways and pipelines, Jordan has always been a vital conduit for trade. Its location on the eastern edge of the Mediterranean Sea and its proximity to major trade routes have made it a hub for commerce and economic activity.
- A Geopolitical Pivot: Jordan’s proximity to Israel and the Palestinian territories has made it a key player in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. Its role in peace negotiations and its efforts to promote regional stability have been crucial in navigating the complex political landscape of the Middle East.
Challenges and Opportunities:
Despite its strategic advantages, Jordan faces significant challenges, stemming from its arid climate, limited water resources, and its geopolitical context.
- Water Scarcity: Jordan is one of the most water-scarce countries in the world, facing increasing pressure on its water resources due to population growth, drought, and regional competition. Sustainable water management is a critical priority for the country’s long-term development.
- Economic Diversification: Jordan’s economy is heavily reliant on foreign aid and trade, making it vulnerable to global economic fluctuations. Diversifying its economy, fostering innovation, and attracting investment are crucial for achieving sustainable economic growth.
- Regional Instability: The ongoing conflicts and political turmoil in neighboring countries pose significant challenges for Jordan, including the influx of refugees, security threats, and economic disruptions.
FAQs about Jordan:
- What is the capital of Jordan? Amman is the capital city of Jordan.
- What is the population of Jordan? The population of Jordan is approximately 11 million.
- What is the official language of Jordan? Arabic is the official language of Jordan.
- What is the currency of Jordan? The Jordanian dinar (JOD) is the official currency of Jordan.
- What are the major industries in Jordan? Jordan’s major industries include tourism, agriculture, manufacturing, and mining.
- What are some of the major tourist attractions in Jordan? Petra, Wadi Rum, Jerash, and the Dead Sea are among the most popular tourist destinations in Jordan.
Tips for Traveling to Jordan:
- Obtain a visa in advance: Visitors from most countries require a visa to enter Jordan.
- Respect local customs: Dress modestly, particularly when visiting religious sites.
- Learn some basic Arabic phrases: This will be helpful when interacting with locals.
- Be prepared for hot weather: Jordan has a hot, arid climate, so pack lightweight, breathable clothing.
- Drink bottled water: Tap water is not always safe to drink.
- Bargain at markets: It is common to bargain for goods at local markets.
- Plan your itinerary in advance: Jordan has many attractions, so it is helpful to plan your trip beforehand.
Conclusion:
Jordan, a nation shaped by its unique geography and history, stands as a vital player in the Middle East. Its strategic location, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage offer a captivating blend of ancient history, modern development, and natural beauty. As Jordan navigates the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, its ability to leverage its strategic position and embrace sustainable development will be crucial for its future prosperity and its role in the region.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Jordan: A Crossroads of History and Geography in the Middle East. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!