Mapping The Arctic: Understanding The Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain
Mapping the Arctic: Understanding the Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain
Related Articles: Mapping the Arctic: Understanding the Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Arctic: Understanding the Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Arctic: Understanding the Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain

The polar bear, a majestic symbol of the Arctic, faces a precarious future. As climate change alters the very landscape upon which it depends, understanding the distribution and dynamics of its habitat becomes paramount. This is where mapping plays a crucial role, providing a visual representation of the polar bear’s shrinking domain and revealing the urgent need for conservation efforts.
A Glimpse into the Polar Bear’s World
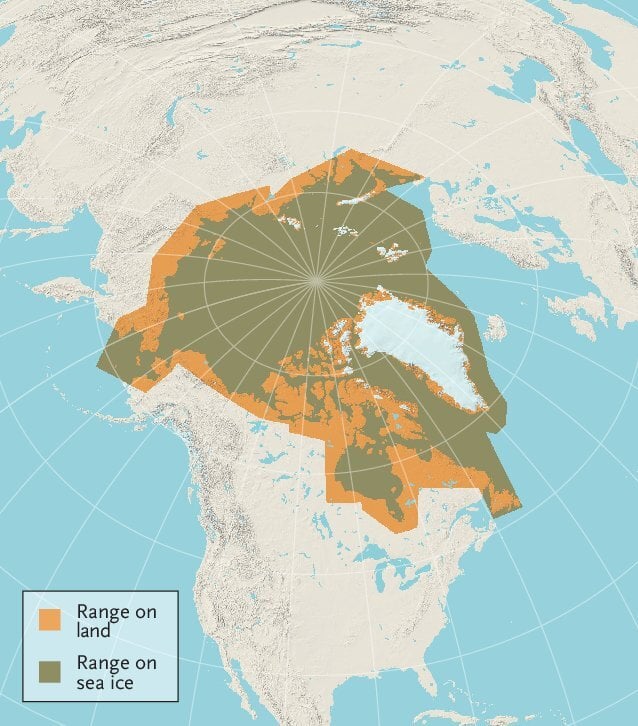
Polar bears are not simply confined to the frozen north; they are intricately linked to the sea ice, a dynamic environment that dictates their survival. Their habitat, encompassing the Arctic Circle and surrounding landmasses, is characterized by:
- Sea Ice: This floating platform serves as the primary hunting ground for polar bears. They rely on it to access seals, their main prey, by waiting near breathing holes or establishing ambush positions.
- Coastal Areas: Polar bears utilize coastal regions for denning, giving birth to cubs, and resting during periods of low sea ice.
- Land Masses: While primarily associated with the sea ice, polar bears also traverse land to reach new hunting grounds, den sites, or to avoid human encounters.
Mapping the Habitat: Unveiling the Dynamics
Mapping the polar bear’s habitat involves more than simply outlining its geographic range. It encompasses a dynamic interplay of factors, including:
- Sea Ice Distribution: The extent and thickness of sea ice are crucial for polar bear survival. Maps illustrating seasonal variations in sea ice coverage provide insights into the availability of hunting grounds and potential threats to polar bear populations.
- Denning Sites: Mapping denning areas, both on land and sea ice, is essential for understanding reproductive success and potential threats from climate change and human activities.
- Human Presence: Mapping human settlements, industrial activities, and shipping routes helps identify potential conflict zones and areas where conservation efforts are needed.
- Climate Change Impacts: Mapping the changing Arctic landscape, including shrinking sea ice extent and thawing permafrost, provides valuable data for understanding the long-term implications for polar bear habitat.
The Importance of Mapping: A Vital Tool for Conservation
Polar bear habitat maps serve as a vital tool for conservation, providing a foundation for:
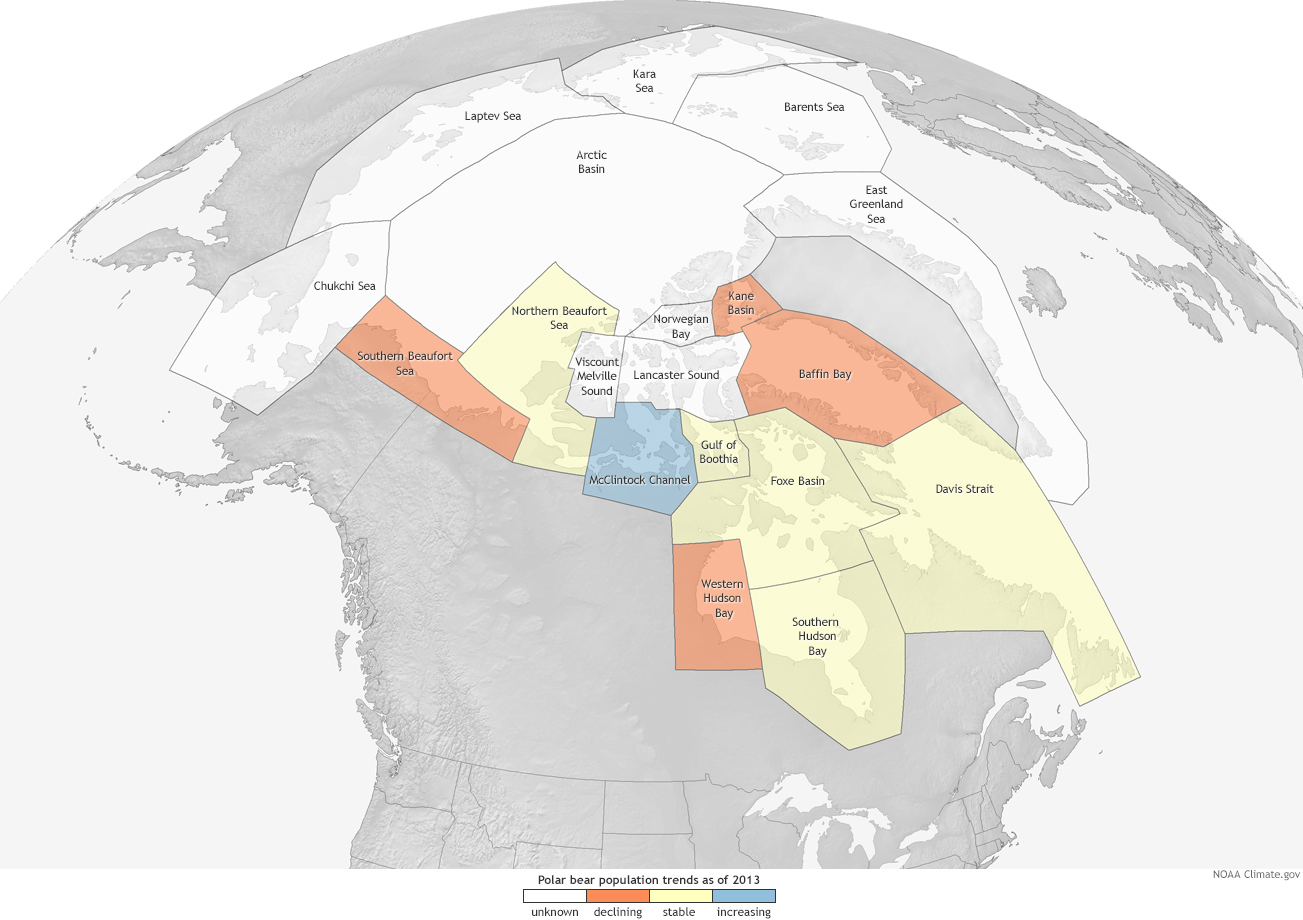
- Population Monitoring: By analyzing habitat data, scientists can track population trends and identify areas where polar bear populations are declining or facing increased threats.
- Targeted Conservation Efforts: Maps can guide conservation efforts by identifying areas where resources should be focused, such as establishing protected areas or implementing management strategies to mitigate human impacts.
- Climate Change Adaptation: By understanding the dynamic nature of the Arctic environment, mapping can help inform strategies for adapting to climate change and minimizing its negative impacts on polar bear populations.
- Public Awareness: Visual representations of the polar bear’s habitat can effectively communicate the challenges faced by these iconic animals and inspire public support for conservation efforts.
FAQs on Polar Bear Habitat Maps
Q: What are the key challenges in mapping polar bear habitat?
A: Mapping polar bear habitat presents several challenges, including:
- Remote and Inaccessible Terrain: The Arctic is a vast and challenging environment to access, making data collection difficult and expensive.
- Dynamic Nature of Sea Ice: The constantly changing nature of sea ice requires continuous monitoring and sophisticated techniques for accurate mapping.
- Limited Data Availability: Data on polar bear populations, denning sites, and human activities can be scarce and fragmented, making it difficult to create comprehensive maps.
- Technological Limitations: Mapping technologies, such as satellite imagery and remote sensing, are constantly evolving, and data interpretation requires specialized expertise.
Q: How are polar bear habitat maps created?
A: Polar bear habitat maps are created using a combination of methods, including:
- Satellite Imagery: High-resolution satellite images provide data on sea ice extent, land cover, and human activities.
- Remote Sensing: Using sensors on aircraft or satellites, scientists can collect data on sea ice thickness, snow depth, and vegetation.
- Field Surveys: On-ground data collection through field surveys provides valuable information on denning sites, polar bear movements, and prey availability.
- GIS (Geographic Information System): GIS software is used to integrate and analyze data from various sources to create comprehensive maps.
Q: What are some of the benefits of using polar bear habitat maps?
A: Polar bear habitat maps offer numerous benefits, including:
- Improved Understanding of Habitat Dynamics: Maps provide a comprehensive view of the changing Arctic environment and its impact on polar bear populations.
- Targeted Conservation Planning: Maps guide conservation efforts by identifying areas where resources should be focused to protect polar bears.
- Effective Communication of Conservation Needs: Maps can effectively communicate the challenges facing polar bears and the importance of conservation efforts.
- Scientific Research and Monitoring: Maps provide valuable data for scientific research, monitoring population trends, and understanding the effects of climate change.
Tips for Using Polar Bear Habitat Maps
- Consult Reliable Sources: Ensure the maps you use are created by reputable organizations, such as the World Wildlife Fund, the Polar Bear Specialist Group, or government agencies.
- Consider the Date and Source of the Data: Maps are snapshots of a dynamic environment, so consider the date of the data and the methods used for its collection.
- Look for Key Information: Pay attention to the legend and scale of the map to understand the data represented.
- Integrate Data from Multiple Sources: Combine information from different maps to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the polar bear’s habitat.
- Use Maps to Advocate for Conservation: Share maps with others to raise awareness of the challenges facing polar bears and the importance of conservation efforts.
Conclusion: A Call for Action
Mapping the polar bear’s habitat is crucial for understanding the challenges it faces and guiding conservation efforts. As the Arctic landscape continues to transform, these maps provide a vital tool for monitoring, protecting, and ultimately ensuring the survival of this iconic species. By combining scientific knowledge with advanced mapping techniques, we can better understand the complex interplay between climate change, habitat loss, and polar bear populations. This knowledge empowers us to take informed action and safeguard the future of these magnificent creatures.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Arctic: Understanding the Polar Bear’s Shrinking Domain. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!