Mapping The Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data
Mapping the Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data
Related Articles: Mapping the Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data

The Earth, a dynamic and intricate system, is constantly in motion. This motion, however, is not always gentle. Powerful forces within the planet, coupled with external influences from the sun and other celestial bodies, can unleash catastrophic events we call natural disasters. These events, ranging from earthquakes and volcanic eruptions to hurricanes and wildfires, have the potential to reshape landscapes, disrupt ecosystems, and devastate human populations.
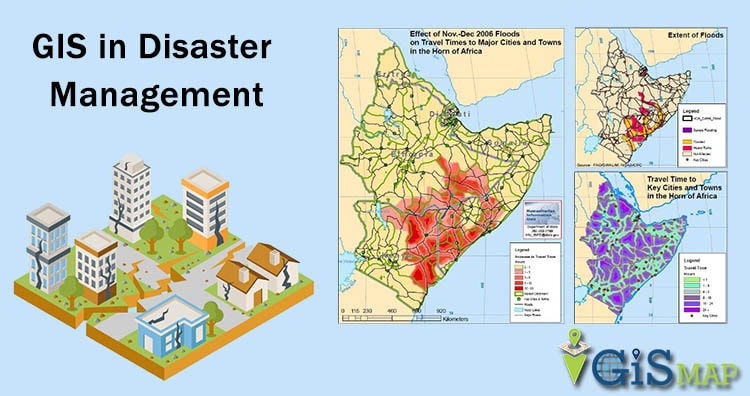
Understanding the spatial patterns of these disasters is crucial for mitigating their impact and building resilience. This is where maps of natural disasters come into play, serving as powerful tools for visualizing, analyzing, and ultimately, predicting these events.
Visualizing the Unseen: The Power of Geographic Data
Maps of natural disasters are not merely static representations of past events. They are dynamic, interactive tools that allow us to visualize the spatial distribution of these events across the globe, revealing crucial insights into their patterns and frequencies.
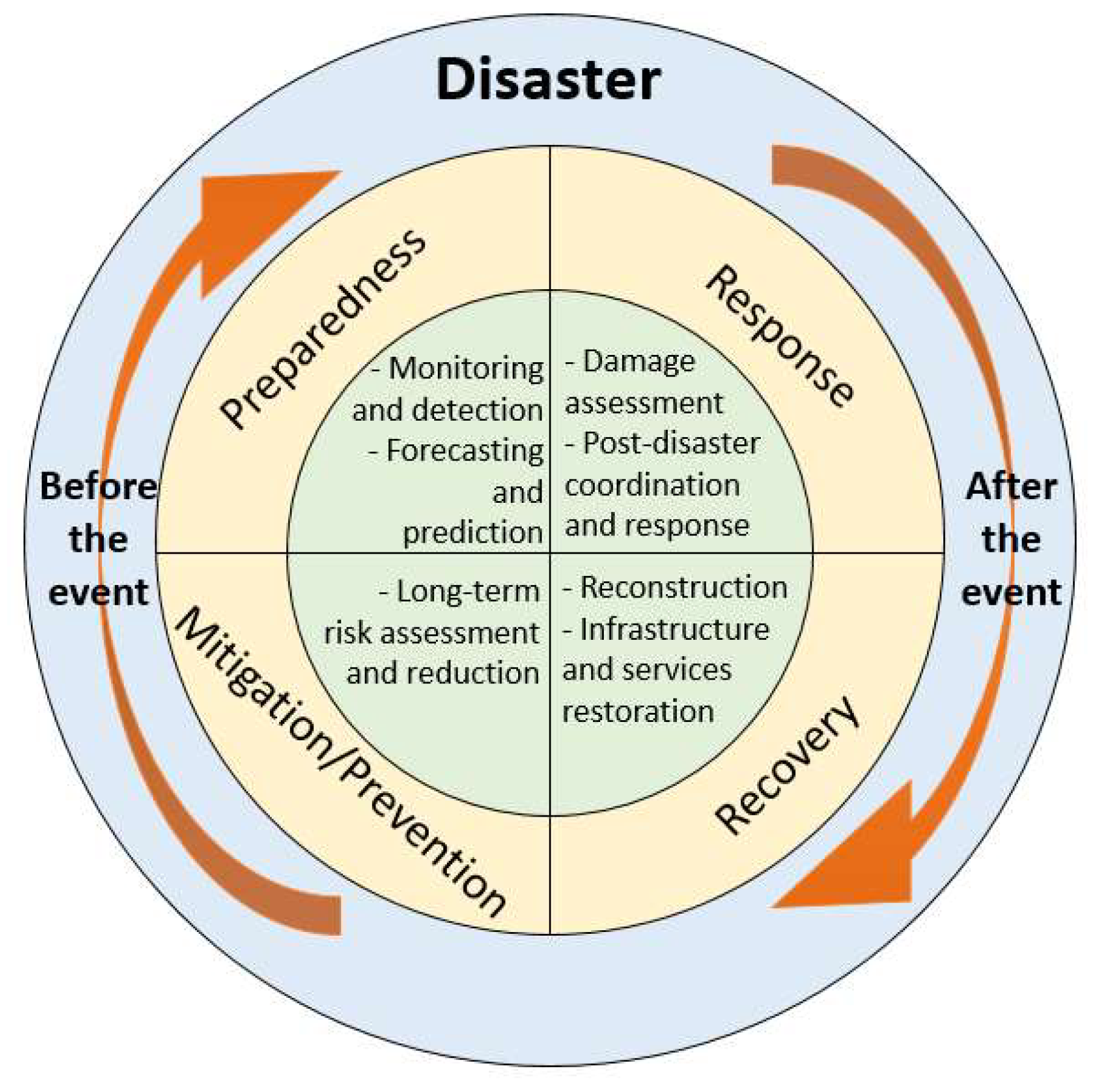
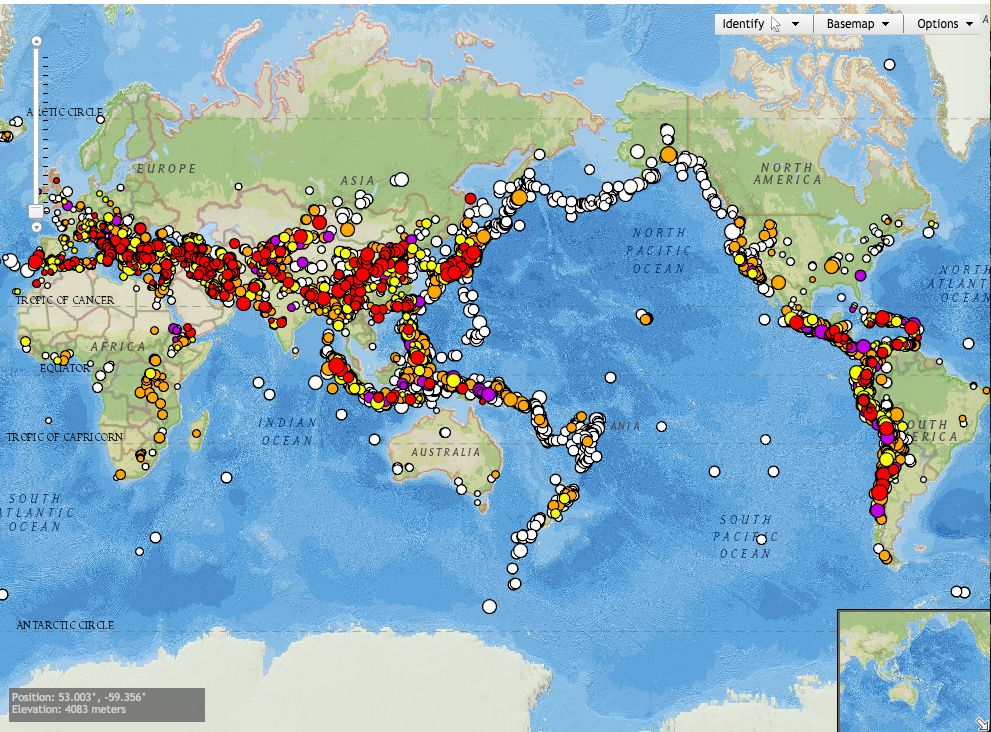
- Identifying High-Risk Zones: By mapping historical data on earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, floods, droughts, and other disasters, we can identify regions particularly vulnerable to these events. This information is vital for developing targeted disaster preparedness strategies, focusing resources on areas most likely to be impacted.
- Understanding Spatial Relationships: Mapping allows us to analyze the relationship between natural disasters and geographical factors. For instance, mapping earthquake epicenters can reveal fault lines, while mapping hurricane tracks can highlight areas prone to storm surges. This understanding is essential for informing urban planning, infrastructure development, and land-use decisions.
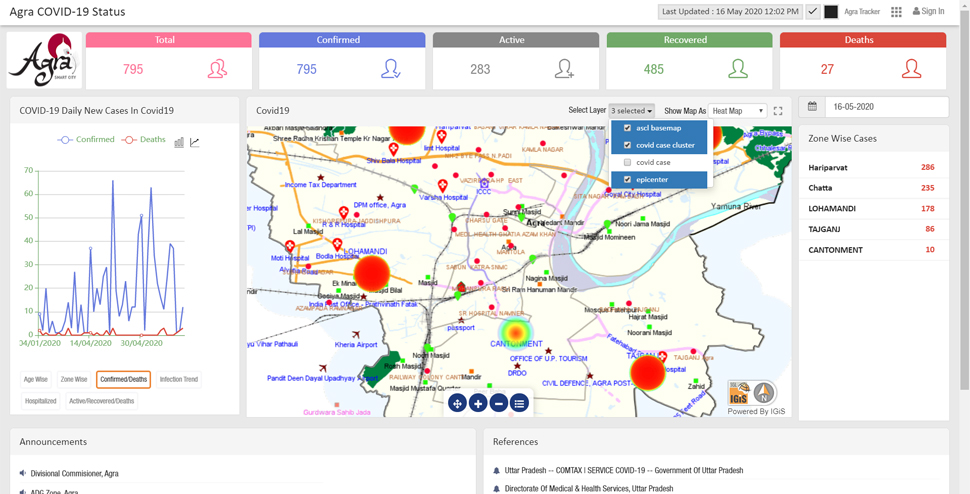
- Visualizing the Impact: Maps can show the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, highlighting areas affected by flooding, landslides, or wildfires. This information is crucial for assessing the impact of disasters, mobilizing aid effectively, and guiding post-disaster recovery efforts.
Beyond Visualization: Analyzing the Data
Maps of natural disasters are not just for visual understanding. They are powerful analytical tools that enable us to extract valuable insights from geographic data.
- Identifying Trends: By analyzing historical data on natural disasters, we can identify trends and patterns in their occurrence. This helps us understand how these events are evolving over time, providing valuable information for predicting future events and developing proactive mitigation strategies.
- Quantifying Risk: Through statistical analysis of mapped data, we can quantify the risk associated with different types of natural disasters in specific locations. This information is crucial for insurance companies, policymakers, and disaster management agencies to assess risk, develop appropriate policies, and allocate resources effectively.
- Developing Early Warning Systems: By integrating real-time data on weather patterns, seismic activity, and other relevant factors with historical disaster data, we can develop sophisticated early warning systems. These systems provide valuable lead time for evacuation, preparedness, and mitigation measures, potentially saving lives and minimizing damage.
The Importance of Open Access and Collaboration
The effectiveness of maps of natural disasters hinges on the accessibility and sharing of data. Open access to geographically referenced data on natural disasters allows researchers, governments, and communities to collaborate effectively, enabling a more comprehensive understanding of these events and leading to more robust mitigation strategies.
FAQs on Maps of Natural Disasters
1. What types of data are used to create maps of natural disasters?
Maps of natural disasters typically use a variety of data sources, including:
- Historical records: Historical accounts of past disasters, including eyewitness reports, newspaper articles, and scientific records, provide valuable insights into the frequency and intensity of past events.
- Satellite imagery: Satellite images can capture the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, providing valuable information for assessing the impact and guiding relief efforts.
- Ground-based sensors: Sensors deployed on the ground can collect data on seismic activity, atmospheric conditions, and other factors relevant to predicting and monitoring natural disasters.
- Model simulations: Computer models can simulate the behavior of natural disasters, allowing us to predict the potential impact of future events and develop mitigation strategies.
2. How are maps of natural disasters used in disaster preparedness and response?
Maps of natural disasters play a crucial role in disaster preparedness and response by:
- Identifying high-risk zones: Maps help identify areas most vulnerable to specific types of disasters, allowing for targeted preparedness efforts, including evacuation plans, infrastructure hardening, and community awareness programs.
- Developing evacuation routes: Maps can be used to plan efficient evacuation routes, ensuring the safe and timely movement of people away from danger zones.
- Allocating resources: Maps provide valuable information for allocating resources effectively during disaster response, ensuring that aid reaches those most in need.
- Assessing the impact: Maps help assess the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, providing crucial information for coordinating rescue operations, distributing relief supplies, and planning post-disaster recovery efforts.
3. What are the limitations of maps of natural disasters?
While maps of natural disasters are powerful tools, they have limitations:
- Data availability: The accuracy and completeness of data used to create maps can vary, depending on the availability of historical records, monitoring systems, and other data sources.
- Predictive limitations: While maps can help identify high-risk zones and predict the likelihood of certain events, they cannot predict the exact timing, location, or intensity of natural disasters with absolute certainty.
- Human factors: The effectiveness of disaster preparedness and response measures depends not only on the availability of data but also on the human capacity to interpret it, make informed decisions, and implement appropriate actions.
Tips for Utilizing Maps of Natural Disasters
- Choose the right map: Select a map that is relevant to your specific needs, considering the type of natural disaster, the geographic area, and the intended use of the map.
- Understand the data sources: Familiarize yourself with the data sources used to create the map, ensuring that the data is accurate, reliable, and relevant to your needs.
- Interpret the information effectively: Be able to interpret the information presented on the map, understanding the scales, symbols, and other visual elements used to convey data.
- Integrate with other data: Combine map data with other relevant information, such as demographic data, infrastructure information, and social vulnerability indicators, to develop a comprehensive understanding of the potential impact of natural disasters.
- Stay informed and updated: Keep up-to-date with the latest information on natural disasters, including real-time data, forecasts, and warnings, to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
Conclusion: A Powerful Tool for a Safer Future
Maps of natural disasters are not just static representations of past events. They are dynamic tools that allow us to understand the spatial patterns of these events, analyze their impact, and develop effective mitigation strategies. By harnessing the power of geographic data, we can improve our understanding of natural disasters, build resilience, and create a safer future for all.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Fury: Understanding Natural Disasters Through Geographic Data. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!