Mapping The Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide To Nuclear Power Plants In The United States
Mapping the Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Related Articles: Mapping the Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Mapping the Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mapping the Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nuclear Power Plants in the United States
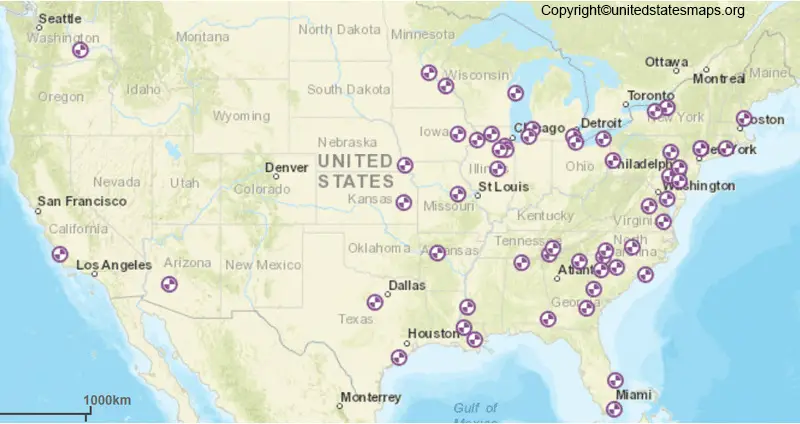
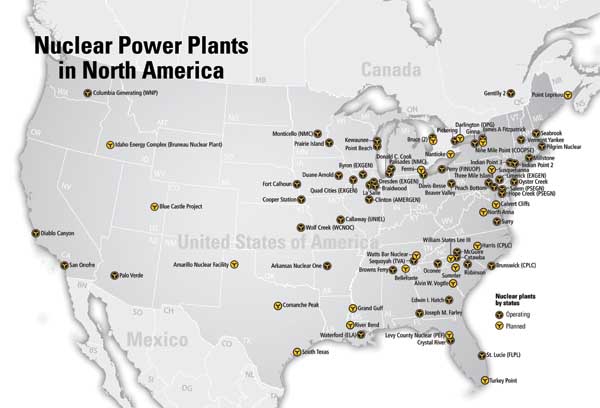
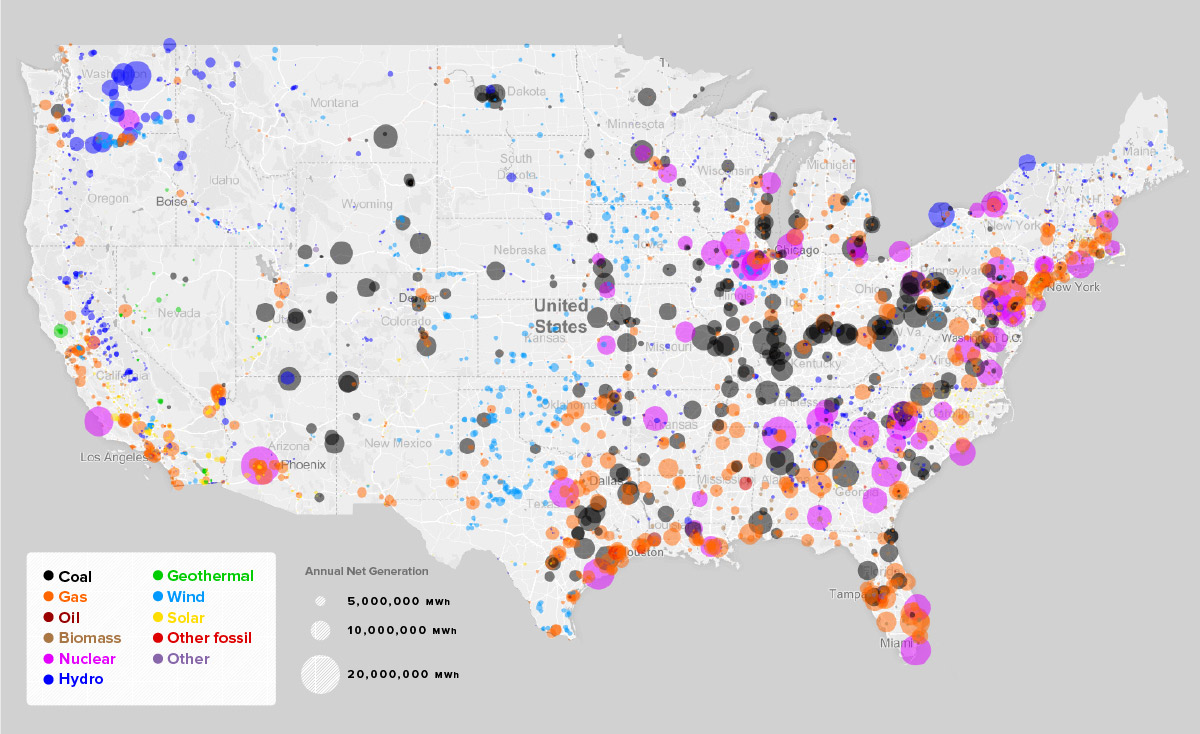
The United States possesses a diverse energy landscape, and nuclear power plants play a significant role in meeting the nation’s energy demands. Understanding the distribution and operation of these facilities is crucial for informed decision-making regarding energy policy, environmental impact, and public safety. A nuclear plant map of the United States provides a visual representation of this intricate network, offering valuable insights into the geographical distribution, operational status, and potential implications of nuclear energy production across the country.
The Geographical Distribution of Nuclear Power Plants:
The United States boasts 92 operating nuclear power plants located across 30 states. This widespread presence highlights the strategic importance of nuclear energy in various regions. The map reveals clusters of nuclear plants in specific areas, reflecting historical factors such as proximity to water sources, population density, and existing infrastructure.
Key Regions with High Concentrations of Nuclear Plants:
- The Southeast: States like Georgia, South Carolina, and North Carolina house a significant number of nuclear power plants, fueled by the region’s abundant water resources and demand for reliable electricity.
- The Midwest: States like Illinois, Pennsylvania, and Michigan are home to numerous nuclear facilities, largely due to their industrial development and reliance on baseload power.
- The Northeast: States like New York, Connecticut, and Massachusetts have a notable presence of nuclear plants, reflecting the region’s high energy consumption and focus on clean energy sources.
- The West Coast: States like California and Washington have a smaller number of nuclear plants, but they play a crucial role in providing clean energy to densely populated urban areas.
Understanding the Map’s Importance:
The nuclear plant map serves as a valuable tool for various stakeholders:
- Policymakers: It informs policy decisions regarding energy independence, environmental regulations, and nuclear waste management.
- Energy Companies: It assists in planning new plant construction, optimizing operations, and managing resource allocation.
- Environmental Organizations: It facilitates monitoring environmental impact, assessing potential risks, and advocating for responsible nuclear energy practices.
- Public: It provides transparency and access to information about nuclear power plants in their local communities, fostering informed dialogue and public engagement.
The Benefits of Utilizing a Nuclear Plant Map:
- Visualizing the Network: The map offers a clear and concise representation of the geographical distribution of nuclear plants, facilitating a better understanding of their location and proximity to major population centers.
- Tracking Plant Status: The map can be updated with real-time information on plant operation, maintenance schedules, and any safety incidents, providing a comprehensive overview of the nuclear power industry’s current state.
- Assessing Environmental Impact: The map allows for analyzing the potential environmental consequences of nuclear power generation, including water usage, thermal pollution, and radioactive waste disposal.
- Promoting Transparency: The map fosters public awareness and transparency by providing readily accessible information about nuclear power plants, enabling informed public participation in energy discussions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Nuclear Plant Maps:
1. What type of data is included in a nuclear plant map?
A nuclear plant map typically includes information such as plant name, location, capacity (in megawatts), reactor type, operating status, and any significant events or incidents.
2. How are nuclear plants classified on the map?
Plants are often classified by their reactor type, operating status (operational, under construction, or decommissioned), and ownership.
3. Where can I find a reliable nuclear plant map?
Several organizations, including the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), the World Nuclear Association, and the Energy Information Administration (EIA), provide comprehensive nuclear plant maps.
4. What are the potential risks associated with nuclear power plants?
The potential risks associated with nuclear power plants include accidents, radioactive waste disposal, and the potential for terrorism.
5. What is the future of nuclear power in the United States?
The future of nuclear power in the United States is uncertain, with debates surrounding its safety, cost-effectiveness, and the potential for advanced reactor technologies.
Tips for Utilizing a Nuclear Plant Map Effectively:
- Focus on Relevant Information: Identify the specific data you need based on your purpose, such as plant capacity, reactor type, or operational status.
- Compare and Contrast: Use the map to compare different regions, plant types, or operating statuses, drawing insightful conclusions.
- Consider Environmental Factors: Analyze the map in conjunction with other geographical data, such as water resources, population density, and seismic activity, to assess potential environmental risks.
- Stay Informed: Regularly check for updates and changes to the map to ensure you have the most current information.
Conclusion:
A nuclear plant map of the United States serves as a valuable tool for understanding the distribution, operation, and potential implications of nuclear power generation. By providing a visual representation of this complex energy landscape, the map empowers policymakers, energy companies, environmental organizations, and the public to make informed decisions, engage in constructive dialogue, and contribute to the responsible development and utilization of nuclear energy. As the nation continues to navigate the complexities of energy production and consumption, the nuclear plant map remains a crucial resource for fostering transparency, promoting informed decision-making, and shaping the future of nuclear energy in the United States.
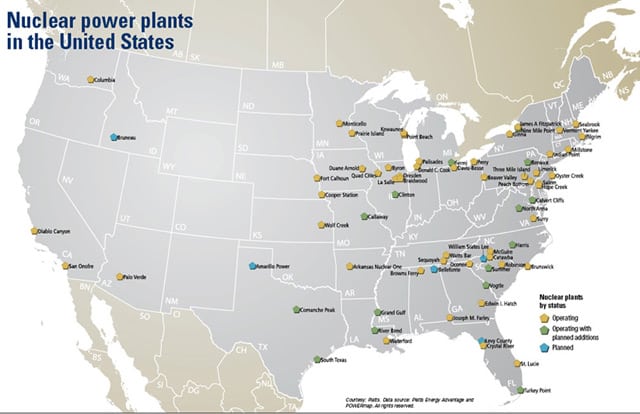
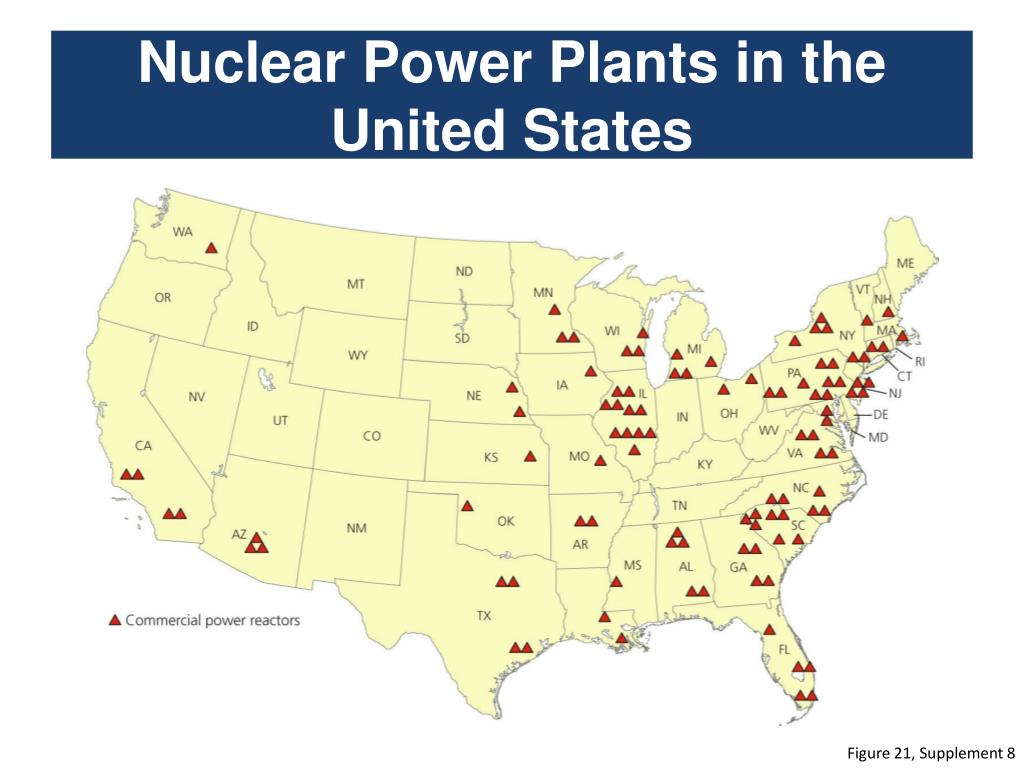
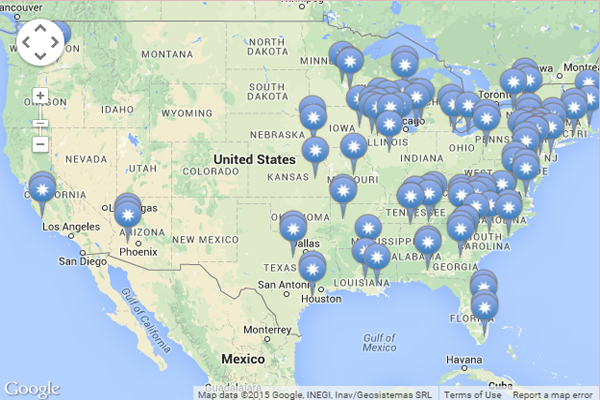
![U.S. Nuclear Power Plants and Production by State [1650x1275] : MapPorn](https://external-preview.redd.it/IabWt3J8zmHtcCP04mPXZQaKuufPN2t7tvlvUtSatUU.png?width=960u0026crop=smartu0026auto=webpu0026s=35c6857a877c048ddb83a9b7b0f8b2ef93024b3b)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mapping the Nuclear Landscape: A Comprehensive Guide to Nuclear Power Plants in the United States. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!