Navigating The Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps

The digital world, a vibrant tapestry of interconnected systems and data, is constantly under siege. Malicious actors, driven by financial gain, political agendas, or sheer mischief, relentlessly seek vulnerabilities to exploit. In this complex and ever-evolving landscape, navigating the intricate web of cyber threats requires a comprehensive and dynamic tool – the cyberthreat map.
Defining the Cyberthreat Map:
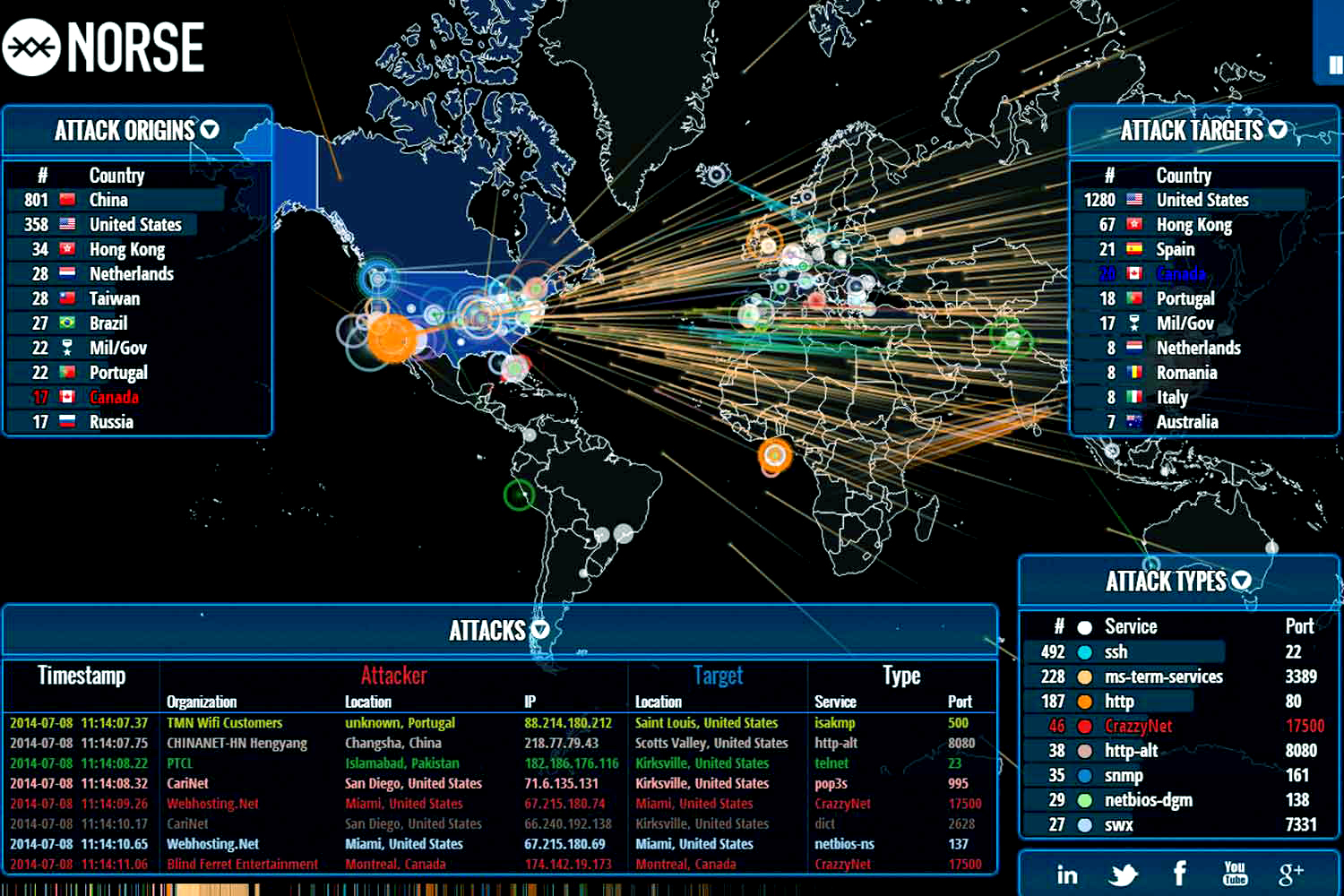
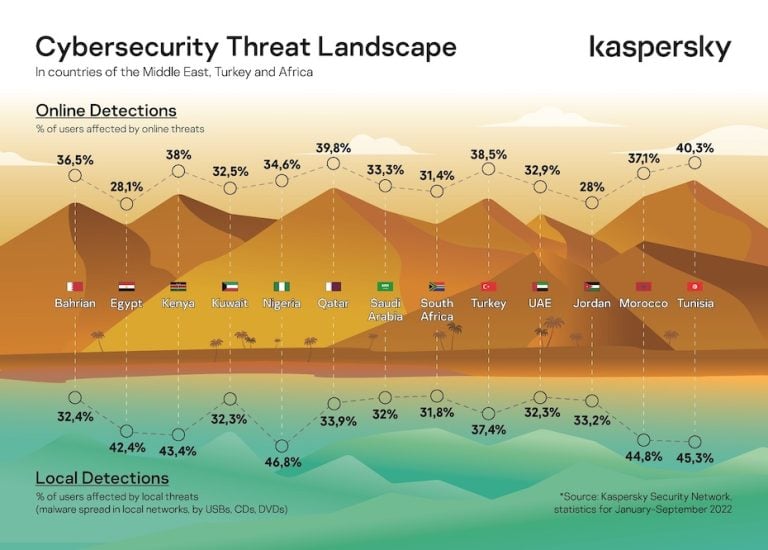
A cyberthreat map, in its essence, is a visual representation of the global cyber threat landscape. It functions as a dynamic dashboard, aggregating and displaying real-time data on various cyber threats, their origins, targets, and potential impact. These maps leverage a diverse range of information, including:
- Threat Actor Profiles: Detailed information on the motives, tactics, and capabilities of various cyber threat actors, including nation-states, organized crime groups, and individual hackers.
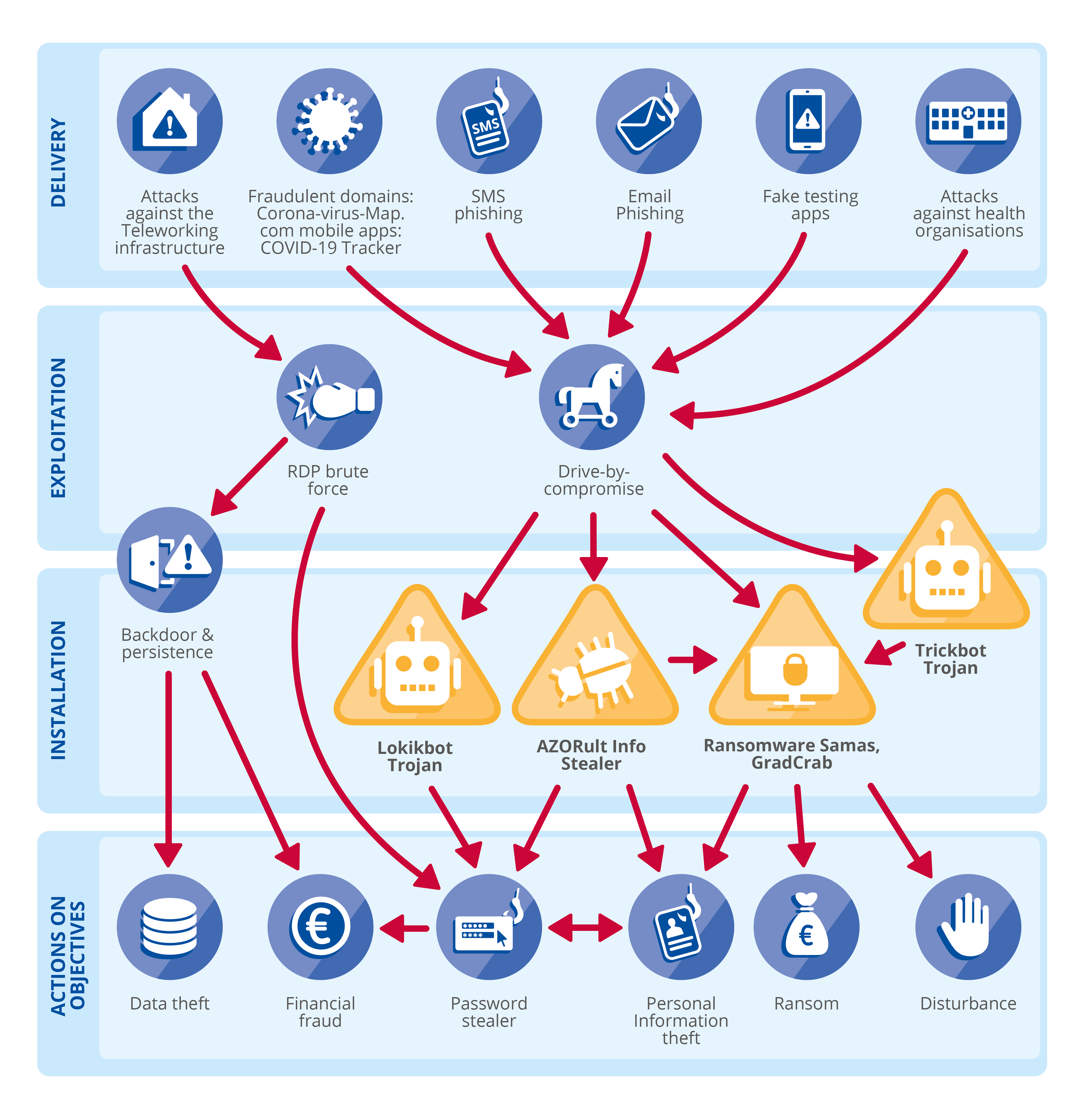
- Attack Vectors: Identifying the common methods used by attackers to infiltrate systems, such as phishing emails, malware, and social engineering.
- Vulnerability Data: Tracking known weaknesses in software, hardware, and network configurations that attackers exploit.
- Attack Trends: Monitoring the evolving nature of cyberattacks, including the emergence of new attack vectors, targeting preferences, and attack frequency.
- Geographic Distribution: Mapping the location of cyberattacks, their origins, and the geographic spread of impacted systems.
Benefits of Using Cyberthreat Maps:
The value of cyberthreat maps lies in their ability to provide a holistic view of the cyber threat landscape, empowering organizations and individuals to:
- Gain Situational Awareness: By visualizing the global threat landscape, organizations can better understand the specific threats they face, their origins, and potential impact.
- Proactive Threat Mitigation: The insights gleaned from these maps enable organizations to identify and prioritize vulnerabilities, implement appropriate security measures, and proactively address potential risks.
- Informed Decision-Making: Cyberthreat maps provide valuable data to support informed decision-making regarding cybersecurity investments, resource allocation, and incident response strategies.
- Enhanced Collaboration: By sharing threat intelligence, cyberthreat maps facilitate collaboration between organizations, security researchers, and government agencies, fostering a collective approach to cybersecurity.
- Improved Incident Response: During a cyberattack, the map provides critical information about the attacker, their tactics, and potential targets, enabling faster and more effective incident response.
Types of Cyberthreat Maps:
Cyberthreat maps come in various forms, each offering unique perspectives and functionalities:
- General Threat Maps: These maps provide a broad overview of the global cyber threat landscape, highlighting major threats, attack vectors, and regions most affected.
- Industry-Specific Maps: These maps focus on the unique threats faced by specific industries, such as healthcare, finance, or manufacturing, providing targeted insights and resources.
- Threat Actor-Specific Maps: These maps offer detailed information about the activities, tactics, and targets of specific threat actors, providing a deep understanding of their modus operandi.
- Vulnerability-Focused Maps: These maps prioritize vulnerabilities and highlight those most commonly exploited by attackers, enabling organizations to focus their security efforts.
Utilizing Cyberthreat Maps Effectively:
To leverage the full potential of cyberthreat maps, organizations should consider the following:
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly reviewing the map and analyzing the latest threat data is crucial to staying informed about evolving threats.
- Integration with Security Tools: Integrating the map with existing security tools, such as intrusion detection systems and vulnerability scanners, enhances threat detection and response capabilities.
- Sharing Threat Intelligence: Sharing threat information with other organizations, security researchers, and government agencies fosters collaboration and collective defense against cyber threats.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of the map and incorporating feedback from users ensures its relevance and value.
FAQs about Cyberthreat Maps:
Q: Who creates and maintains cyberthreat maps?
A: Cyberthreat maps are developed and maintained by a variety of entities, including:
- Government Agencies: National security agencies and law enforcement organizations often create and maintain maps to track cyber threats and support national security efforts.
- Security Companies: Cybersecurity companies develop maps as part of their threat intelligence services, providing insights to their clients.
- Research Institutions: Universities and research organizations contribute to the development of maps through their research on cyber threats and attack techniques.
- Open Source Communities: Collaborative efforts within open-source communities contribute to the creation and maintenance of maps, often focusing on specific threats or attack vectors.
Q: What are the limitations of cyberthreat maps?
A: While powerful tools, cyberthreat maps have limitations:
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the data used to create these maps depends on the quality and reliability of the underlying sources, which can vary.
- Real-Time Updates: Maintaining real-time updates for all threats can be challenging, as the cyber threat landscape is constantly evolving.
- Data Interpretation: Interpreting the information presented on the map requires expertise in cybersecurity and threat analysis, which can be challenging for non-technical users.
- Bias and Perspective: The information presented on a map may reflect the biases and perspectives of the organization creating it, potentially influencing the interpretation of the data.
Q: How can organizations access and use cyberthreat maps?
A: Access to cyberthreat maps varies depending on the provider and the level of service offered:
- Publicly Available Maps: Some maps are publicly accessible and provide a general overview of the cyber threat landscape.
- Subscription-Based Services: Many security companies offer subscription-based services that provide access to more detailed maps and threat intelligence.
- Custom Maps: Organizations can commission the development of custom maps tailored to their specific needs and industry.
Tips for Using Cyberthreat Maps Effectively:
- Understand the Map’s Scope: Before using a map, carefully review its scope and the specific threats it covers to ensure it aligns with your organization’s needs.
- Consider the Data Source: Evaluate the reliability and credibility of the data sources used to create the map to assess the accuracy of the information presented.
- Integrate with Existing Tools: Integrate the map with existing security tools and processes to enhance threat detection and response capabilities.
- Develop a Response Plan: Use the information provided by the map to develop a comprehensive plan for responding to potential cyber threats.
Conclusion:
Cyberthreat maps are essential tools for navigating the complex and ever-evolving cyber threat landscape. They provide valuable insights into the origins, targets, and impact of cyber threats, empowering organizations and individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate risks and enhance their cybersecurity posture. By leveraging the information provided by these maps, organizations can improve their situational awareness, make informed decisions, and effectively respond to cyber threats, ultimately strengthening their resilience against the ever-present threat of cyberattacks.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Cyberthreat Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!