Navigating The Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps
Related Articles: Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps

The modern world is built on a complex web of interconnected networks, facilitating the seamless flow of information and data. At the heart of this digital infrastructure lies a technology that has revolutionized communication: fiber optics. Fiber optic cables, with their ability to transmit data at incredible speeds, have become the backbone of our digital world. However, to fully grasp the intricate workings of this network, one needs to understand the critical role of fiber optic maps.
What are Fiber Optic Maps?
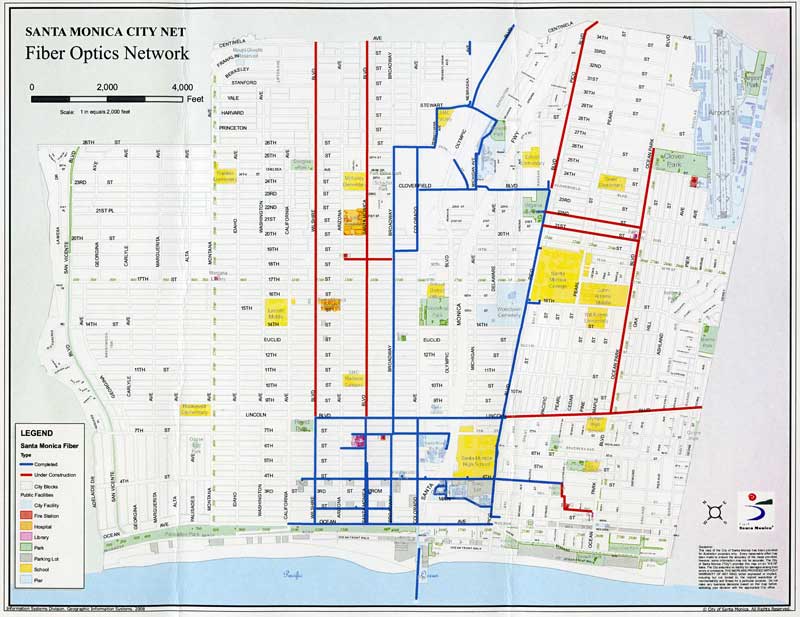
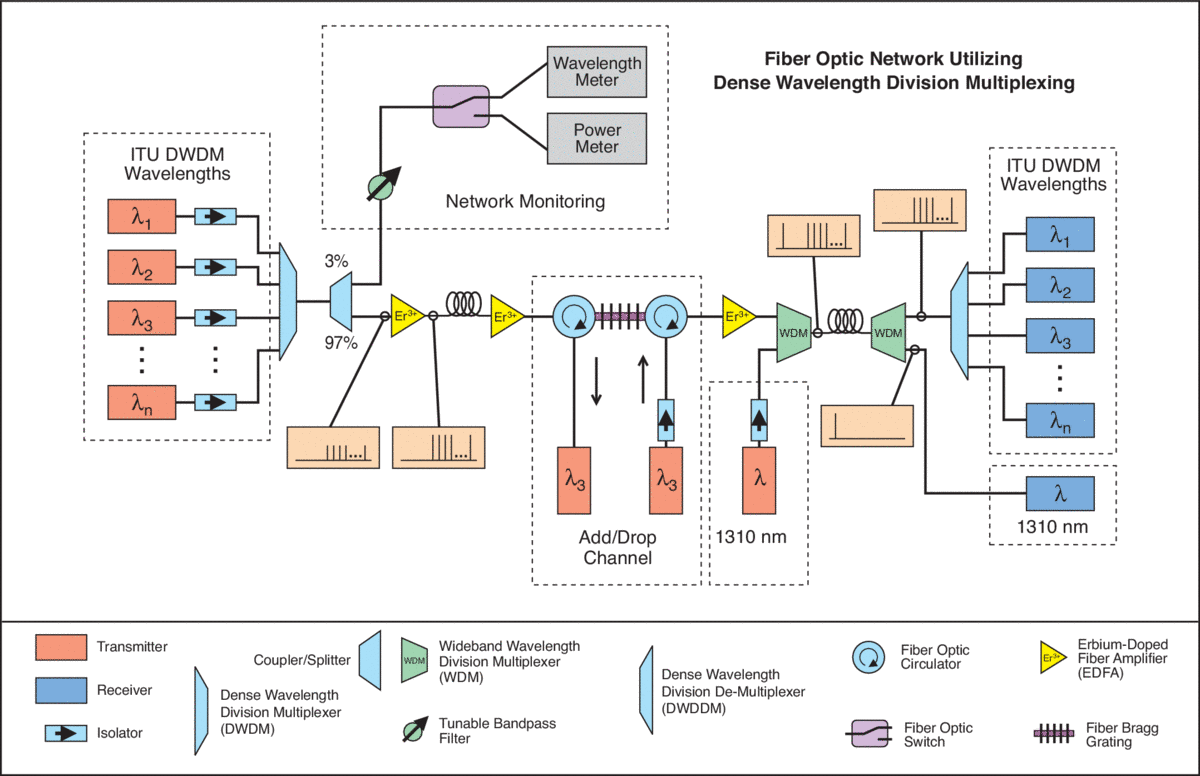
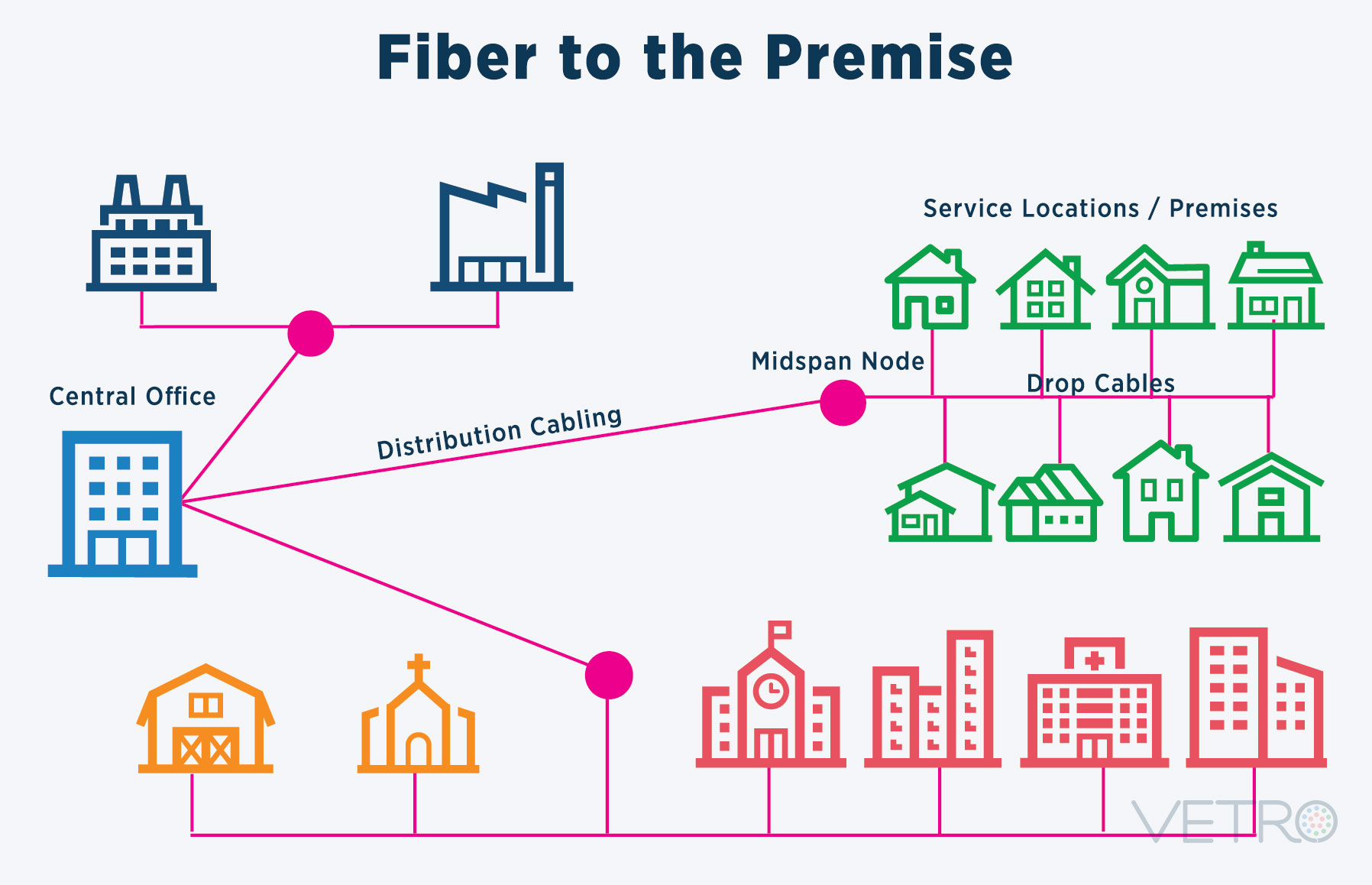
Fiber optic maps, also known as fiber optic network maps, are visual representations of the physical infrastructure of fiber optic networks. These maps depict the intricate network of cables, nodes, and equipment that connect various locations, enabling the transmission of data. They serve as essential tools for network engineers, technicians, and decision-makers, providing crucial information for planning, maintenance, troubleshooting, and network expansion.
Types of Fiber Optic Maps
Fiber optic maps come in various forms, each tailored to specific needs and purposes. Common types include:
- Physical Maps: These maps depict the physical location of fiber optic cables, showing their routes, connections, and infrastructure components. They are invaluable for planning cable installations, maintenance activities, and identifying potential issues.
- Logical Maps: These maps focus on the logical connections within the network, highlighting the flow of data between different devices and systems. They are used for network planning, traffic analysis, and understanding the overall network topology.
- Network Performance Maps: These maps visualize network performance metrics, such as latency, bandwidth usage, and signal strength. They aid in identifying bottlenecks, optimizing network performance, and ensuring optimal data transmission.
- Geographic Information System (GIS) Maps: These maps integrate fiber optic network data with geographical information, providing a comprehensive understanding of the network’s spatial distribution and potential impact on various locations.
Benefits of Fiber Optic Maps
Fiber optic maps offer numerous benefits, making them indispensable for effective network management and operation:
- Enhanced Network Visibility: Fiber optic maps provide a clear and comprehensive overview of the network infrastructure, allowing for better understanding of its connectivity, capacity, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Simplified Planning and Deployment: These maps facilitate efficient network planning by enabling engineers to identify optimal routes for new cable installations, minimizing costs and maximizing network performance.
- Effective Troubleshooting and Maintenance: By visualizing the network, technicians can quickly identify and resolve network issues, ensuring uninterrupted service and minimizing downtime.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Fiber optic maps allow for efficient allocation of network resources, ensuring that bandwidth and capacity are utilized effectively, maximizing network performance and minimizing costs.
- Improved Security: By providing a clear view of network infrastructure, fiber optic maps aid in identifying potential security vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate security measures, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring network integrity.
Applications of Fiber Optic Maps
Fiber optic maps play a crucial role in various industries and applications:
- Telecommunications: Telecommunications companies rely heavily on fiber optic maps for network planning, maintenance, and service provisioning, ensuring reliable and efficient communication services.
- Data Centers: Data centers, where vast amounts of data are processed and stored, utilize fiber optic maps for network management, ensuring optimal data transfer and storage capacity.
- Government and Military: Government agencies and military organizations use fiber optic maps for secure communication networks, ensuring data integrity and operational efficiency.
- Education and Healthcare: Educational institutions and healthcare facilities use fiber optic maps for reliable data transmission, supporting online learning, telehealth services, and critical medical operations.
- Transportation and Logistics: Transportation and logistics companies utilize fiber optic maps for network connectivity, enabling real-time tracking, traffic management, and efficient delivery operations.
FAQs about Fiber Optic Maps
Q: What is the difference between a physical and logical fiber optic map?
A: Physical maps depict the physical location of cables and infrastructure components, while logical maps focus on the logical connections between devices and systems within the network.
Q: How are fiber optic maps created?
A: Fiber optic maps are typically created using specialized software tools that integrate data from various sources, including network documentation, field surveys, and geographic information systems.
Q: Who uses fiber optic maps?
A: Fiber optic maps are used by network engineers, technicians, project managers, network administrators, and decision-makers in various industries.
Q: What are the challenges associated with using fiber optic maps?
A: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date maps can be challenging due to constant network changes, infrastructure updates, and the need for ongoing data collection.
Tips for Using Fiber Optic Maps Effectively
- Ensure Accuracy: Verify the accuracy of the map data by comparing it to actual network configurations and performing regular updates.
- Utilize Collaboration Tools: Share maps with relevant stakeholders, facilitating communication and collaboration for network planning and maintenance.
- Integrate with Other Systems: Integrate fiber optic maps with other network management tools, providing a comprehensive view of the network infrastructure.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Analyze map data to identify trends, optimize network performance, and make informed decisions about network expansion.
Conclusion
Fiber optic maps are essential tools for navigating the complex digital landscape, providing valuable insights into the intricate workings of fiber optic networks. By visualizing network infrastructure, these maps empower network professionals to plan, maintain, troubleshoot, and optimize network performance, ensuring reliable and efficient data transmission. As technology continues to advance and data demands grow, fiber optic maps will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of our interconnected world.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Digital Landscape: Understanding Fiber Optic Maps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!