Navigating The Landscape: Exploring The Differences Between Java Maps And Hashmaps
Navigating the Landscape: Exploring the Differences Between Java Maps and Hashmaps
Related Articles: Navigating the Landscape: Exploring the Differences Between Java Maps and Hashmaps
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Landscape: Exploring the Differences Between Java Maps and Hashmaps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Landscape: Exploring the Differences Between Java Maps and Hashmaps

In the realm of Java programming, data structures play a pivotal role in organizing and manipulating information efficiently. Among these, maps and hashmaps stand out as essential tools for storing and retrieving data based on key-value pairs. While both offer similar functionalities, understanding their underlying mechanisms and inherent differences is crucial for making informed choices in your code.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Maps in Java
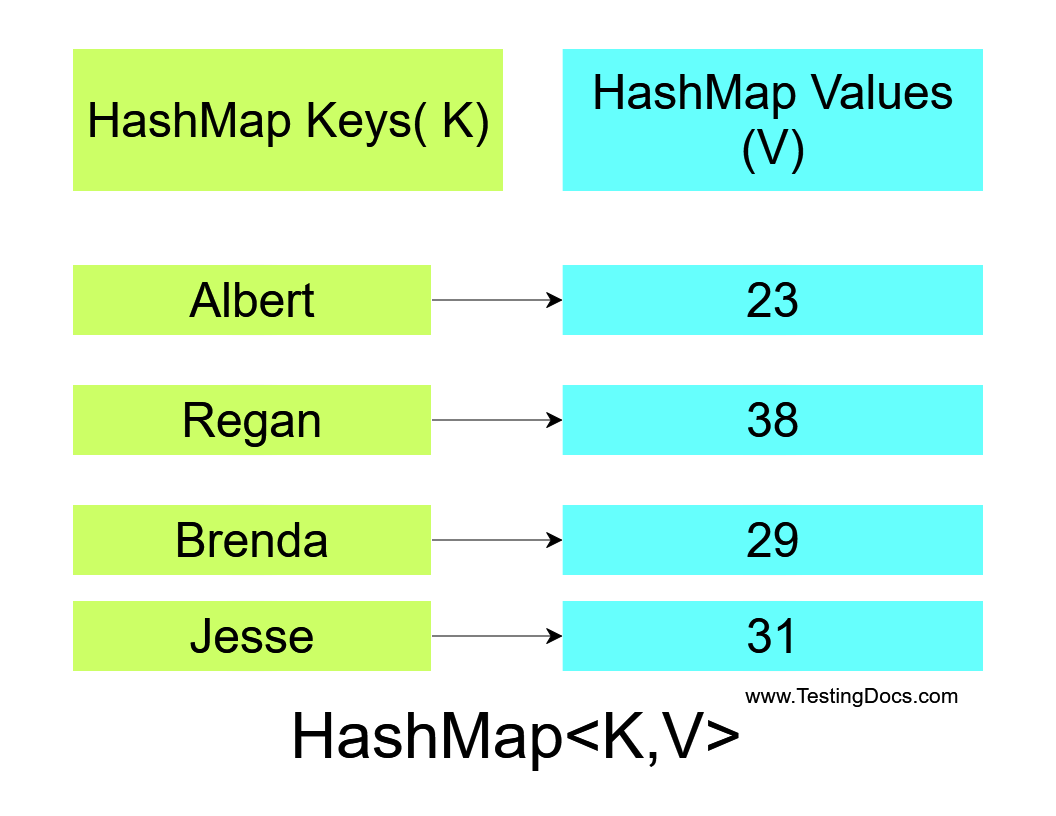
At its core, a Java Map represents a collection of key-value pairs. Each key is unique, serving as an identifier to locate its corresponding value. This structure allows for efficient retrieval of values by simply providing the associated key. The Map interface in Java defines a standard contract for working with these key-value pairs, specifying methods for common operations like adding, removing, retrieving, and iterating over the entries.
Exploring the Implementation: Hashmaps in Java
The HashMap class in Java is a concrete implementation of the Map interface. It utilizes a hash table data structure to store and access key-value pairs. Hash tables employ a hash function to map keys to specific indices within an array, allowing for fast lookup and retrieval. This approach makes HashMap a highly efficient choice for scenarios where frequent searches and insertions are expected.
Key Differences: Unveiling the Distinctions
While HashMap is a popular implementation of Map, it’s important to recognize their distinct characteristics.
-
Order of Elements: A
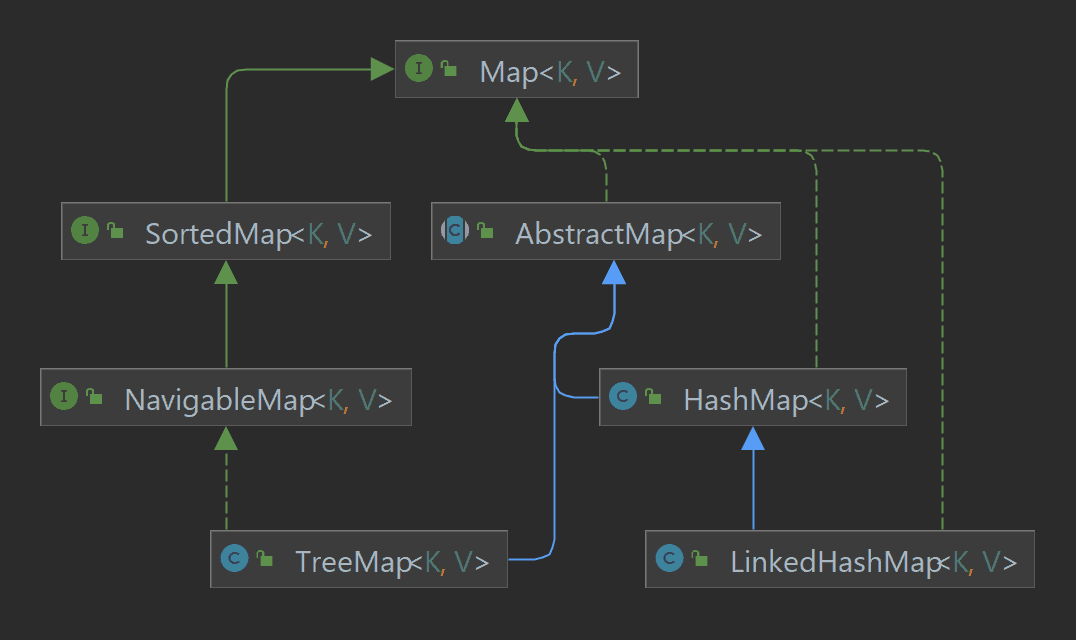
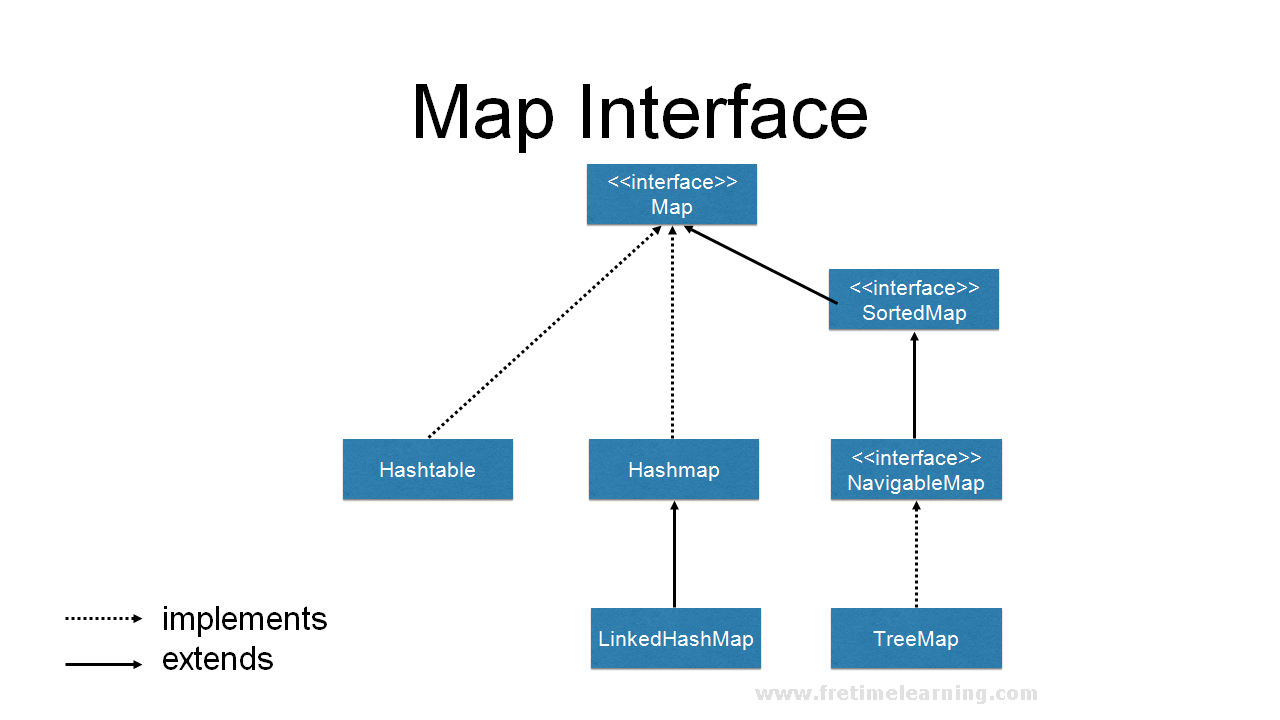
HashMapdoes not maintain the order in which elements are inserted. This means that iterating over aHashMapdoes not guarantee a predictable sequence. On the other hand, theLinkedHashMapclass, a subclass ofHashMap, preserves the order of insertion, making it suitable for scenarios where element order is significant. -
Null Keys and Values:
HashMapallows for a single null key and multiple null values. However, it’s crucial to note that the presence of a null key can impact the performance ofHashMapoperations, as it requires additional checks during hash calculations. -
Thread Safety:
HashMapis not inherently thread-safe. In multi-threaded environments, concurrent modifications to aHashMapcan lead to unpredictable behavior and potential data corruption. To address this, Java provides theConcurrentHashMapclass, which offers thread-safe operations and improved concurrency performance.
Choosing the Right Tool: Selecting Between Maps and Hashmaps
The choice between Map and HashMap depends on the specific requirements of your application. If you prioritize the ability to retrieve values based on their associated keys and performance is a key factor, HashMap is often the preferred choice. However, if you need to maintain the order of elements or require thread-safe operations, LinkedHashMap or ConcurrentHashMap respectively, might be more suitable.
Benefits of Maps and Hashmaps in Java
-
Efficient Data Retrieval: Maps and hashmaps provide efficient retrieval of values based on their corresponding keys. This makes them ideal for scenarios where fast lookup is crucial, such as caching systems, symbol tables, and dictionaries.
-
Flexibility and Extensibility: Maps and hashmaps are highly flexible data structures that can accommodate various data types for keys and values. This allows developers to represent complex relationships and manage diverse data sets effectively.
-
Scalability and Performance: Hashmaps, in particular, exhibit excellent scalability and performance characteristics. Their hash-based approach allows for efficient storage and retrieval, even for large datasets.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. What is the difference between a Map and a HashMap in Java?
A Map is an interface that defines the contract for storing and retrieving key-value pairs. A HashMap is a concrete implementation of the Map interface that utilizes a hash table for efficient storage and retrieval.
2. When should I use a HashMap over a Map?
Use a HashMap when you need a highly efficient data structure for storing and retrieving data based on keys, particularly in scenarios where performance is a key concern.
3. Is HashMap thread-safe?
No, HashMap is not inherently thread-safe. Concurrent modifications to a HashMap in a multi-threaded environment can lead to data corruption.
4. What is the difference between a HashMap and a LinkedHashMap?
A LinkedHashMap maintains the order in which elements are inserted, while a HashMap does not. LinkedHashMap is suitable when element order is important, while HashMap prioritizes performance.
5. What is a ConcurrentHashMap?
ConcurrentHashMap is a thread-safe implementation of Map that provides efficient concurrent operations. It is suitable for scenarios where multiple threads need to access and modify the map concurrently.
Tips for Effective Map and HashMap Usage
-
Choose the appropriate implementation: Select the most suitable
Mapimplementation (e.g.,HashMap,LinkedHashMap,ConcurrentHashMap) based on your specific requirements. -
Handle null keys and values carefully: Be mindful of null keys and values, as they can impact performance and potentially lead to unexpected behavior.
-
Consider thread safety: If your application involves multiple threads accessing and modifying the map, ensure you choose a thread-safe implementation or implement appropriate synchronization mechanisms.
-
Optimize hash functions: For
HashMap, ensure that the hash function is well-designed to minimize collisions and maximize performance.
Conclusion: Mastering the Power of Maps and Hashmaps
Maps and hashmaps are fundamental data structures in Java, providing efficient storage and retrieval mechanisms for key-value pairs. Understanding their differences, benefits, and considerations for thread safety is crucial for making informed choices and optimizing your code for performance and reliability. By leveraging the power of these structures, developers can build robust and efficient applications that effectively manage and manipulate data, ultimately enhancing the overall user experience.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Landscape: Exploring the Differences Between Java Maps and Hashmaps. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!