Scandinavia: A Corner Of The World Steeped In History And Innovation
Scandinavia: A Corner of the World Steeped in History and Innovation
Related Articles: Scandinavia: A Corner of the World Steeped in History and Innovation
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Scandinavia: A Corner of the World Steeped in History and Innovation. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Scandinavia: A Corner of the World Steeped in History and Innovation

Scandinavia, a region nestled in Northern Europe, comprises the countries of Denmark, Norway, Sweden, and often includes Finland and Iceland. Though geographically diverse, these nations share a common heritage, marked by Viking sagas, stunning landscapes, and a commitment to social welfare.
A Geographical Overview
Scandinavia’s location on the world map is defined by its proximity to the Arctic Circle. This position brings distinct characteristics:
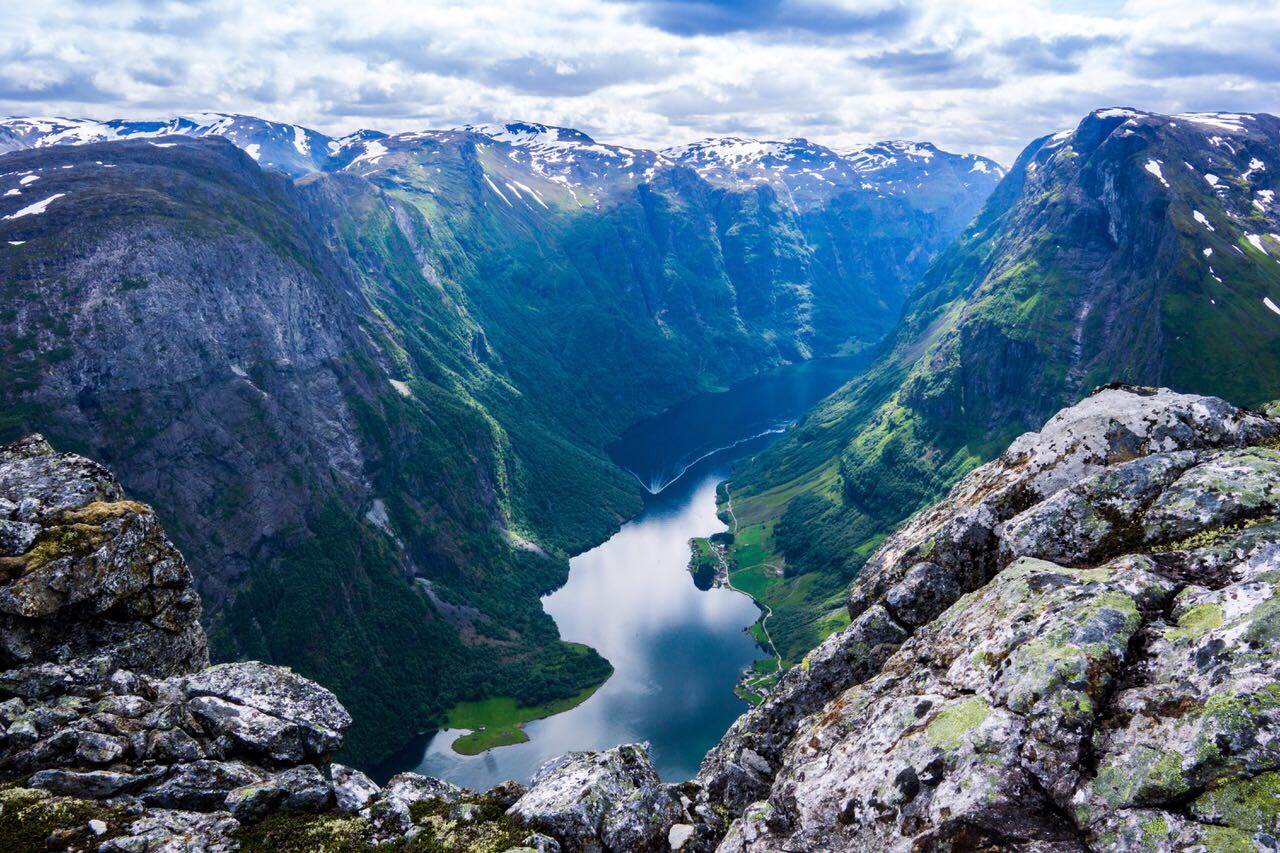
- Dramatic Landscapes: From the towering peaks of the Norwegian fjords to the vast Swedish forests and the icy plains of Lapland, Scandinavia’s geography is a tapestry of dramatic contrasts.
- Unique Climate: The region experiences long, dark winters and short, bright summers. This unique climate has shaped Scandinavian culture, lifestyle, and even architecture.
- Strategic Location: Situated between the North Sea and the Baltic Sea, Scandinavia holds a strategic position in Northern Europe, influencing trade routes and geopolitical dynamics.
Historical Tapestry
Scandinavia’s history is a rich tapestry woven with the threads of Viking raids, medieval kingdoms, and modern revolutions.
- The Viking Age: From the 8th to the 11th centuries, Vikings from Scandinavia embarked on voyages of exploration and conquest, leaving their mark on history and shaping the region’s identity.
- Medieval Kingdoms: During the Middle Ages, Scandinavia was home to powerful kingdoms, each with its unique culture and traditions.
- Modern Transformations: The 19th and 20th centuries witnessed significant transformations, including industrialization, social reforms, and the rise of democratic ideals.
Cultural Identity and Shared Values
Scandinavian culture is characterized by a strong emphasis on social welfare, environmental consciousness, and a deep appreciation for nature.
- Social Welfare Systems: These nations are renowned for their robust social welfare systems, prioritizing equality and providing access to healthcare, education, and social security.
- Environmentalism: Scandinavians have a strong commitment to environmental sustainability, prioritizing renewable energy sources and promoting responsible resource management.
- Nature’s Embrace: The region’s dramatic landscapes have fostered a deep connection to nature, inspiring art, literature, and a love for outdoor recreation.
Economic Powerhouse
Scandinavia is a significant economic force in Europe, known for its technological innovation, sustainable practices, and strong social safety nets.
- Innovation and Technology: The region has become a hub for technological innovation, with companies like Nokia, Ericsson, and Spotify leading the way in various sectors.
- Sustainable Development: Scandinavian nations prioritize sustainable practices, focusing on renewable energy, circular economy models, and environmental conservation.
- Social Welfare and Equality: The region’s robust social welfare systems ensure a high standard of living for its citizens, promoting equality and social cohesion.
Beyond the Stereotypes
Scandinavia is often depicted through stereotypes, but beneath the surface lies a complex and evolving region.
- Beyond the Stereotypes: While known for its social welfare systems and progressive values, the region is also home to diverse perspectives, political debates, and cultural nuances.
- Navigating Challenges: Like any region, Scandinavia faces its share of challenges, including income inequality, integration of immigrants, and climate change.
FAQs
Q: What is the difference between Scandinavia and Nordic countries?
A: The term "Scandinavia" typically refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. The term "Nordic countries" includes these three, plus Finland and Iceland. This broader definition recognizes cultural and historical connections among these five nations.
Q: What are the main languages spoken in Scandinavia?
A: The primary languages are Danish, Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish, and Icelandic.
Q: What are the main industries in Scandinavia?
A: The region has a diverse economy, with key industries including technology, renewable energy, forestry, fishing, and tourism.
Tips for Visiting Scandinavia
- Embrace the Seasons: Experience the region’s beauty across different seasons, from the vibrant summer landscapes to the snowy winter wonderland.
- Explore the Outdoors: Hike through breathtaking fjords, kayak along the coastline, or ski through pristine forests.
- Indulge in Local Cuisine: Savor the flavors of fresh seafood, traditional dishes, and Nordic-inspired gastronomy.
- Respect Local Customs: Be mindful of social norms, such as punctuality and respect for personal space.
- Learn a Few Phrases: While English is widely spoken, learning a few basic phrases in the local language can enhance your experience.
Conclusion
Scandinavia, a region of breathtaking landscapes and innovative minds, holds a unique place on the world map. From its Viking heritage to its progressive social models, the region has shaped its own identity while contributing to global progress. Understanding Scandinavia’s history, culture, and values provides a deeper appreciation for this corner of the world, where nature and innovation intertwine to create a vibrant and evolving society.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Scandinavia: A Corner of the World Steeped in History and Innovation. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!