Susa: A Crossroads Of Ancient Civilizations
Susa: A Crossroads of Ancient Civilizations
Related Articles: Susa: A Crossroads of Ancient Civilizations
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Susa: A Crossroads of Ancient Civilizations. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Susa: A Crossroads of Ancient Civilizations
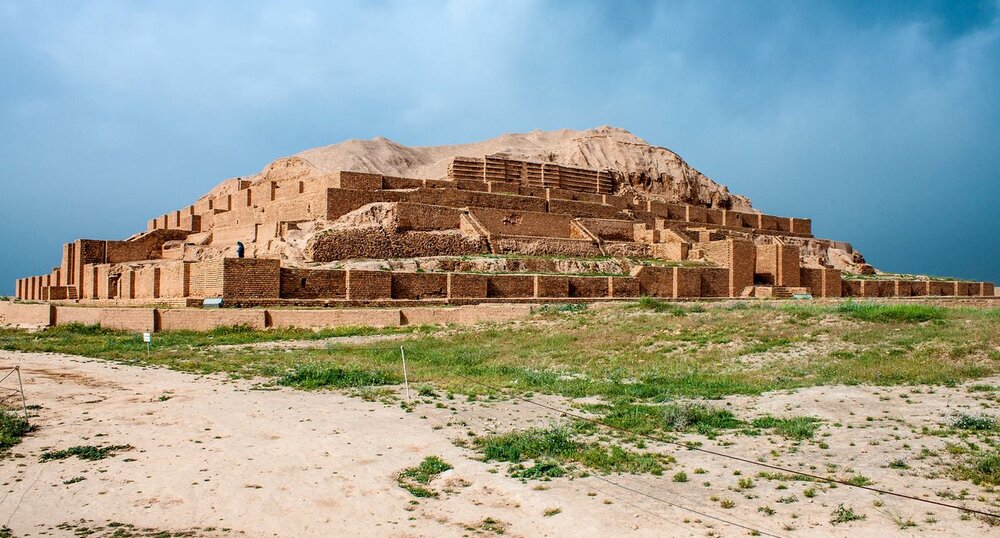

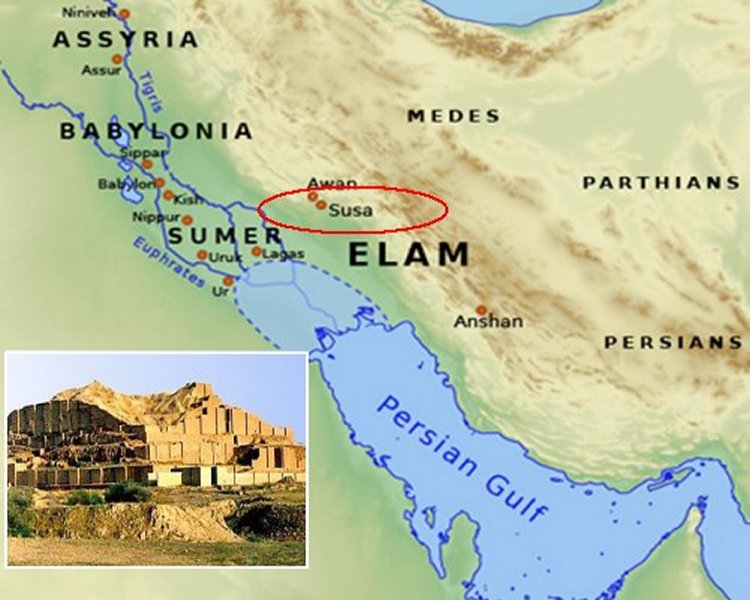
Susa, an ancient city located in southwestern Iran, holds a significant place in the tapestry of human history. Situated at the confluence of the Karkheh and Dez rivers, Susa’s strategic location made it a vital hub for trade and cultural exchange, fostering a rich and complex history spanning millennia.
A Glimpse into Antiquity:
Susa’s origins can be traced back to the 4th millennium BCE, with evidence suggesting it was a thriving urban center during the Uruk period. This early civilization, renowned for its advanced city planning and writing system, left its mark on Susa, laying the foundation for its future growth.
The Rise of Elam:
The city’s fortunes truly took a turn during the Elamite period (c. 2700-539 BCE), when Susa became the capital of this powerful and independent kingdom. The Elamites, known for their sophisticated art, architecture, and writing system, transformed Susa into a magnificent city. Excavations have unearthed impressive palaces, temples, and ziggurats, testament to the Elamites’ artistic and architectural prowess.
The Achaemenid Dynasty:
Following the conquest of Elam by the Achaemenid dynasty in the 6th century BCE, Susa became a prominent royal city within the vast Persian Empire. Cyrus the Great, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, recognized the city’s strategic importance and made it his winter residence. Susa’s role as a center of power was further solidified under Darius I and Xerxes I, who commissioned the construction of magnificent palaces and administrative buildings, including the iconic Apadana Palace.
A Legacy of Cultural Fusion:
The Achaemenid period witnessed a remarkable cultural fusion in Susa. The city became a melting pot of influences, drawing upon the traditions of the Elamites, Persians, and other cultures within the empire. This cultural exchange is evident in the art, architecture, and religious practices of the period.
The Seleucid and Parthian Eras:
After the fall of the Achaemenid Empire, Susa remained an important city under the Seleucid and Parthian dynasties. While these empires did not hold the same level of grandeur as the Achaemenids, they continued to maintain Susa as a significant administrative center.
The Sassanid Dynasty:
The Sassanid Empire, which ruled Persia from the 3rd to the 7th centuries CE, witnessed a resurgence of Susa’s importance. The Sassanids, known for their architectural prowess, restored and expanded the city, making it a prominent center of learning and trade.
The Islamic Period:
Following the Arab conquest of Persia in the 7th century CE, Susa’s fortunes declined. While it remained a significant town under Islamic rule, its importance diminished compared to its earlier glory.
Modern Discoveries:
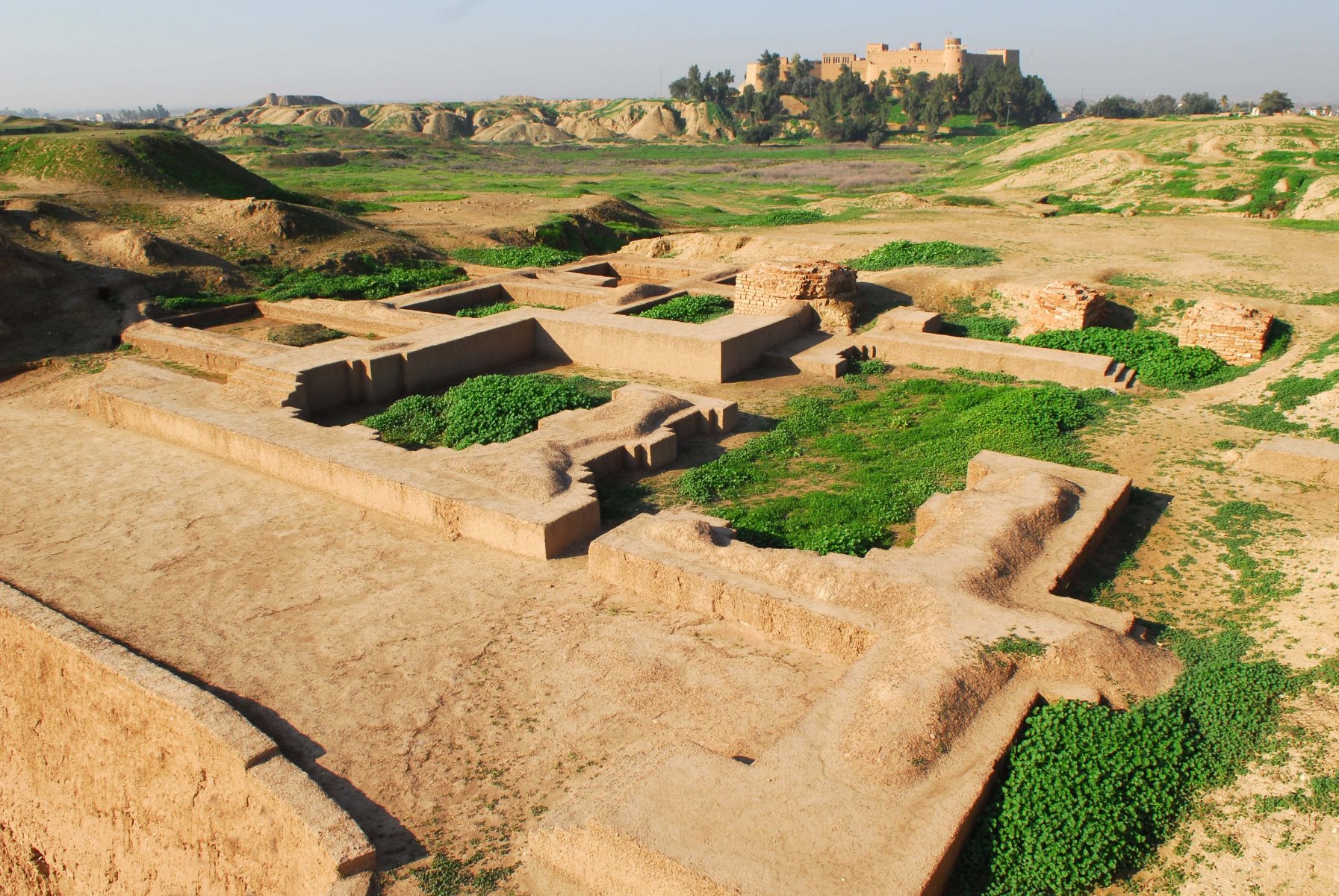
In the 19th and 20th centuries, archaeological excavations at Susa brought to light a wealth of information about the city’s past. The discoveries, including the Royal Tombs of the Elamites, the Apadana Palace, and the vast archives of cuneiform tablets, have provided invaluable insights into the history, culture, and civilization of ancient Persia.
Susa: A Legacy of Cultural Exchange and Power:
Susa’s history is a testament to its enduring significance as a crossroads of civilizations. The city’s strategic location, its role as a capital city for multiple empires, and its rich cultural heritage have left an indelible mark on the world. From the ancient Elamites to the Achaemenid kings, Susa served as a vital center of power, trade, and cultural exchange, shaping the course of history in the ancient Near East.
FAQs about Susa:
Q: What are the most significant archaeological discoveries at Susa?
A: Some of the most notable discoveries at Susa include:
- The Royal Tombs of the Elamites: These tombs, dating back to the 3rd millennium BCE, are a testament to the Elamites’ wealth and artistic skills.
- The Apadana Palace: Built by Darius I, this grand palace is a masterpiece of Achaemenid architecture, featuring impressive columns and intricate carvings.
- The Archives of Cuneiform Tablets: These tablets, containing administrative records, legal documents, and literary texts, provide invaluable insights into the daily life and governance of ancient Persia.
Q: What role did Susa play in the Achaemenid Empire?
A: Susa was one of the most important cities in the Achaemenid Empire. It served as the winter residence of the Persian kings, and it was a major center of administration, trade, and culture.
Q: What is the significance of Susa’s strategic location?
A: Susa’s location at the confluence of the Karkheh and Dez rivers made it a vital hub for trade routes connecting Mesopotamia, Persia, and other regions. This strategic location contributed to the city’s prosperity and its role as a center of cultural exchange.
Q: What are some of the notable architectural features of Susa?
A: Susa boasts several architectural marvels, including:
- The Apadana Palace: This magnificent palace, built by Darius I, is a testament to the Achaemenid Empire’s architectural prowess.
- The Ziggurat of Susa: This towering structure, dedicated to the Elamite god Inshushinak, was an important religious center.
- The Royal Tombs of the Elamites: These tombs, located in the nearby mountains, are adorned with intricate carvings and reliefs.
Tips for Visiting Susa:
- Plan your visit during the cooler months: Susa experiences hot summers, so it is best to visit during the spring or autumn.
- Hire a local guide: A knowledgeable guide can provide valuable insights into the history and culture of Susa.
- Explore the archaeological sites: The ruins of the Apadana Palace, the ziggurat, and the Royal Tombs are must-see attractions.
- Visit the Susa Museum: This museum houses a collection of artifacts from the city’s long and rich history.
- Take a day trip to nearby Shushter: This ancient city, located about 100 kilometers from Susa, is home to several historical sites, including the Shushter Watermills, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Conclusion:
Susa stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of ancient civilizations. Its rich history, spanning millennia, is a testament to the power, creativity, and resilience of the people who called this city home. From its origins as an early urban center to its role as a prominent royal city within the Achaemenid Empire, Susa has played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history. The city’s archaeological treasures and its enduring cultural legacy continue to fascinate and inspire, offering a window into the past and a reminder of the interconnectedness of human civilizations.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Susa: A Crossroads of Ancient Civilizations. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!