The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool For Understanding And Addressing Biodiversity Loss
The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Addressing Biodiversity Loss
Related Articles: The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Addressing Biodiversity Loss
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Addressing Biodiversity Loss. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Addressing Biodiversity Loss
The Earth’s biodiversity is facing an unprecedented crisis. Species are disappearing at an alarming rate, driven by human activities such as habitat loss, climate change, and pollution. To effectively address this crisis, we need comprehensive tools to understand the scale and scope of the problem. The Extinction Map is one such tool, providing a powerful visual representation of global biodiversity loss and the threats facing different species.
Understanding the Extinction Map
The Extinction Map is not a physical map in the traditional sense. It is a digital platform that compiles and visualizes data on species extinction risk, using a combination of scientific research, conservation efforts, and public participation. The platform leverages advanced mapping technologies and data visualization techniques to create interactive maps that display the distribution of species, their extinction risk, and the factors contributing to their decline.
Key Features of the Extinction Map:
- Species Distribution Maps: The Extinction Map allows users to visualize the geographic distribution of different species across the globe. This provides a clear picture of where species are found and the potential threats they face in their specific locations.
- Extinction Risk Assessments: The platform integrates data from the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List, which provides comprehensive assessments of the extinction risk for thousands of species. Users can explore the map to identify species classified as critically endangered, endangered, or vulnerable.
- Threat Analysis: The Extinction Map goes beyond simply displaying species distribution and extinction risk. It also allows users to explore the specific threats facing different species, such as habitat loss, climate change, overexploitation, and pollution. This information is crucial for understanding the underlying drivers of biodiversity loss and developing targeted conservation strategies.
- Interactive Features: The Extinction Map is designed to be user-friendly and interactive. Users can zoom in and out of the map, explore specific regions, and filter data based on various criteria. This allows for a more personalized and engaging experience, facilitating deeper understanding and exploration of the data.
- Citizen Science Integration: The Extinction Map encourages public participation through citizen science initiatives. Users can contribute data on species sightings, habitat changes, and other relevant information, helping to improve the accuracy and completeness of the platform’s data.
The Importance of the Extinction Map
The Extinction Map serves as a vital tool for a range of stakeholders, including:
- Conservationists: The platform provides valuable information for developing and implementing effective conservation strategies. By understanding the distribution, extinction risk, and threats facing specific species, conservationists can prioritize resources and efforts to protect vulnerable populations.
- Policymakers: The Extinction Map offers a clear and compelling visual representation of the biodiversity crisis, highlighting the urgent need for policy changes and resource allocation to address the problem.
- Researchers: The platform provides a valuable data resource for scientists studying biodiversity, extinction, and conservation. The comprehensive data and interactive features allow for in-depth analysis and modeling of various factors contributing to biodiversity loss.
- Educators: The Extinction Map can be used as a powerful educational tool to raise awareness about biodiversity loss and inspire action. The interactive nature of the platform makes it engaging for students of all ages, promoting deeper understanding and appreciation for the natural world.
- The Public: The Extinction Map empowers individuals to learn about the threats facing biodiversity and take action to support conservation efforts. By providing access to information and fostering awareness, the platform encourages responsible stewardship of the planet’s natural resources.
FAQs about the Extinction Map:
Q: What data sources are used for the Extinction Map?
A: The Extinction Map relies on a variety of data sources, including the IUCN Red List, scientific publications, citizen science contributions, and government databases. These sources are carefully vetted and validated to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the information presented.
Q: How often is the data on the Extinction Map updated?
A: The data on the Extinction Map is continuously updated as new information becomes available. The platform incorporates regular updates from the IUCN Red List, scientific publications, and citizen science contributions.
Q: Can I contribute data to the Extinction Map?
A: Yes, the Extinction Map encourages citizen science contributions. Users can submit data on species sightings, habitat changes, and other relevant information through the platform’s dedicated interface. This data helps to improve the accuracy and completeness of the map’s information.
Q: Is the Extinction Map available in multiple languages?
A: The Extinction Map is currently available in English, but efforts are underway to make the platform accessible in multiple languages. This will allow for wider reach and engagement with global audiences.
Tips for Using the Extinction Map:
- Explore different regions: The Extinction Map allows you to zoom in and out of the map, exploring specific regions and countries. This can help you understand the local threats to biodiversity and the conservation efforts underway.
- Filter data by species, threat, or region: The platform offers various filtering options to tailor your exploration based on your interests. This allows you to focus on specific species, threats, or geographic areas.
- Use the interactive features: The Extinction Map is designed to be user-friendly and interactive. Take advantage of the zoom, pan, and filter options to explore the data in a more engaging way.
- Share the information with others: The Extinction Map provides a powerful visual representation of the biodiversity crisis. Share the platform with friends, family, and colleagues to raise awareness and inspire action.
Conclusion:
The Extinction Map is a powerful tool for understanding and addressing the global biodiversity crisis. By providing comprehensive data on species extinction risk, threats, and conservation efforts, the platform empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions and take action to protect the planet’s irreplaceable biodiversity. The interactive nature of the map, coupled with its user-friendly interface, makes it accessible to a wide audience, fostering awareness, engagement, and ultimately, a more sustainable future for all.





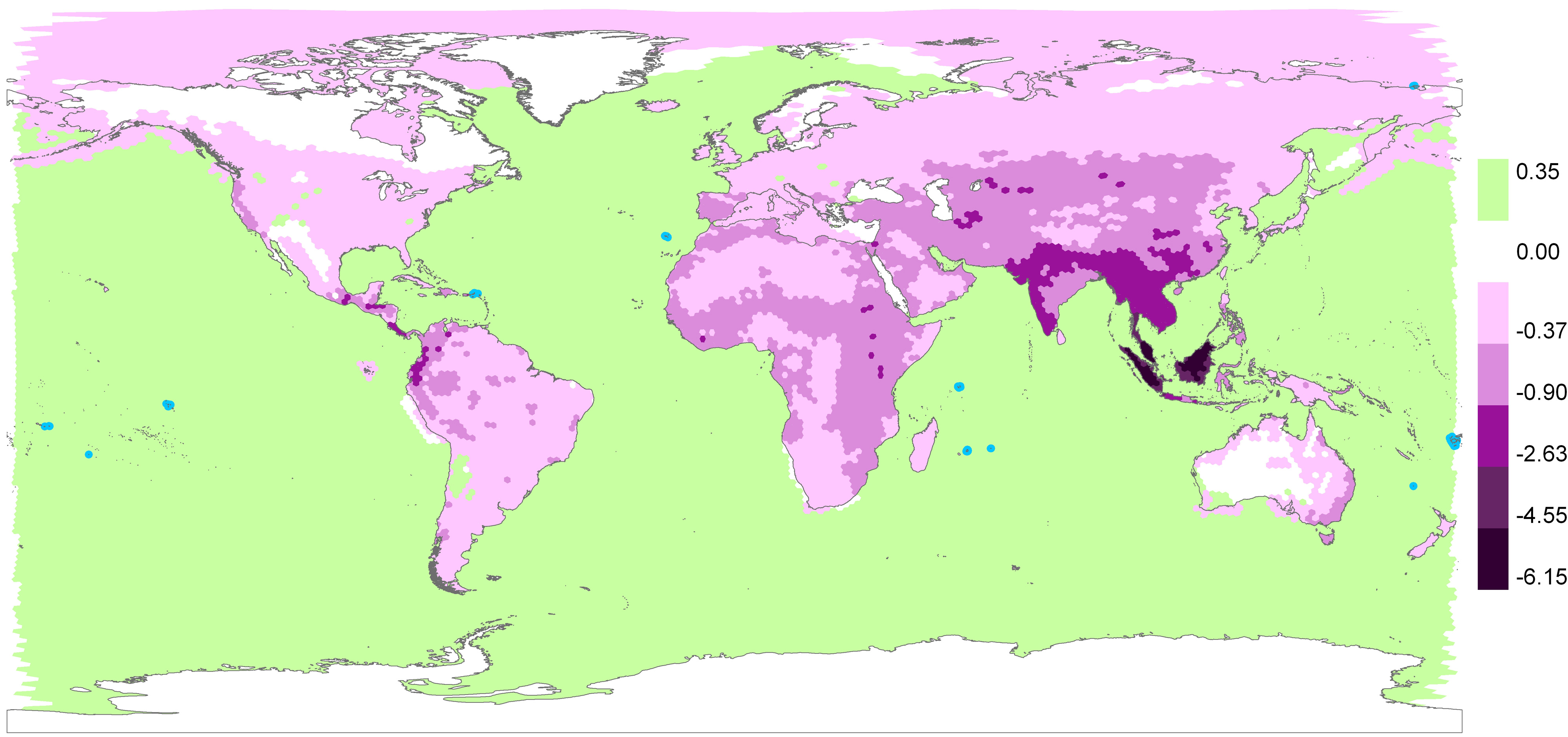
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16218434/Screen_Shot_2019_05_07_at_9.39.50_AM.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Extinction Map: A Powerful Tool for Understanding and Addressing Biodiversity Loss. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
