Unraveling The Tapestry Of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration
Unraveling the Tapestry of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration
Related Articles: Unraveling the Tapestry of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Tapestry of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Tapestry of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration

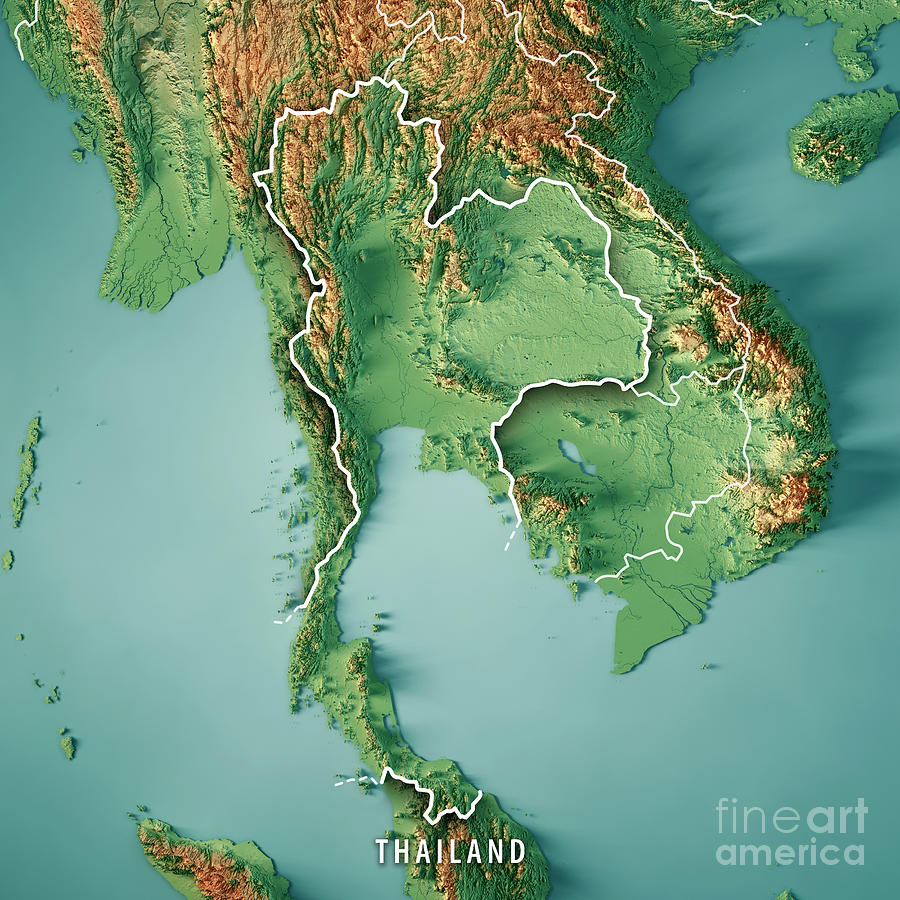
Thailand, the "Land of Smiles," is a vibrant Southeast Asian nation renowned for its diverse landscapes, rich cultural heritage, and welcoming people. Understanding the geography of Thailand, through the lens of its map, is crucial for appreciating its history, culture, and the unique challenges and opportunities it faces.
A Glimpse into the Landscape
The map of Thailand reveals a country shaped like an elongated peninsula, stretching from the Malay Peninsula in the south to the border with Myanmar in the north. This geographic configuration has profoundly shaped Thailand’s history, influencing its interactions with neighboring countries and its role in the region’s trade networks.
The Dominant Physical Features:
- The Central Plains: This fertile, low-lying region, encompassing the Chao Phraya River Delta, is the heart of Thailand. It is the country’s agricultural powerhouse, producing rice, sugar cane, and other essential crops. The central plains are densely populated and home to major cities like Bangkok, the capital.
- The Khorat Plateau: Located in the northeastern region, this plateau is characterized by its undulating terrain and semi-arid climate. It is less densely populated than the central plains and is known for its agricultural production, particularly cassava and maize.
- The Northern Mountains: This region, bordering Myanmar and Laos, is dominated by the rugged terrain of the Thanon Thong Chai Range. It is home to numerous national parks, including Doi Inthanon National Park, which boasts the highest peak in Thailand.
- The Eastern Highlands: This region, bordering Cambodia, is characterized by its rolling hills and dense forests. It is home to numerous waterfalls and caves, attracting tourists seeking adventure and natural beauty.
- The Southern Peninsula: This region, stretching southwards from the Kra Isthmus, is known for its stunning beaches, tropical islands, and diverse marine life. The Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand, flanking the peninsula, are vital for fishing and tourism.
Navigating the Terrain: Regions and Provinces
Thailand is divided into 76 provinces, each with its own unique characteristics and cultural nuances. Understanding the geographical distribution of these provinces is crucial for comprehending the country’s diverse socio-economic landscape.
The North: This region, encompassing provinces like Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, and Mae Hong Son, is known for its rich cultural heritage, ancient temples, and stunning mountainous scenery. It is also a significant producer of agricultural products, including coffee, tea, and rubber.
The Northeast: This region, known as Isaan, encompasses provinces like Khon Kaen, Ubon Ratchathani, and Nakhon Ratchasima. Isaan is characterized by its fertile plains, its unique cultural traditions, and its role as a major agricultural producer.
The Central Region: This region, encompassing provinces like Bangkok, Ayutthaya, and Nakhon Pathom, is the economic and cultural heart of Thailand. It is home to major industries, bustling cities, and historical sites.
The East: This region, encompassing provinces like Chonburi, Rayong, and Chanthaburi, is known for its coastal beauty, its industrial development, and its role as a major tourist destination.
The South: This region, encompassing provinces like Phuket, Krabi, and Surat Thani, is renowned for its stunning beaches, tropical islands, and vibrant marine life. It is a major tourist destination and a significant contributor to the country’s economy.
The Importance of Geographical Knowledge
A thorough understanding of Thailand’s map reveals its inherent interconnectedness, both within its borders and with its neighboring countries. This geographic understanding is crucial for:
- Economic Development: Recognizing the potential and limitations of different regions allows for targeted economic development strategies, fostering sustainable growth and alleviating regional disparities.
- Infrastructure Planning: Understanding the terrain and population distribution is essential for planning efficient transportation networks, communication systems, and access to essential services.
- Environmental Conservation: Identifying environmentally sensitive areas, such as forests, wetlands, and marine ecosystems, is crucial for implementing conservation strategies and mitigating the impact of development.
- Cultural Preservation: Recognizing the unique cultural practices and traditions of different regions allows for the preservation of Thailand’s rich cultural heritage and the promotion of cultural tourism.
- Disaster Management: Understanding the geographical factors that contribute to natural disasters, such as floods, droughts, and earthquakes, is essential for developing effective disaster preparedness and response plans.
FAQs about the Map of Thailand:
1. What are the major rivers in Thailand?
The most significant river in Thailand is the Chao Phraya River, which flows through the central plains and empties into the Gulf of Thailand. Other important rivers include the Mekong River, which forms part of Thailand’s border with Laos and Cambodia, and the Mae Klong River, which flows through the western part of the country.
2. What are the major mountain ranges in Thailand?
The most prominent mountain range in Thailand is the Thanon Thong Chai Range, which runs along the border with Myanmar and Laos. Other notable ranges include the Sankamphaeng Range, the Dawna Range, and the Tenasserim Hills.
3. What are the major islands in Thailand?
Thailand has numerous islands, both in the Andaman Sea and the Gulf of Thailand. Some of the most popular tourist destinations include Phuket, Koh Samui, Koh Phi Phi, and Koh Lanta.
4. What is the climate like in Thailand?
Thailand experiences a tropical monsoon climate, characterized by a hot and humid rainy season from May to October and a dry season from November to April.
5. What are the major cities in Thailand?
The major cities in Thailand include Bangkok, the capital, Chiang Mai, Chiang Rai, Phuket, Pattaya, and Hat Yai.
Tips for Using the Map of Thailand:
- Explore the map in detail: Pay attention to the physical features, major cities, and provinces to gain a comprehensive understanding of the country’s geography.
- Relate the map to historical events: Explore how geographical features have shaped Thailand’s history, from its early kingdoms to its modern development.
- Connect the map to cultural practices: Identify how different regions have developed their own unique cultural traditions and how these traditions are reflected in the map.
- Use the map to plan travel: Identify potential destinations, transportation routes, and points of interest based on your interests and travel preferences.
- Consider the map’s limitations: Remember that maps are static representations of a dynamic world. They can be helpful tools for understanding geography, but they should be used in conjunction with other sources of information.
Conclusion:
The map of Thailand serves as a powerful visual tool for understanding the country’s rich tapestry of geography, culture, and history. By exploring its physical features, regions, and provinces, we gain insights into the complex interplay of nature, society, and economy that shapes this vibrant nation. From the fertile plains of the central region to the rugged mountains of the north, from the bustling cities to the serene beaches, Thailand’s map reveals a captivating and diverse landscape that continues to captivate the imagination.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Tapestry of Thailand: A Geographical Exploration. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!