Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide To Visualizing Trends With Heat Maps
Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Trends with Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Trends with Heat Maps
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Trends with Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Trends with Heat Maps
![Create a Geographic Heat Map in Excel [Guide] Maptive](https://www.maptive.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/excel-heat-maps.jpg)
Heat maps, powerful tools in data visualization, offer a compelling way to represent data distributions and identify trends. Their intuitive visual format, employing color gradients to highlight areas of high and low values, makes complex datasets readily comprehensible. This article delves into the core concepts of heat maps, exploring their applications, benefits, and limitations.
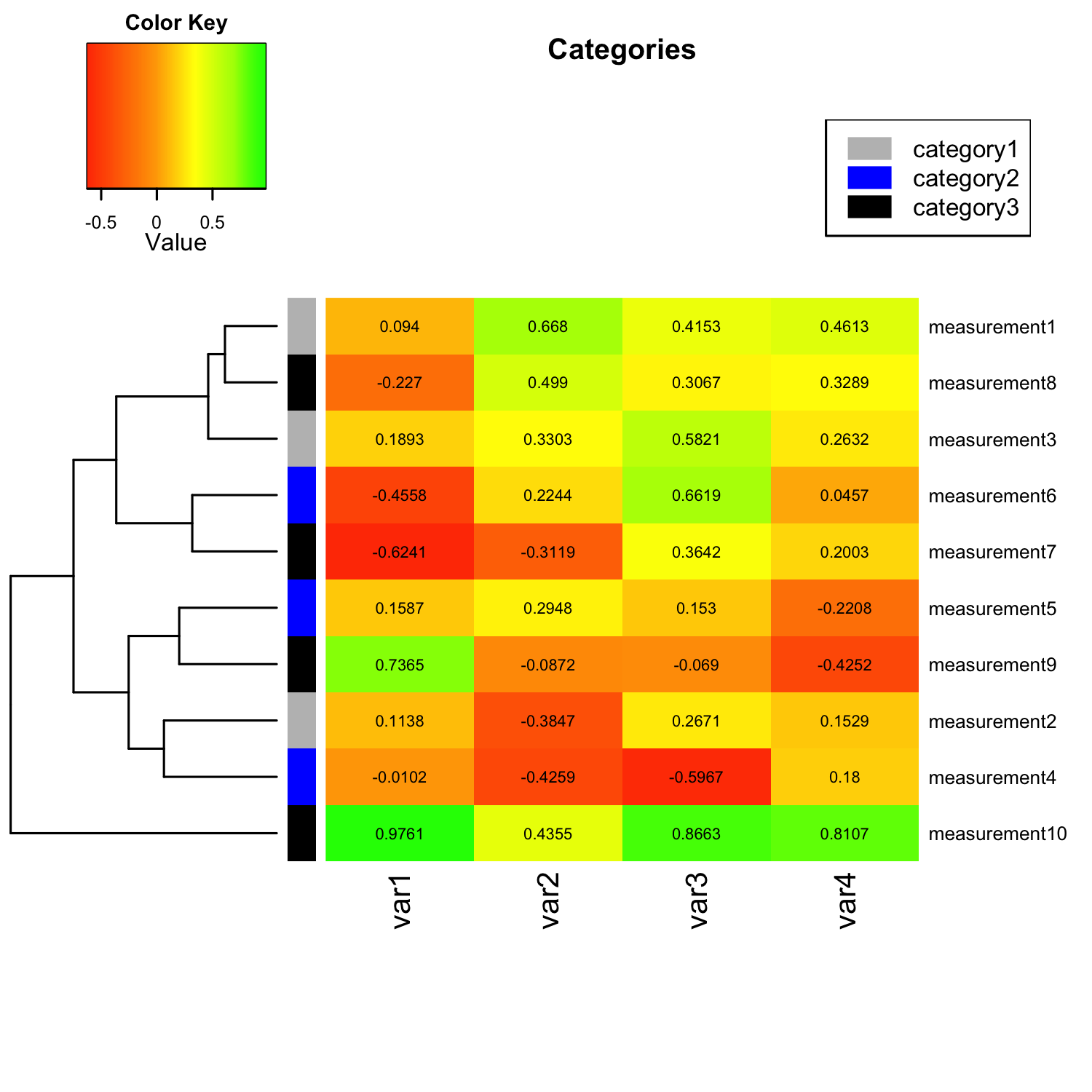
Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
At their heart, heat maps are graphical representations where data points are mapped onto a two-dimensional surface, typically a grid or a geographical map. The intensity of color at each location corresponds to the value of the associated data point. Areas with high values are typically depicted in warmer colors (e.g., red, orange, yellow), while lower values are represented by cooler colors (e.g., blue, green). This color gradient provides a visual cue, allowing viewers to quickly identify areas of concentration, outliers, and patterns within the data.
Applications of Heat Maps
The versatility of heat maps makes them applicable across diverse fields, including:
- Business Analytics: Identifying customer demographics, product popularity, and marketing campaign effectiveness.
- Finance: Analyzing stock market trends, identifying investment opportunities, and understanding market sentiment.
- Healthcare: Mapping disease outbreaks, understanding patient demographics, and optimizing resource allocation.
- Marketing: Optimizing website layouts, analyzing user behavior, and understanding customer preferences.
- Sports Analytics: Visualizing player performance, identifying strategic patterns, and optimizing team strategies.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Mapping population density, analyzing environmental factors, and understanding spatial trends.
Benefits of Utilizing Heat Maps
The advantages of employing heat maps are numerous:
- Data Visualization: Heat maps transform complex datasets into easily digestible visual representations, revealing hidden patterns and insights.
- Trend Identification: The color gradient readily highlights areas of high and low values, facilitating the identification of trends and anomalies.
- Comparative Analysis: By comparing multiple heat maps, users can analyze changes over time or across different categories, providing valuable insights.
- Decision Support: The visual representation of data enables informed decision-making by highlighting areas requiring attention or further investigation.
- Communication Enhancement: Heat maps provide a powerful tool for communicating complex data to a wider audience, fostering better understanding and collaboration.
Types of Heat Maps
Heat maps can be categorized into various types based on their application and data representation:
- Grid-Based Heat Maps: These are the most common type, where data is mapped onto a rectangular grid. Each cell represents a specific data point, and the color intensity reflects its value.
- Geographical Heat Maps: These maps are used to visualize data over a geographical area, such as population density, crime rates, or weather patterns.
- Clustered Heat Maps: These maps group similar data points together, revealing clusters or patterns within the data.
- Sequential Heat Maps: These maps depict data changes over time, showcasing trends and transitions.
Building Effective Heat Maps
Creating a visually appealing and informative heat map requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Data Selection: Ensure the data is relevant to the intended analysis and appropriately scaled for the visualization.
- Color Palette: Choose a color palette that effectively contrasts high and low values, enhancing readability and clarity.
- Legend: Provide a clear legend that explains the color gradient and corresponding data values.
- Labels and Annotations: Add labels and annotations to identify specific locations, data points, or trends.
- Interactive Features: Consider incorporating interactive features such as tooltips, zoom capabilities, and data filtering to enhance user engagement.
Limitations of Heat Maps
While heat maps are powerful tools, they also have limitations:
- Oversimplification: Heat maps can oversimplify complex data, potentially masking important details or nuances.
- Dimensionality: Heat maps are typically limited to two dimensions, making it challenging to represent data with multiple variables.
- Interpretation Bias: The interpretation of heat maps can be subjective, influenced by factors such as color perception and individual biases.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Maps
1. What software can I use to create heat maps?
Numerous software tools are available for creating heat maps, including:
- Microsoft Excel: Offers basic heat map functionality.
- Tableau: A powerful data visualization tool with advanced heat map capabilities.
- Power BI: Microsoft’s business intelligence tool featuring heat map creation options.
- R: A statistical programming language with extensive data visualization libraries, including heat map packages.
- Python: A versatile programming language with libraries like matplotlib and seaborn for generating heat maps.
2. How do I choose the right color palette for my heat map?
Selecting an appropriate color palette is crucial for clear visualization. Consider the following factors:
- Data Range: Choose a color palette that effectively contrasts high and low values within the data range.
- Data Type: The color palette should be appropriate for the type of data being visualized (e.g., continuous, categorical).
- Accessibility: Select colors that are accessible to users with color vision deficiencies.
- Visual Appeal: The color palette should be visually appealing and enhance the overall aesthetics of the heat map.
3. What are some best practices for interpreting heat maps?
When interpreting heat maps, consider the following best practices:
- Contextual Awareness: Understand the context of the data being visualized, including the units of measurement and the underlying variables.
- Focus on Trends: Look for patterns, trends, and anomalies within the data, paying attention to areas of high and low values.
- Consider Limitations: Remember that heat maps can oversimplify data and may not capture all nuances.
- Seek Confirmation: Validate your interpretations with additional data analysis or expert opinions.
Tips for Creating Effective Heat Maps
- Keep it Simple: Avoid overcrowding the heat map with too much information.
- Use Clear Labels: Ensure that labels and annotations are concise and easily understandable.
- Provide Context: Include a title, legend, and brief explanation to provide context for the visualization.
- Test and Iterate: Experiment with different color palettes, data representations, and interactive features to find the most effective visualization.
Conclusion
Heat maps offer a powerful and intuitive way to visualize data distributions and identify trends. By leveraging their visual appeal and data-driven insights, users can gain a deeper understanding of complex datasets, facilitating informed decision-making and effective communication. However, it is essential to acknowledge their limitations and interpret results with caution, ensuring that the visualizations are accurate, informative, and contextually relevant. As data visualization techniques continue to evolve, heat maps remain a valuable tool for exploring data patterns and unlocking hidden insights.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling Data Patterns: A Comprehensive Guide to Visualizing Trends with Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
