Unveiling The Physical Landscape Of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, And Coastlines
Unveiling the Physical Landscape of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines
Related Articles: Unveiling the Physical Landscape of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the Physical Landscape of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the Physical Landscape of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines

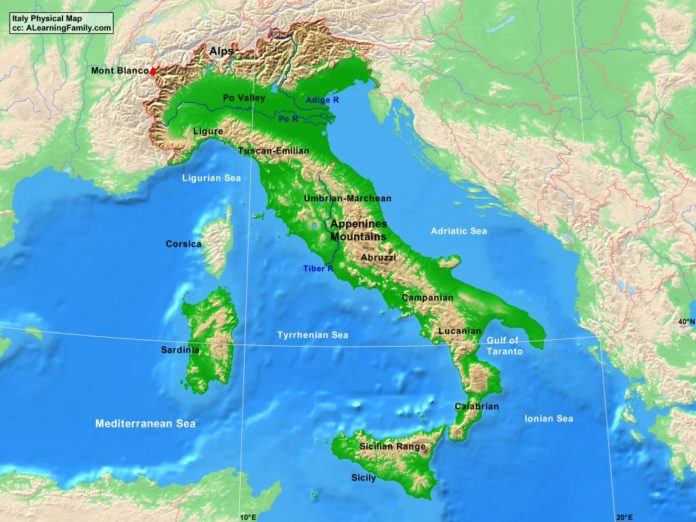
Italy, the "Bel Paese," or beautiful country, is renowned for its rich history, vibrant culture, and captivating landscapes. These landscapes, shaped by millennia of geological forces, are intricately woven into the fabric of Italian life, influencing everything from agriculture and urban development to the nation’s cultural identity. A physical map of Italy serves as a visual guide to this diverse and fascinating terrain, revealing the interplay of mountains, plains, and coastlines that define the peninsula.
The Backbone of Italy: The Apennine Mountains
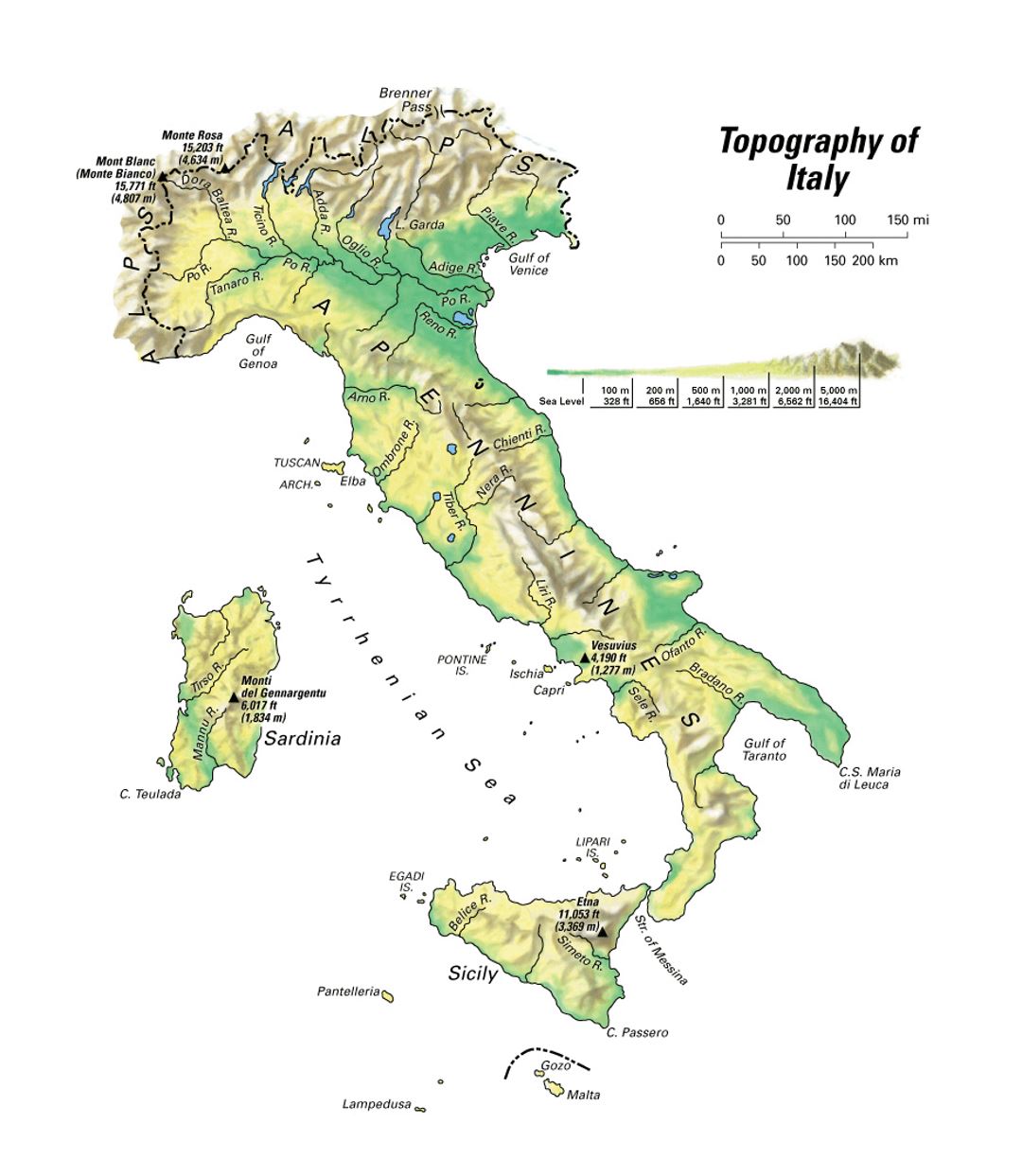
The Apennines, a formidable mountain range stretching the length of the Italian peninsula, form the backbone of the country. Rising from the Ligurian Alps in the north, they traverse the peninsula, culminating in the rugged peaks of Calabria in the south. The Apennines are not a single, continuous range, but rather a complex system of parallel chains and isolated massifs, creating a varied landscape of high peaks, deep valleys, and rolling hills.
The Apennines are a significant factor in Italy’s geography and climate. They act as a barrier to moisture-laden winds from the Mediterranean Sea, causing a rain shadow effect that results in drier conditions on the eastern side of the range. This disparity in rainfall contributes to the distinct agricultural landscapes found on either side of the Apennines. The western slopes, receiving ample rainfall, are characterized by vineyards and olive groves, while the eastern slopes are more suited to cereal crops and sheep grazing.
The Po Valley: A Cradle of Civilization
The Po Valley, located in northern Italy, is a vast plain enclosed by the Alps to the north and the Apennines to the south. It is the largest and most fertile agricultural region in Italy, producing a wide variety of crops, including rice, wheat, and corn. The Po River, which flows through the valley, plays a crucial role in irrigation and transportation. The Po Valley is also home to major industrial centers, such as Milan and Turin, making it a vital economic hub.
The Italian Coastline: A Tapestry of Diversity
Italy’s coastline, extending over 7,600 kilometers, is a testament to the country’s diverse geography. The Mediterranean Sea, which borders the peninsula, has shaped the coastline with its constant erosion and deposition. The result is a tapestry of rocky cliffs, sandy beaches, and picturesque islands.
The northern coastline, bordered by the Adriatic Sea, is generally flat and sandy, with wide beaches and lagoons. The central coastline, facing the Tyrrhenian Sea, is more varied, featuring rocky cliffs, volcanic landscapes, and coastal plains. The southern coastline, bordering the Ionian Sea, is characterized by rugged mountains that plunge directly into the sea, creating stunning vistas.
Volcanic Activity: Shaping the Landscape
Italy is home to several active and extinct volcanoes, which have played a significant role in shaping the country’s landscape. Mount Etna, located in Sicily, is Europe’s largest active volcano and a constant reminder of the dynamic geological forces at play. Vesuvius, near Naples, is another iconic volcano, famous for its devastating eruption that buried Pompeii and Herculaneum in 79 AD.
Volcanic activity has created fertile soils that support diverse agricultural practices, particularly in the regions surrounding Mount Etna and Vesuvius. The volcanic landscapes also attract tourists, drawn to the dramatic beauty of these natural wonders.
The Importance of Understanding Italy’s Physical Geography
A physical map of Italy provides a critical understanding of the country’s geography and its impact on various aspects of life, including:
- Agriculture: The varied terrain and climate influence agricultural practices, leading to the cultivation of diverse crops and livestock. The Po Valley, with its fertile plains, is a major agricultural hub, while the Apennines support vineyards, olive groves, and sheep grazing.
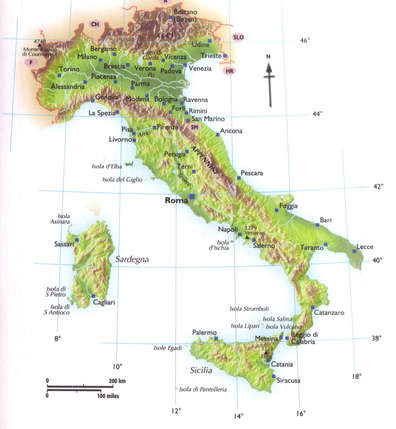
- Urban Development: The distribution of population and the growth of cities are influenced by the physical landscape. Coastal areas and fertile plains have historically attracted settlements, leading to the development of major cities like Rome, Milan, and Naples.
- Transportation: The mountainous terrain poses challenges to transportation infrastructure, but also provides opportunities for scenic routes and unique modes of transport, such as cable cars and ferries.
- Tourism: Italy’s diverse landscape is a major draw for tourists, offering a wide range of experiences, from hiking in the Alps to sunbathing on the beaches of Sicily.
- Cultural Identity: The physical landscape has shaped the cultural identity of Italy, influencing art, literature, and folklore. The mountains, valleys, and coastlines have inspired countless works of art and literature, reflecting the deep connection between the Italian people and their environment.
FAQs about the Physical Map of Italy
1. What are the main geographical features of Italy?
Italy is characterized by the Apennine Mountains, the Po Valley, and a diverse coastline. The Apennines form a spine down the peninsula, while the Po Valley is a fertile plain in the north. The coastline, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, features a mix of sandy beaches, rocky cliffs, and islands.
2. How do the Apennines affect Italy’s climate?
The Apennines act as a barrier to moisture-laden winds, creating a rain shadow effect that results in drier conditions on the eastern side of the range. This disparity in rainfall contributes to the distinct agricultural landscapes found on either side of the mountains.
3. What are the major cities located in the Po Valley?
The Po Valley is home to major industrial and urban centers, including Milan, Turin, Bologna, and Venice.
4. What are some of the most famous volcanoes in Italy?
Italy is home to several active and extinct volcanoes, including Mount Etna in Sicily, Vesuvius near Naples, and Stromboli in the Aeolian Islands.
5. How does the physical landscape of Italy influence its culture?
The diverse landscape of Italy has shaped its culture, influencing art, literature, and folklore. The mountains, valleys, and coastlines have inspired countless works of art and literature, reflecting the deep connection between the Italian people and their environment.
Tips for Exploring Italy’s Physical Landscape
- Hiking and Trekking: The Apennines offer numerous hiking trails, providing stunning views of the Italian countryside.
- Coastal Drives: Explore the scenic Italian coastline by car, stopping at charming coastal towns and beaches.
- Island Hopping: Visit the islands of Sicily, Sardinia, and the Aeolian Islands, each with its unique landscape and culture.
- Cycling Tours: Cycle through the Po Valley, enjoying the flat terrain and picturesque scenery.
- Volcano Tours: Visit active volcanoes like Mount Etna and Vesuvius, experiencing the dramatic beauty of these natural wonders.
Conclusion
A physical map of Italy is a valuable tool for understanding the country’s diverse and fascinating landscape. From the towering Apennines to the fertile Po Valley and the picturesque coastline, the physical features of Italy have shaped its history, culture, and economy. By studying the physical map, we gain a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of this remarkable country.



/the-geography-of-italy-4020744-CS-5c3df74a46e0fb00018a8a3a.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the Physical Landscape of Italy: A Journey Through Mountains, Plains, and Coastlines. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!