Unveiling The World In Color: A Comprehensive Guide To Heat Maps
Unveiling the World in Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Related Articles: Unveiling the World in Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unveiling the World in Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unveiling the World in Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps
Heat maps, a ubiquitous tool in data visualization, offer a powerful means of understanding complex datasets by translating numerical data into a visually intuitive spectrum of color. This spectrum, often ranging from cool blues to fiery reds, allows for quick identification of areas of high and low concentration, revealing patterns and trends that might otherwise remain hidden. The applications of heat maps are vast and diverse, spanning across various fields, from business analytics to scientific research and even everyday life.
Understanding the Essence of Heat Maps
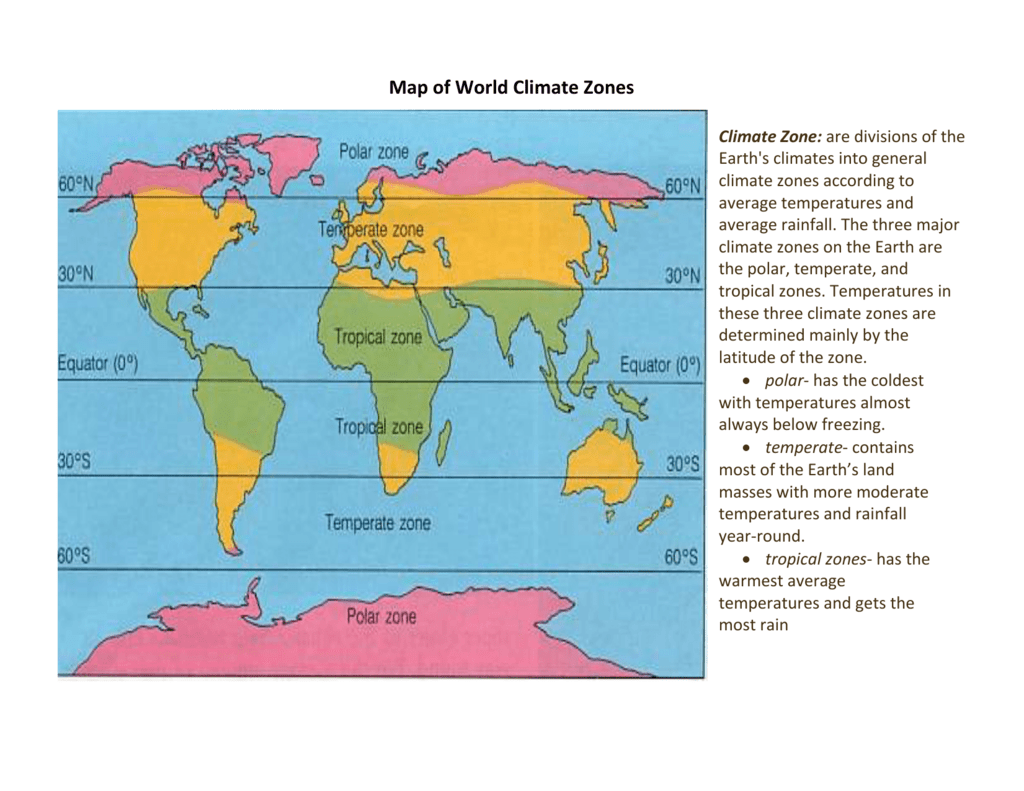
At their core, heat maps are a visual representation of data where color intensity corresponds to the magnitude of the data points. This simple yet effective principle makes them remarkably versatile, capable of conveying insights across different types of data. For instance, in a geographical context, a heat map might depict population density, with areas of high population density shown in vibrant reds and sparsely populated areas in cool blues.
Exploring the Diverse Applications of Heat Maps
The versatility of heat maps extends far beyond geographical representation. Here are some prominent examples:
-
Business Analytics: Heat maps are widely used in business intelligence to identify customer behavior patterns. For example, a website heat map can reveal user interaction patterns, highlighting areas of high engagement (indicated by warmer colors) and areas of disinterest (represented by cooler colors). This information can be invaluable for optimizing website design and enhancing user experience.
-
Marketing: Heat maps are instrumental in analyzing marketing campaigns. By tracking user clicks and interactions on advertisements or promotional materials, marketers can gauge the effectiveness of their campaigns and identify areas requiring improvement.
-
Healthcare: Heat maps are employed in medical imaging to highlight areas of interest in scans, enabling physicians to diagnose conditions more accurately and efficiently. For example, in thermography, heat maps are used to visualize temperature variations on the surface of the body, which can indicate underlying medical conditions.
-
Finance: In the financial sector, heat maps are used to analyze market trends and identify potential investment opportunities. By visualizing stock price fluctuations, investors can gain insights into market volatility and identify patterns that may indicate profitable investment strategies.
-
Research and Development: Heat maps are employed in various research fields, including biology, chemistry, and physics, to analyze experimental data and identify trends and patterns. For example, in drug discovery, heat maps can be used to visualize the interaction of drug molecules with target proteins, enabling researchers to develop more effective and targeted therapies.
Benefits of Using Heat Maps
The use of heat maps offers several key advantages:
-
Easy Interpretation: Heat maps are intuitive and easy to interpret, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. The simple color gradient makes it effortless to identify areas of high and low concentration, revealing patterns and trends at a glance.
-
Data Visualization: Heat maps offer a compelling and effective means of visualizing large datasets, making it easier to identify key insights and patterns that might otherwise be obscured by raw data. This visual representation enhances data comprehension and facilitates effective communication of findings.
-
Trend Identification: By highlighting areas of high and low concentration, heat maps facilitate the identification of trends and patterns within the data. This enables users to make informed decisions based on data-driven insights rather than relying on intuition or speculation.
-
Comparison and Analysis: Heat maps are ideal for comparing data across different groups or categories. By juxtaposing multiple heat maps, users can identify similarities and differences, revealing valuable insights and informing decision-making.
-
Interactive Exploration: Modern heat map software often incorporates interactive features, allowing users to zoom in on specific areas of interest, filter data, and explore the underlying data points. This dynamic approach enhances data exploration and facilitates deeper analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions about Heat Maps
Q: What are the different types of heat maps?
A: There are several types of heat maps, each tailored to specific applications. Some common types include:
-
Sequential heat maps: These maps use a single color gradient to represent data values, with warmer colors indicating higher values and cooler colors representing lower values.
-
Diverging heat maps: These maps utilize two color gradients, often diverging from a neutral midpoint, to represent data values above and below a specific threshold.
-
Categorical heat maps: These maps use different colors to represent distinct categories within the data.
Q: How do I create a heat map?
A: Creating a heat map is relatively straightforward. Several software tools and online platforms offer user-friendly interfaces for generating heat maps from various data sources. Popular options include:
-
Microsoft Excel: Excel’s built-in charting features allow users to create basic heat maps from tabular data.
-
Google Sheets: Similar to Excel, Google Sheets offers a range of charting tools, including heat maps, accessible through its spreadsheet interface.
-
Tableau: Tableau is a powerful data visualization platform that offers advanced heat map creation capabilities, allowing users to customize the appearance and functionality of their heat maps.
-
Power BI: Power BI, another popular data visualization platform, offers comprehensive heat map creation tools, enabling users to create interactive and insightful heat maps.
Q: What are some tips for creating effective heat maps?
A: To create effective and informative heat maps, consider these tips:
-
Choose the right color scheme: Select a color scheme that is visually appealing and easily interpretable. Avoid using too many colors or a color scheme that is difficult to distinguish.
-
Use clear labels and legends: Ensure that the axes and labels are clear and concise, providing sufficient context for understanding the data. Include a legend to explain the color gradient and the corresponding data values.
-
Consider the audience: Tailor the heat map’s complexity and level of detail to the target audience. Avoid overwhelming users with too much information or overly technical representations.
-
Optimize for visual clarity: Ensure that the heat map is visually appealing and easy to understand. Avoid overcrowding the map with too much data or distracting elements.
Conclusion
Heat maps have become an indispensable tool for data visualization, offering a powerful means of understanding complex datasets and revealing hidden patterns and trends. Their versatility and ease of interpretation make them valuable across various fields, from business analytics to scientific research. By leveraging the power of heat maps, users can gain valuable insights, make informed decisions, and effectively communicate data-driven findings. As data continues to grow exponentially, heat maps will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in helping us navigate the complexities of the information age and make sense of the world around us.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unveiling the World in Color: A Comprehensive Guide to Heat Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!