Visualizing Data: Harnessing The Power Of Maps With Excel
Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel
Related Articles: Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel
- 3.1 Bringing Data to Life with Maps
- 3.2 The Power of Visual Insights
- 3.3 A Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping Excel Data
- 3.4 Examples of Mapping Excel Data in Action
- 3.5 Frequently Asked Questions about Mapping Excel Data
- 3.6 Tips for Effective Mapping with Excel Data
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel
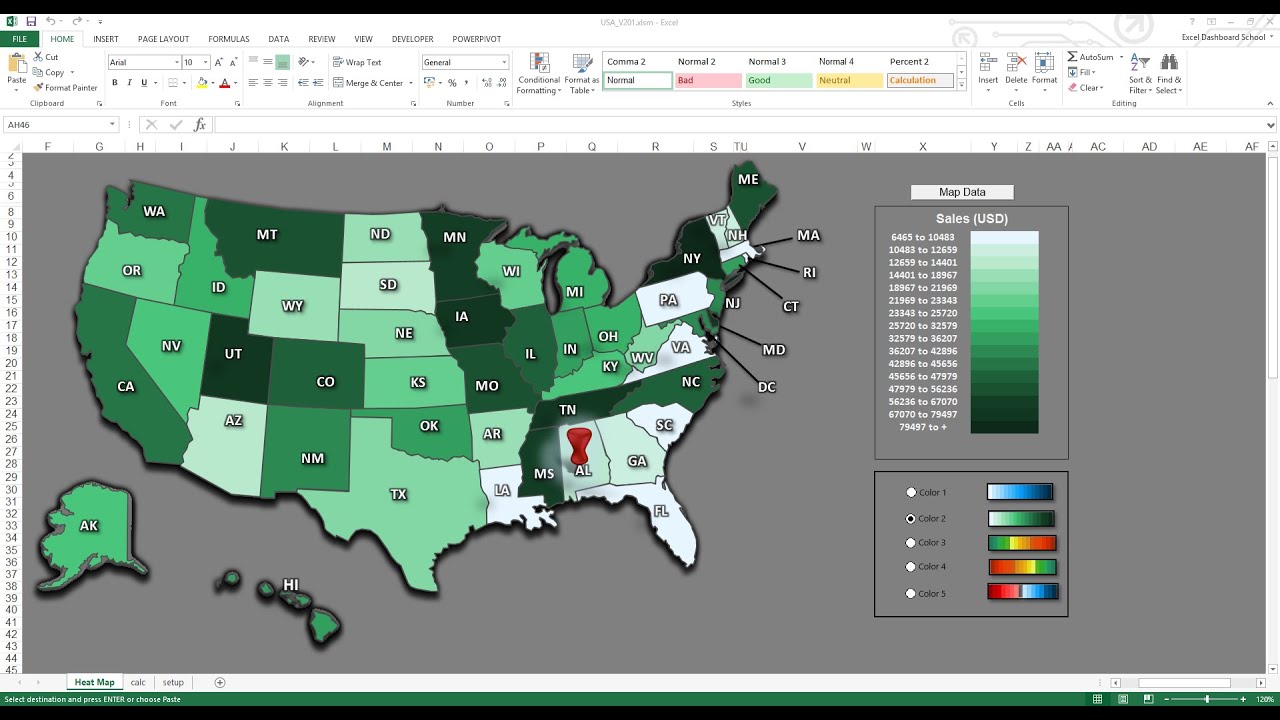
In the realm of data analysis, the ability to visualize information is paramount. While spreadsheets like Excel excel at organizing and manipulating data, they often fall short in presenting a clear and insightful picture. This is where the integration of maps with Excel data comes into play, offering a powerful tool for transforming raw data into compelling visual narratives.
Bringing Data to Life with Maps
Maps provide a natural and intuitive way to represent geographical data. By overlaying Excel data onto a map, analysts can gain a deeper understanding of spatial patterns, trends, and relationships that might remain hidden in spreadsheets. This process, often referred to as "geocoding," involves associating geographical coordinates (latitude and longitude) with data points. These coordinates can then be used to plot data on a map, creating visually rich and informative representations.
The Power of Visual Insights
The benefits of using maps with Excel data are multifaceted:
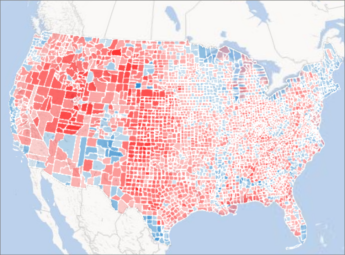
- Enhanced Understanding: Maps enable analysts to identify spatial patterns, clusters, and outliers that might be missed in spreadsheets. For instance, visualizing sales data on a map could reveal regional variations or high-performing sales territories.
- Improved Communication: Maps offer a powerful tool for communicating complex data to a wider audience. They can be used to present findings in a clear, concise, and easily digestible manner, fostering better understanding and collaboration.
- Data Exploration: Maps facilitate exploration of data by allowing users to interact with the visualization. Zooming in and out, filtering data, and selecting specific areas can reveal new insights and uncover hidden relationships.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: By visualizing data geographically, analysts can gain valuable insights that inform strategic decision-making. For example, a map depicting customer locations could guide marketing campaigns or optimize logistics routes.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Mapping Excel Data
The process of mapping Excel data in Excel is relatively straightforward, involving the following steps:
- Data Preparation: Ensure your Excel data includes relevant geographical information, such as addresses, postal codes, or city names.
- Geocoding: Use Excel’s built-in geocoding functionality or a third-party geocoding service to convert addresses into latitude and longitude coordinates.
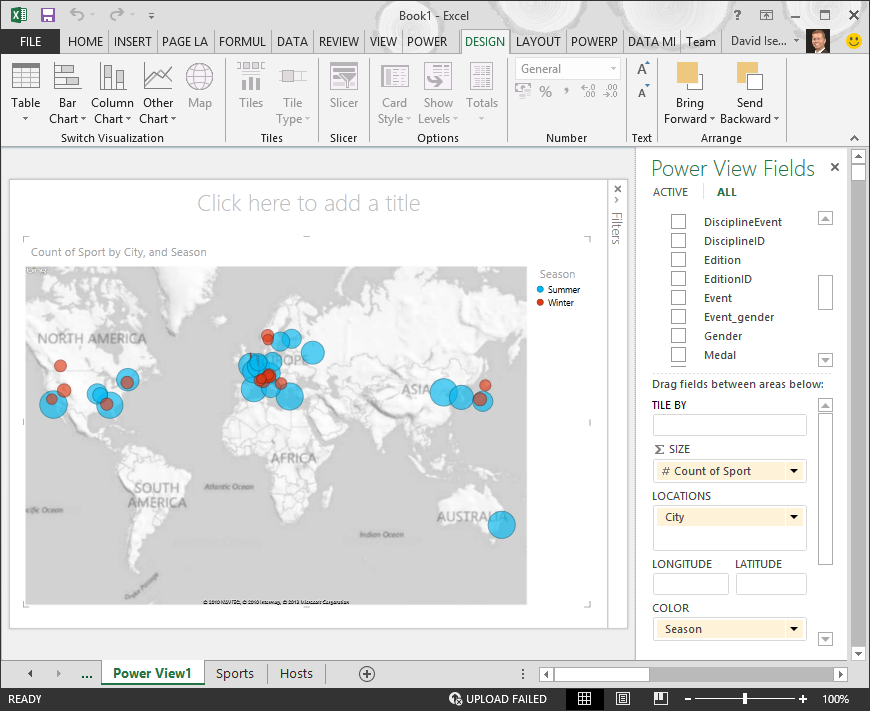
- Map Creation: Choose a suitable map platform, such as Google Maps, Bing Maps, or ArcGIS Online, and import your geocoded data.
- Customization: Customize the map by adding markers, labels, color schemes, and other visual elements to enhance the visual appeal and clarity of the visualization.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the map to identify trends, patterns, and insights that might be missed in spreadsheets.
Examples of Mapping Excel Data in Action
The applications of mapping Excel data are vast and extend across various industries. Here are some examples:
- Real Estate: Visualizing property listings on a map can help potential buyers identify properties in desired locations and understand market trends.
- Retail: Mapping store locations and customer demographics can guide site selection, marketing strategies, and inventory management.
- Healthcare: Visualizing disease outbreaks or healthcare facility locations can assist in public health initiatives and resource allocation.
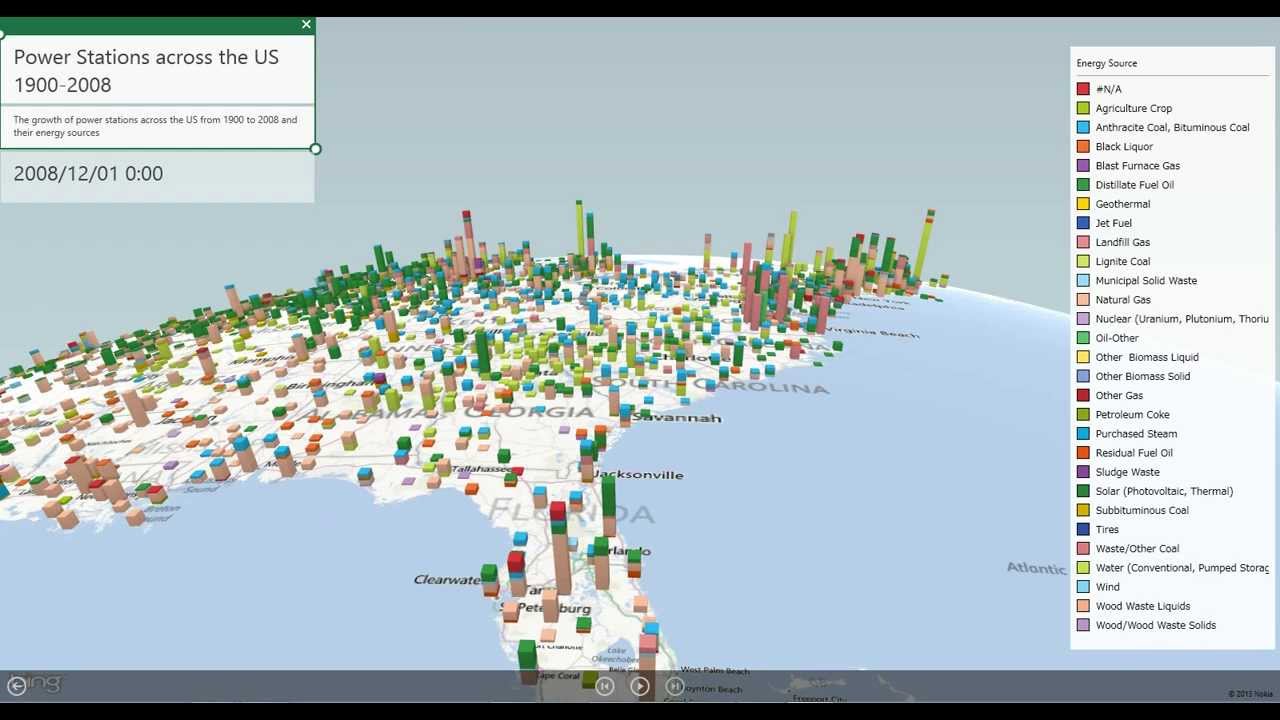
- Transportation: Mapping traffic patterns, accident hotspots, or public transit routes can optimize transportation systems and improve safety.
- Environmental Studies: Visualizing pollution levels, deforestation rates, or wildlife populations can inform environmental policies and conservation efforts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mapping Excel Data
Q: What types of data can be mapped with Excel?
A: Excel data that includes geographical information, such as addresses, postal codes, city names, or latitude and longitude coordinates, can be mapped.
Q: What are the best tools for mapping Excel data?
A: Excel itself offers limited mapping capabilities. However, several third-party tools and platforms, such as Google Maps, Bing Maps, ArcGIS Online, and Power BI, provide robust mapping functionality that integrates seamlessly with Excel.
Q: How can I ensure accurate geocoding?
A: Use reliable geocoding services and ensure your data contains accurate and complete address information. Double-check the geocoded results for accuracy before using them for mapping.
Q: What are some best practices for creating effective maps?
A: Use clear and concise labels, choose appropriate color schemes, and ensure the map is visually appealing and easy to understand. Consider using interactive elements to enhance user engagement and data exploration.
Tips for Effective Mapping with Excel Data
- Choose the Right Map Platform: Select a platform that aligns with your data type, visualization needs, and technical expertise.
- Optimize Data for Mapping: Ensure your data is clean, accurate, and includes relevant geographical information.
- Experiment with Different Map Styles: Explore various map types, such as road maps, satellite imagery, or thematic maps, to find the best representation for your data.
- Use Visual Hierarchy: Emphasize important data points using different marker sizes, colors, or labels.
- Incorporate Interactive Elements: Allow users to zoom in, filter data, and select specific areas for a more engaging and insightful experience.
Conclusion
Mapping Excel data unlocks a world of visual insights, transforming raw data into compelling narratives that reveal patterns, trends, and relationships. By leveraging the power of maps, analysts can enhance their understanding of data, communicate findings effectively, and make informed decisions based on geographical context. As data becomes increasingly spatial in nature, the ability to visualize it on maps will become an essential skill for anyone seeking to harness the full potential of data analysis.


![]()

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Visualizing Data: Harnessing the Power of Maps with Excel. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!